
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172364
Author: Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 33, Problem 31P
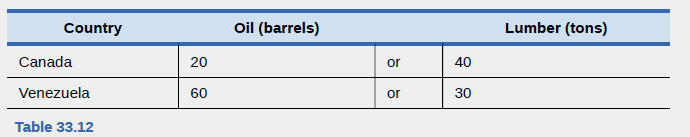
Review the numbers for Canada and Venezuela from Table 33.12 which describes how many barrels of oil and tons of lumber the workers can produce. Use these numbers to answer the rest of this question.
- Draw a production possibilities frontier for each country. Assume there are 100 workers in each country. Canadians and Venezuelans desire both oil and lumber. Canadians want at least 2,000 tons of lumber. Mark a point on their production possibilities where they can get at least 3,000 tons.
- Assume that the Canadians specialize completely because they figured out they have a
comparative advantage in lumber. They are willing to give up 1,000 tons of lumber. How much oil should they ask for in return for this lumber to be as well off as they were with no trade? How much should they ask for if they want to gain from trading with Venezuela? Note:
We can think of this “ask” as the relative price or trade price of lumber.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
not use ai please
Please give me true answer this financial accounting question
not use ai
Chapter 33 Solutions
Principles of Economics 2e
Ch. 33 - True or False: The source of comparative advantage...Ch. 33 - Brazil can produce 100 pounds of beef or 10 autos....Ch. 33 - In France it takes one worker to produce one...Ch. 33 - In Germany it takes three workers to make one...Ch. 33 - How can there be any economic gains for a country...Ch. 33 - Table 33.15 shows how the average costs of...Ch. 33 - If the removal of trade banters is so beneficial...Ch. 33 - What is absolute advantage? What is comparative...Ch. 33 - Under what conditions does comparative advantage...Ch. 33 - What factors does Paul Krugman identity that...
Ch. 33 - Is it possible to have a comparative advantage in...Ch. 33 - How does comparative advantage lead to gains from...Ch. 33 - What is intra-industry trade?Ch. 33 - What are the two main sources of economic gains...Ch. 33 - What is splitting up the value chain?Ch. 33 - Are the gains from international trade more likely...Ch. 33 - Are differences in geography behind the...Ch. 33 - Why does the United States not have an absolute...Ch. 33 - Look at Exercise 33.2. Compute the opportunity...Ch. 33 - You just overheard your friend say the following:...Ch. 33 - Look at Table 33.9. Is there a range of trades for...Ch. 33 - You just got a job in Washington, D.C. You move...Ch. 33 - Does intra-industry trade contradict the theory of...Ch. 33 - Do consumers benefit from intra-industry trade?Ch. 33 - Why might intra-industry trade seem surprising...Ch. 33 - In World Trade Organization meetings, what do you...Ch. 33 - Why might a low-income country put up barriers to...Ch. 33 - Can a nations comparative advantage change over...Ch. 33 - France and Tunisia both have Mediterranean...Ch. 33 - In Japan, one worker can make 5 tons of rubber or...Ch. 33 - Review the numbers for Canada and Venezuela from...Ch. 33 - In Exercise 33.31, is there an ask where...Ch. 33 - From earlier chapters you will recall that...Ch. 33 - Consider two countries: South Korea and Taiwan....Ch. 33 - If trade increases world GDP by 1 per year, what...
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Horizontal analysis(Learning Objective 2)15-20 min. What were the dollar and percentage changes in Fesslers Fin...
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
The put option’s leverage ratio is -1.9. Introduction: Expected return is the method of finding the average ant...
Corporate Finance (4th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance) - Standalone book
E2-13 Identifying increases and decreases in accounts and normal balances
Learning Objective 2
Insert the mis...
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Communication Activity 9-1
In 150 words or fewer, explain the different methods that can be used to calculate d...
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Financial Chapters (Book & Access Card)
Questions For Review
12-4. How is the concept of the value package useful in marketing to consumers and industr...
Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in Intro to Business)
The weaknesses of payback period method of calculation. Introduction: Every investment requires a time period t...
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Explain if any states are not a “friendly” place for tax preparers, payday lenders, title pawn lenders, and “credit approved” used car dealers to operate in and what they have done, regulation-wise.arrow_forwardExplain the regulation or lack of regulation of payday lenders, title pawn lenders, and “credit-approved” used car dealers in Alabama.arrow_forwardExplain why people should avoid the business model of payday lenders, title pawn lenders, and “credit approved” used car dealers.arrow_forward
- Explain why people fall prey to payday lenders, title pawn lenders, and “credit-approved” used car dealers.arrow_forwardPlease answer the following.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows the hypothetical domestic supply and demand for baseball caps in the country of Spain. Domestic Supply and Demand for Baseball Caps Price (€ per cap) 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Spain Dd 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Baseball caps (thousands per month) Suppose that the world price of baseball caps is €2 and there are no import restrictions on this product. Assume that Spanish consumers are indifferent between domestic and imported baseball caps. Instructions: Enter your answers as whole numbers. a. What quantity of baseball caps will domestic suppliers supply to domestic consumers? thousand b. What quantity of baseball caps will be imported? thousand Now suppose a tariff of €1 is levied against each imported baseball cap. c. After the tariff is implemented, what quantity of baseball caps will domestic suppliers supply to domestic consumers? thousand d. After the tariff is implemented, what quantity of baseball caps will be imported? thousandarrow_forward
- May I please have the solutions for the following assignment? as 2025arrow_forwardResponse to J.C. Ethics Statement Raising our products' global profile requires a firm commitment to doing the right thing by society and the environment. By switching to a more energy-efficient cloud architecture, BillRight Software, Inc. will reduce its carbon footprint while also ensuring the absolute security of all customer data. Fair labor standards, a diverse and inclusive workforce, and giving back to the communities where our employees live and work are some of our core values. Following local regulations, accepting cultural variances, and actively participating in community development projects are all ways our brand and product will uphold our ethical values globally (Corcoran, 2024; Kotler et al., 2023; Kotler & Keller, 2024; Solomon & Russell, 2024). How MKTG 525 Gets You Together with Classmates? Different points of view in dealing with classmates from many backgrounds exposes you to many points of view, ideas, and techniques. This variety enriches the learning…arrow_forward3. Case 2) Coal plants exit, and Solar generation enters the market Now, let's consider a scenario where the coal power plant (#1) shuts down and exits the market, and a solar generation facility is constructed. The capacity of the solar generation facility is the same as the coal power plant that went out of business. The generation capacities of this market are shown below, along with their MC. Table 3: Power Plant Capacity and Marginal Cost: Case 2 Plant # Energy Source Capacity (MW) MC (S/MWh) 2 Oil 100 90 3 Natural Gas 500 50 4 Nuclear 600 0 5 Solar 300 5 Note that the solar plant (#5) can generate electricity only from 7 AM until 5PM. During these hours, the plant can generate up to its full capacity (300 MW) but cannot generate any when unavailable. (a) Draw a supply curve for each hourly market (4AM, 10 AM, 2PM, 6PM). (b) Find the market clearing prices and calculate how much electricity each power plant generates in the hourly market (4AM, 10AM, 2PM, and 6PM). (c) Find the…arrow_forward
- Respond to L.R. To analyze consumer spending, you must review the macroeconomic indicators of Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) and Retail Sales over the past year. Selected Macroeconomic indicators Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) measure the value of household goods and services consumed and are a key indicator of consumer spending. - Retail Sales: This tracks the total receipts of retail stores and provides insight into consumer demand and spending trends. - Patterns over the past year: Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Over the past year, PCE has steadily increased, reflecting consumer confidence and willingness to spend. The growth rate has been moderate, driven by wage growth, low unemployment rates, and government stimulus measures. However, inflationary pressures have also impacted real purchasing power, leading to a mixed outlook. - Retail sales have also experienced fluctuations but have generally trended upwards. After a…arrow_forward4. Case 3) Electricity demand increases due to increased EV adoption We will continue using the Case 2 supply curve (with the solar plant in operation) for this analysis. Suppose that electricity consumption from electric vehicles (EV) increases significantly. Consequently, electricity demand in the wholesale market increases at every hour. The new demand levels are shown in Table 5 below. The market operator has backup power plants (using natural gas) ready, with a total capacity of 300 MW and a MC of $100/MWh. Table 5: Hourly Demand (selected hours) Hour Demand (MWh) 4 AM 800 10 AM 1000 ... 2 PM 1100 ... 6 PM 1300 (a) Find the market clearing prices and calculate how much electricity each power plant generates in the hourly market (4AM, 10AM, 2PM, and 6PM). Is there a specific hourly market in which the market operator will need to dispatch backup generation? (b) Compare the Case 2 scenario with the Case 3 scenario in terms of CO2 emissions and average electricity price. Based on…arrow_forward2. Case 1) NG price decreases Now, suppose that the price of natural gas decreased substantially, causing the marginal cost of the NG power plant to decrease to MC = $35/MWh. The demand is the same as in Case 0. (a) Draw a new supply curve that reflects the MC change of the NG power plant. (b) Find the market clearing prices and calculate how much electricity each power plant generates in the hourly market (4AM, 10AM, 2PM, and 6PM). (c) What happened to the coal power plant? (d) Do you think the market outcomes (like average price) and the total CO2 emissions have improved under this Case 1 scenario (use the emissions data provided in the lecture slides)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc



 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:9781544336329
Author:Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:SAGE Publications, Inc





Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning