
Principles Of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781680920864
Author: Timothy Taylor, Steven A. Greenlaw, David Shapiro
Publisher: MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 33, Problem 31P
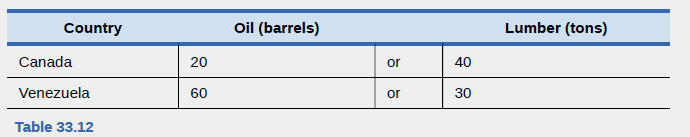
Review the numbers for Canada and Venezuela from Table 33.12 which describes how many barrels of oil and tons of lumber the workers can produce. Use these numbers to answer the rest of this question.
- Draw a production possibilities frontier for each country. Assume there are 100 workers in each country. Canadians and Venezuelans desire both oil and lumber. Canadians want at least 2,000 tons of lumber. Mark a point on their production possibilities where they can get at least 3,000 tons.
- Assume that the Canadians specialize completely because they figured out they have a
comparative advantage in lumber. They are willing to give up 1,000 tons of lumber. How much oil should they ask for in return for this lumber to be as well off as they were with no trade? How much should they ask for if they want to gain from trading with Venezuela? Note:
We can think of this “ask” as the relative price or trade price of lumber.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Only human experts solved it. Direction: Do a total of 5 of this, instruction and the topic is provided in the picture. Strictly write this in bond paper.
NOTE: strictly use nautical almanac. This is about maritime navigation.
not use ai please
Use the following table to work Problems 5 to 9.
Minnie's Mineral Springs, a single-price monopoly,
faces the market demand schedule:
Price
Quantity demanded
(dollars per bottle)
10
8
(bottles per hour)
0
1
6
2
4
3
2
4
0
5
5. a. Calculate Minnie's total revenue schedule.
b. Calculate its marginal revenue schedule.
6. a. Draw a graph of the market demand curve
and Minnie's marginal revenue curve.
b. Why is Minnie's marginal revenue less than
the price?
7. a. At what price is Minnie's total revenue maxi-
mized?
b. Over what range of prices is the demand for
water from Minnie's Mineral Springs elastic?
8. Why will Minnie not produce a quantity at which
the market demand for water is inelastic?
Chapter 33 Solutions
Principles Of Economics 2e
Ch. 33 - True or False: The source of comparative advantage...Ch. 33 - Brazil can produce 100 pounds of beef or 10 autos....Ch. 33 - In France it takes one worker to produce one...Ch. 33 - In Germany it takes three workers to make one...Ch. 33 - How can there be any economic gains for a country...Ch. 33 - Table 33.15 shows how the average costs of...Ch. 33 - If the removal of trade banters is so beneficial...Ch. 33 - What is absolute advantage? What is comparative...Ch. 33 - Under what conditions does comparative advantage...Ch. 33 - What factors does Paul Krugman identity that...
Ch. 33 - Is it possible to have a comparative advantage in...Ch. 33 - How does comparative advantage lead to gains from...Ch. 33 - What is intra-industry trade?Ch. 33 - What are the two main sources of economic gains...Ch. 33 - What is splitting up the value chain?Ch. 33 - Are the gains from international trade more likely...Ch. 33 - Are differences in geography behind the...Ch. 33 - Why does the United States not have an absolute...Ch. 33 - Look at Exercise 33.2. Compute the opportunity...Ch. 33 - You just overheard your friend say the following:...Ch. 33 - Look at Table 33.9. Is there a range of trades for...Ch. 33 - You just got a job in Washington, D.C. You move...Ch. 33 - Does intra-industry trade contradict the theory of...Ch. 33 - Do consumers benefit from intra-industry trade?Ch. 33 - Why might intra-industry trade seem surprising...Ch. 33 - In World Trade Organization meetings, what do you...Ch. 33 - Why might a low-income country put up barriers to...Ch. 33 - Can a nations comparative advantage change over...Ch. 33 - France and Tunisia both have Mediterranean...Ch. 33 - In Japan, one worker can make 5 tons of rubber or...Ch. 33 - Review the numbers for Canada and Venezuela from...Ch. 33 - In Exercise 33.31, is there an ask where...Ch. 33 - From earlier chapters you will recall that...Ch. 33 - Consider two countries: South Korea and Taiwan....Ch. 33 - If trade increases world GDP by 1 per year, what...
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Horizontal analysis(Learning Objective 2)15-20 min. What were the dollar and percentage changes in Fesslers Fin...
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
The put option’s leverage ratio is -1.9. Introduction: Expected return is the method of finding the average ant...
Corporate Finance (4th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance) - Standalone book
E2-13 Identifying increases and decreases in accounts and normal balances
Learning Objective 2
Insert the mis...
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Communication Activity 9-1
In 150 words or fewer, explain the different methods that can be used to calculate d...
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Financial Chapters (Book & Access Card)
Questions For Review
12-4. How is the concept of the value package useful in marketing to consumers and industr...
Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in Intro to Business)
The weaknesses of payback period method of calculation. Introduction: Every investment requires a time period t...
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Not use ai pleasearrow_forwardThe Firm's Output Decision (Study Plan 12.2) Use the following table to work Problems 4 to 6. Pat's Pizza Kitchen is a price taker. Its costs are Output (pizzas per hour) Total cost (dollars per hour) 0 10 1 21 2 30 3 41 4 54 5 69 4. Calculate Pat's profit-maximizing output and economic profit if the market price is (i) $14 a pizza. (ii) $12 a pizza. (iii) $10 a pizza. 5. What is Pat's shutdown point and what is Pat's economic profit if it shuts down temporarily? 6. Derive Pat's supply curve.arrow_forwardUse the following table to work Problems 27 and 28. ProPainters hires students at $250 a week to paint houses. It leases equipment at $500 a week. The table sets out its total product schedule. Labor (students) 1 Output (houses painted per week) 2 23 5 3 9 4 12 5 14 6 15 27. If ProPainters paints 12 houses a week, calculate its total cost, average total cost, and marginal cost. At what output is average total cost a minimum? 28. Explain why the gap between ProPainters' total cost and total variable cost is the same no matter how many houses are painted.arrow_forward
- Use the following table to work Problems 17 to 20. The table shows the production function of Jackie's Canoe Rides. Labor Output (rides per day) (workers per day) Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 10 20 40 55 65 20 40 60 75 85 30 65 75 90 100 40 75 85 100 110 Canoes 10 20 30 40 Jackie's pays $100 a day for each canoe it rents and $50 a day for each canoe operator it hires. 19. a. On Jackie's LRAC curve, what is the average cost of producing 40, 75, and 85 rides a week? b. What is Jackie's minimum efficient scale?arrow_forwardPlease solve this questions step by step handwritten solution and do not use ai thank youarrow_forwardPlease solve questions 3 and 4 step by step handwritten solution and no ai toolsarrow_forward
- Please solve questions 1 and 2 step by step handwritten solution and no ai toolsarrow_forwardNot use ai pleasearrow_forward1. Riaz has a limited income and consumes only Apple and Bread. His current consumption choice is 3 apples and 5 bread. The price of apple is $3 each, and the price of bread is $2.5 each. The last apple added 5 units to Sadid's utility, while the last bread added 7 units. Is Riaz making the utility-maximizing choice? Why or why not? Do you suggest any adjustment in Riaz's consumption bundle? Why or why not? Give reasons in support of your answer. State the condition for a consumer's utility maximizing choice and illustrate graphically. 2. Consider the following table of long-run total costs for three different firms: Quantity Total Cost ($) Firm A Firm B Firm C 1 60 11 21 2 70 24 34 3 80 39 49 4 90 56 66 5 100 75 85 6 110 96 106 7 120 119 129 Does each of these firms experience economies of scale or diseconomies of scale? Explain your answer with necessary calculations.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc



 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:9781544336329
Author:Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:SAGE Publications, Inc





Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning