
Concept explainers
(a)
The distance between the object and the final image.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The distance of an object is
The focal length of the lens is
The focal length of a second lens is
The distance of the second lens is
Formula used:
Draw a ray diagram to show the image distance and its properties.
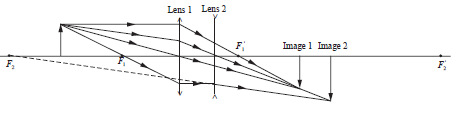
Write the expression for the thin lens equation for the first lens.
Here,
Rearrange the above equation to calculate the image distance for first lens.
Write the expression for the thin lens equation for the second lens.
Here,
Rearrange the above equation to calculate the image distance for second lens.
Write the expression for the object distance for second lens.
Here,
Write the expression for object to image distance.
Here,
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the object to the final image distance is
(b)
The overall magnification of the system.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The object distance for the first lens is
The image distance for the first lens is
The object distance for the second lens is
The image distance for the second lens is
Formula used:
Write the expression for the lateral magnification of the image formed by the first lens.
Here,
Write the expression for the lateral magnification of the image formed by the second lens.
Here,
Write the expression for the overall magnification for a system of two lenses.
Here,
Substitute
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the overall magnification is
(c)
Whether the object is real or virtual and upright or inverted.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The final image distance from the second lens is
The overall magnification for the system of two lenses is
Introduction:
A real image is formed by an object when all the outgoing parallel rays from the object are appeared to converge to a point. For positive image distance the image is real and for negative image distance the image is virtual.
The image distance,
Conclusion:
Thus, the image is real and inverted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 32 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- A capacitor with a capacitance of C = 5.95×10−5 F is charged by connecting it to a 12.5 −V battery. The capacitor is then disconnected from the battery and connected across an inductor with an inductance of L = 1.55 H . At the time 2.35×10−2 s after the connection to the inductor is made, what is the current in the inductor? At that time, how much electrical energy is stored in the inductor?arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





