
Fill in the blanks in this concept map to help you tie together key concepts concerning transport in plants.
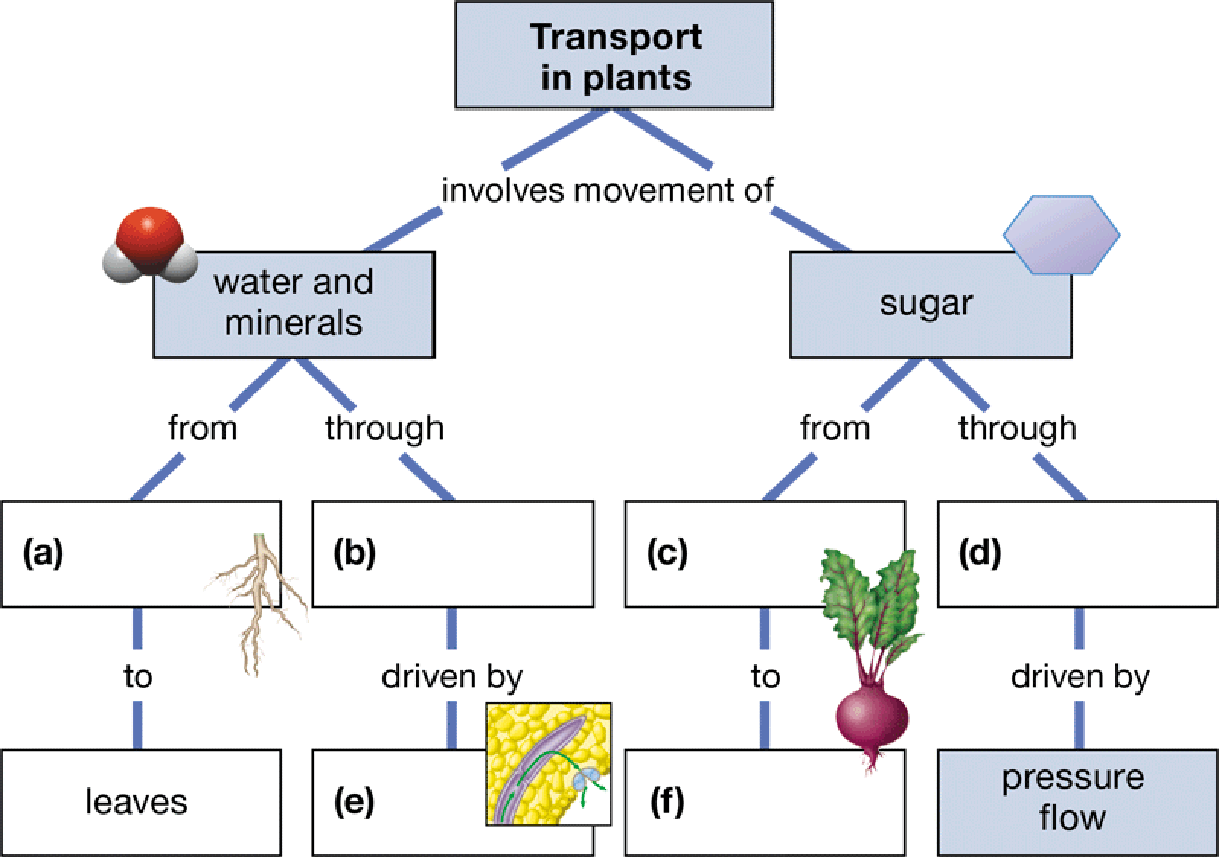
To create: The concept map that depicts transportation in plant.
Introduction: Angiosperms are the most developed group in the plant kingdom. They comprise the root system, root hairs, shoot system, leaves, petioles, blades, stems, nodes, internodes, and flower. They are seed-bearing plants that are covered.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig: 1 shows a complete concept map of transport in plants.
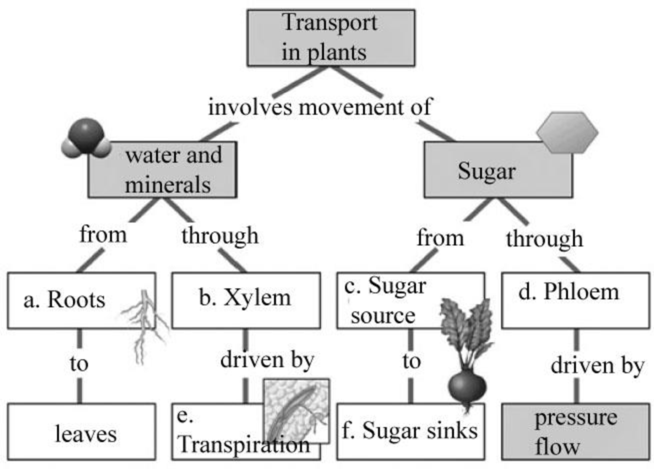
Figure 1: The concept map depicting the concept in transport in plants.
(a)
Correct answer: Roots.
Roots are the part of the root system that helps in uptake of water and minerals from the surrounding to the shoot system. Hence, the correct answer is roots.
(b)
Correct answer: Xylem.
Xylem is the vascular bundles present in the inner region of the stem that sends water and minerals through them to the rest of the plant body. Hence, the correct answer is xylem.
(c)
Correct answer: Sugar source.
Sugar source is the leaves where, by the process of photosynthesis, the sugar is made. Hence, the correct answer is sugar source.
(d)
Correct answer: Phloem.
Phloem is a type of vascular bundle through which the sugar sources are transported to the rest of the plant body. Hence, the correct answer is phloem.
(e)
Correct answer: Transpiration.
It is the process of loss of water from the plant through the leaves. This helps in maintaining the osmotic balance. Hence, the correct answer is transpiration.
(f)
Correct answer: Sugar sinks.
It is the region where the prepared sugar is stored till the plant is in requirement of energy. When such a situation arises, the plant supplies the sugar from these stored regions. Hence, the correct answer is sugar sinks.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 32 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Biology with eText -- Access Card Package (8th Edition)
- 1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward50 mg dose of a drug is given orally to a patient. The bioavailability of the drug is 0.2. What is the volume of distribution of the drug if the plasma concentration is 1 mg/L? Be sure to provide units.arrow_forwardDetermine Kd and Bmax from the following Scatchard plot. Make sure to include units.arrow_forward
- Choose a catecholamine neurotransmitter and describe/draw the components of the synapse important for its signaling including synthesis, packaging into vesicles, receptors, transporters/degradative enzymes. Describe 2 drugs that can act on this system.arrow_forwardThe following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. a) Which has a higher potency? b) Which is has a higher efficacy? c) What is the approximate Kd of capsaicin in uM? (you can round to the nearest power of 10)arrow_forwardWhat is the rate-limiting-step for serotonin synthesis?arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax- Basic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage






