
Concept explainers
To label: The structures of the respiratory system in the given figure.
Introduction: The respiratory system is responsible for providing an airway for the movement of air (oxygen) in and out (carbon dioxide) of the body. There are three crucial parts of the respiratory system, namely the muscles of respiration, the lungs, and the airways. The nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles are known as airways.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
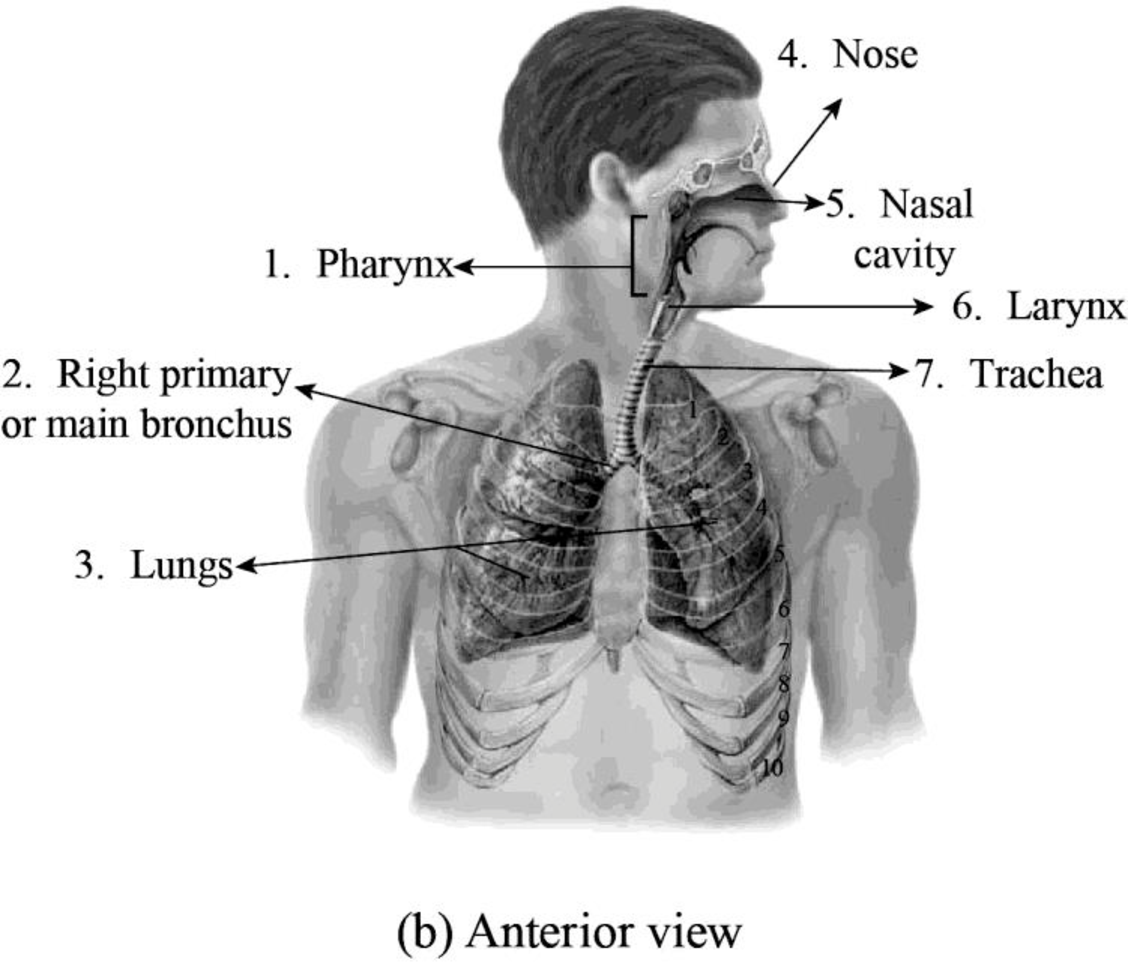
Fig.1: Structures of the respiratory system.
Explanation of Solution
Pharynx: It is a cone-shaped passageway behind the oral as well as the nasal cavities and above the larynx and the esophagus. It connects the oral and nasal cavities. It acts as a passageway for the movement of food.
Right primary or main bronchus: It is shorter, wider, and more vertical when compared to the left main bronchus.
Lungs: A pair of spongy, air-filled organ that is involved in processing the gas exchange is known as lungs.
Nose and the nasal cavity: The main external opening and the first part of the body’s airway is nose and the nasal cavity. The only visible part of the respiratory system is the nose. The nose includes external nares through which air enters the nasal cavity. The main function of the nasal cavity is to moisten, warm, and filter the air before it reaches the lungs.
Larynx: It is also known as the voice box and it is present at the top of the neck. It is involved in producing sound, breathing, and also protects the trachea from aspiration of food.
Trachea: It is a tube-like system that carries air.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 32 Solutions
EBK LABORATORY MANUAL FOR ANATOMY AND P
- 22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is the label ?arrow_forwardCan you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forward
- Describe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardWhat are the functions of the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





