
Concept explainers
News flash: The following table presents the circulation (in thousands) for the top 25 U.S. daily newspapers in both print and digital editions.
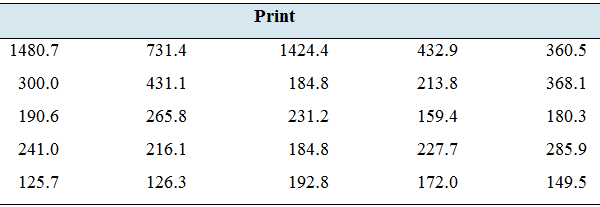
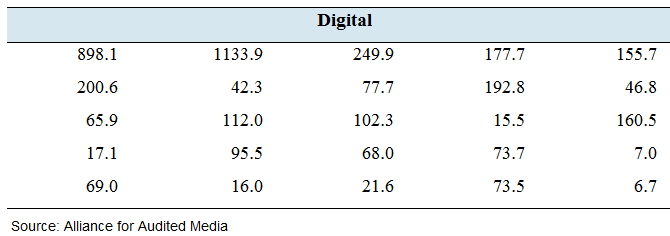
- Find the
mean andmedian circulation for print editions. - Find the mean and median circulation for digital editions.
- The editor of an Internet news source says that digital circulation is more than half of print circulation. Do the data support this claim?
(a)
To Find: the mean and median circulation for print editions.
Answer to Problem 46E
For print editions, mean circulation = 335.07 and median circulation
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Formula used:
Calculation- Mean and Median circulation for print editions,
For Median, first arrange data in sequential order,
Thus, for print editions, mean circulation 335.07 and median circulation
(b)
To Find: To Find the mean and median circulation for print editions.
Answer to Problem 46E
For digital editions, mean circulation 163.19 and median circulation
Explanation of Solution
Calculation- Mean and Median circulation for digital editions,
For Median, first arrange data in sequential order,
Thus, for digital editions, mean circulation
(c)
To Check: Whether digital circulation is more than half of print circulation.
Answer to Problem 46E
Digital circulation is not more than half of print circulation.
Explanation of Solution
By looking at mean and median number of print and digital circulation,
For print editions, mean circulation 335.07 and median circulation
For digital editions, mean circulation 163.19 and median circulation
So, it can be said from above data, the claim by an editor that digital circulation is more than half of print circulation is incorrect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Elementary Statistics
- (b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) E(X)E(Y);arrow_forward(d) Under what conditions do we say that a random variable X is integrable, specifically when (i) X is a non-negative random variable and (ii) when X is a general random variable?arrow_forward29. State the Borel-Cantelli Lemmas without proof. What is the primary distinction between Lemma 1 and Lemma 2?arrow_forward
- The masses measured on a population of 100 animals were grouped in the following table, after being recorded to the nearest gram Mass 89 90-109 110-129 130-149 150-169 170-189 > 190 Frequency 3 7 34 43 10 2 1 You are given that the sample mean of the data is 131.5 and the sample standard deviation is 20.0. Test the hypothesis that the distribution of masses follows a normal distribution at the 5% significance level.arrow_forwardstate without proof the uniqueness theorm of probability functionarrow_forward(a+b) R2L 2+2*0=? Ma state without proof the uniqueness theorm of probability function suppose thatPandQ are probability measures defined on the same probability space (Q, F)and that Fis generated by a π-system if P(A)=Q(A) tax for all A EthenP=Q i. e. P(A)=Q(A) for alla g // معدلة 2:23 صarrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL



