
Concept explainers
Cultured Skin for Healing Wounds Diabetes is a disorder in which the blood sugar level is not properly controlled. Among other effects, it reduces blood flow to the lower legs and feet. As a result, about 3 million diabetes patients have ulcers (open wounds that do not heal) on their feet. Each year, about 80,000 require amputations.
Several companies provide cultured cell products designed to promote the healing of diabetic foot ulcers. FIGURE 31.15 shows the results of a clinical experiment that tested the effect of one such cultured skin product versus standard treatment for diabetic foot wounds. Patients were randomly assigned to either the experimental treatment group or the control group, and their progress was monitored for 12 weeks.
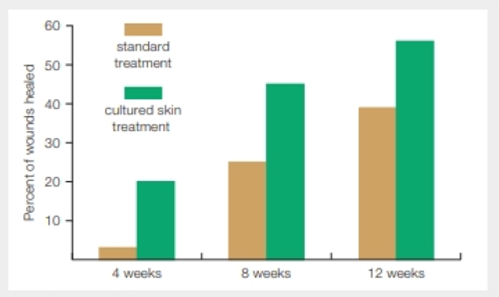
FIGURE 31.15 Treatment of diabetic food ulcers. Results of a multicenter study of the effects of standard treatment versus use of a cultured cell product for diabetic foot ulcers. Bars show the percentage of foot ulcers that had completely healed.
What percentage of wounds had healed at 8 weeks when treated the standard way? When treated with cultured skin?
To determine: The percentage of wounds healed at 8 weeks when treated with standard treatment and when treated with cultured skin treatment.
Concept introduction: Diabetes is a group of disorders in which the body possesses high blood sugar level. This type of disease can lead to foot ulcers due to the decreased flow of blood into the legs and feet. They are caused when the nerves are damaged, which can lead to painless wounds that can ultimately cause ulcers that are the wounds that do not heal. Some experiments were conducted in order to heal the wounds. The patients were randomly treated using standard treatment and cultured skin treatment.
Explanation of Solution
Refer to Fig. 31.15, “Treatment of diabetic food ulcers”, in the textbook. The bar graph shows an experiment that was conducted to heal the wounds of diabetic foot ulcers. It involved the participation of many patients who were randomly treated using standard treatment and cultured skin treatment, and their improvement was observed for about 12 weeks. According to the observations, a bar graph was plotted, which shows the percentage of wounds healed versus the number of weeks. Each bar represents the percentage of foot ulcers that had healed completely. The orange color indicates the standard treatment, and green color indicates the cultured skin treatment.
The percentage of wounds healed at 8 weeks when treated with standard treatment was 24%. The percentage of wounds healed at 8 weeks when treated with cultured skin treatment was 45 %. The cultured skin treatment had a greater percentage when compared with the standard treatment.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 31 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- What is behavioral adaptarrow_forward22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is the label ?arrow_forward
- Can you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forwardglg 112 mid unit assignment Identifying melting processesarrow_forwardGive only the mode of inheritance consistent with all three pedigrees and only two reasons that support this, nothing more, (it shouldn't take too long)arrow_forward
- Oarrow_forwardDescribe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning





