
Three long, current-carrying wires are parallel to one another and separated by a distance d. The magnitudes and directions of the currents are shown in Figure P30.91. Wires 1 and 3 are fixed, but wire 2 is free to move. Wire 2 is displaced to the right by a small distance x. Determine the net force (per unit length) acting on wire 2 and the angular frequency of the resulting oscillation. Assume the mass per unit length of wire 2 is λ and x ≪ d.
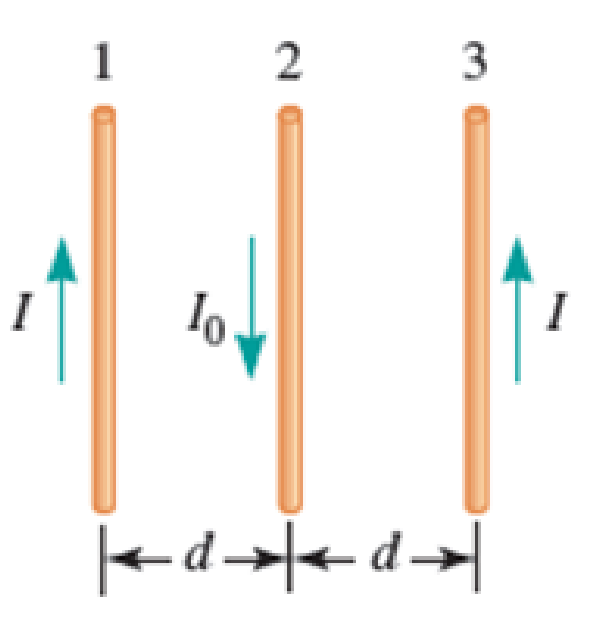
FIGURE P30.91
(a)
The net force per unit length acting on wire
Answer to Problem 91PQ
The net force (per unit length) acting on wire
Explanation of Solution
The wire
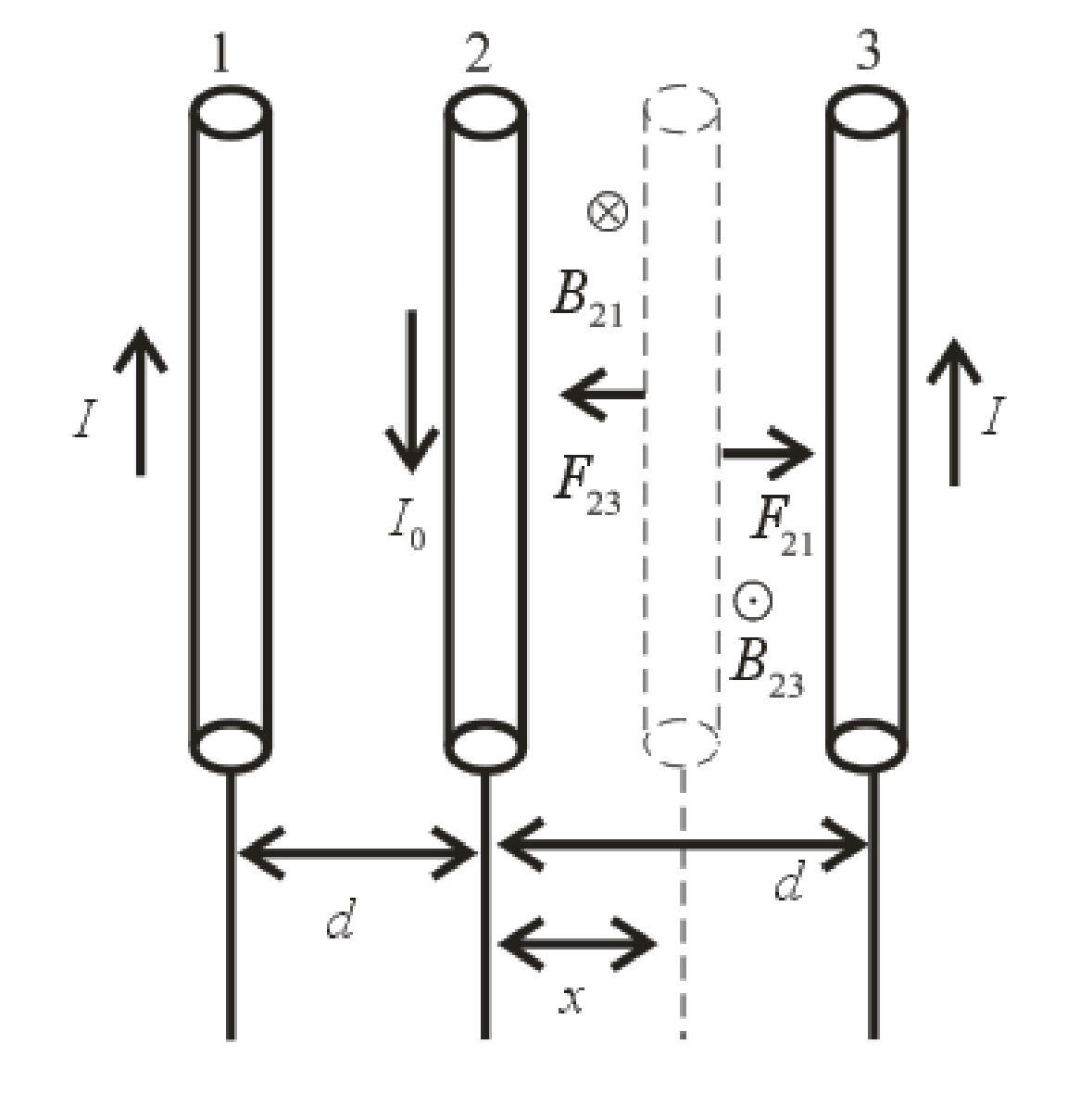
The direction of magnetic field on wire
Write the expression of the force between two parallel current carrying conductors per unit length.
Here,
Substitute
Here,
Substitute
Here,
Write the expression for the net force on wire
Conclusion:
Substitute
Since
This implies that
Thus, the net force (per unit length) acting on wire
(b)
The angular frequency of the resulting oscillation.
Answer to Problem 91PQ
The angular frequency of the resulting oscillating is
Explanation of Solution
Rewrite the equation (V).
Since, the wire
Write the expression for the force experienced by the wire
Rearrange the above expression.
Here,
Substitute
Rearrange the above expression.
Write the general expression for our oscillating wave.
Here,
Compare equation (VIII) is and (IX) for the coefficient of
Conclusion:
Hence, the angular frequency of the resulting oscillation is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- Three moles of an ideal gas undergo a reversible isothermal compression at 20.0° C. During this compression, 1900 J of work is done on the gas. For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Entropy change in a free expansion. Part A What is the change of entropy of the gas? ΤΕ ΑΣΦ AS = Submit Request Answer J/Karrow_forward5.97 Block A, with weight 3w, slides down an inclined plane S of slope angle 36.9° at a constant speed while plank B, with weight w, rests on top of A. The plank is attached by a cord to the wall (Fig. P5.97). (a) Draw a diagram of all the forces acting on block A. (b) If the coefficient of kinetic friction is the same between A and B and between S and A, determine its value. Figure P5.97 B A S 36.9°arrow_forwardPlease take your time and solve each part correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- help me answer this with explanations! thanks so mucharrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Alreadyarrow_forwardWhat fuel economy should be expected from a gasoline powered car that encounters a total of 443N of resistive forces while driving down the road? (Those forces are from air drag, rolling resistance and bearing losses.) Assume a 30% thermodynamic efficiency.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward12. What is the angle between two unit vectors if their dot product is 0.5?arrow_forwardIf the car in the previous problem increases its power output by 10% (by pressing the gas pedal farther down), at what rate will the car accelerate? Hint: Consider the net force. In the previous problem the power was 31.8kWarrow_forward
- What power is required (at the wheels) for a 1400 kg automobile to climb a 4% grade at a constant speed 30 m/s while it is opposed by drag and rolling resistance forces totaling 500 N?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardAs a box is lifted against gravity and placed on a shelf, how does the work done by the lifter compare with the work done by gravity? What is the net work done on the box? What does this imply about its change in kinetic energy? Use definitions and mathematics from this chapter to answer these questions.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





