
PHY F/SCIENTIST MOD MASTERING 24 MO
17th Edition
ISBN: 9780137319497
Author: Knight
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 30, Problem 75EAP
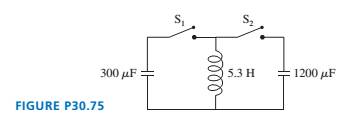
The 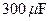 capacitor in FIGURE P30.75 is initially charged to ,
capacitor in FIGURE P30.75 is initially charged to , 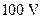 the
the 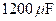 capacitor is uncharged, and the switches are both open.
capacitor is uncharged, and the switches are both open.
a. What is the maximum voltage to which you can charge the 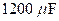 capacitor by the proper closing and opening of the two switches?
capacitor by the proper closing and opening of the two switches?
b. How would you do it? Describe the sequence in which you would close and open switches and the times at which you would do so. The first switch is closed at . 
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solution
Cam mechanisms are used in many machines. For example, cams open and close the valves in your car engine to admit gasoline vapor to each cylinder and to allow the escape of exhaust.
The principle is illustrated in the figure below, showing a follower rod (also called a pushrod) of mass m resting on a wedge of mass M. The sliding wedge duplicates the function of a
rotating eccentric disk on a camshaft in your car. Assume that there is no friction between the wedge and the base, between the pushrod and the wedge, or between the rod and the guide
through which it slides. When the wedge is pushed to the left by the force F, the rod moves upward and does something such as opening a valve. By varying the shape of the wedge, the
motion of the follower rod could be made quite complex, but assume that the wedge makes a constant angle of 0 = 15.0°. Suppose you want the wedge and the rod to start from rest and
move with constant acceleration, with the rod moving upward 1.00 mm in 8.00 ms. Take m…
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 30 Solutions
PHY F/SCIENTIST MOD MASTERING 24 MO
Ch. 30 - Prob. 1CQCh. 30 - You want to insert a loop of copper wire between...Ch. 30 - A vertical, rectangular loop of copper wire is...Ch. 30 - Does the loop of wire in FIGURE Q30.4 have a...Ch. 30 - s5. The two loops of wire in FIGURE Q30.5 are...Ch. 30 - FIGURE Q30.6 shows a bar magnet being pushed...Ch. 30 - A bar magnet is pushed toward a loop of wire as...Ch. 30 - FIGURE Q30.8 shows a bar magnet. a coil of wire,...Ch. 30 - Prob. 9CQCh. 30 - An inductor with a 2.0 A current stores energy. At...
Ch. 30 - Prob. 11CQCh. 30 - Prob. 12CQCh. 30 - Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the three...Ch. 30 - For the circuit of FIGURE Q30.14: a. What is the...Ch. 30 - The earth’s magnetic field strength is 5.0105T ....Ch. 30 - A potential difference of 0.050 V is developed...Ch. 30 - A 10 -cm-long wire is pulled along a U-shaped...Ch. 30 - What is the magnetic flux through the loop shown...Ch. 30 - FIGURE EX30.5 shows a 10cm10cm square bent at a 90...Ch. 30 - Prob. 6EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 7EAPCh. 30 - FIGURE EX30.8 shows a 2.0 -cm-diameter solenoid...Ch. 30 - Prob. 9EAPCh. 30 - 10. A solenoid is wound as shown in FIGURE...Ch. 30 - 11. The metal equilateral triangle in FIGURE...Ch. 30 - The current in the solenoid of FIGURE EX3O.12 is...Ch. 30 - The loop in FIGURE EX30.13 is being pushed into...Ch. 30 - FIGURE EX30.14 shows a 10-cm-diameter loop in...Ch. 30 - Prob. 15EAPCh. 30 - 16. A -turn coil of wire cm in diameter is in a...Ch. 30 - A 5.0 -cm-diameter coil has 20 turns and a...Ch. 30 - FIGURE EX30.18 shows the current as a function of...Ch. 30 - The magnetic field in FIGURE EX30.19 is decreasing...Ch. 30 - The magnetic field inside a -cm-diameter solenoid...Ch. 30 - Scientists studying an anomalous magnetic field...Ch. 30 - Prob. 22EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 23EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 24EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 25EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 26EAPCh. 30 - How much energy is stored in a -cm-diameter,...Ch. 30 - MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a medical...Ch. 30 - Prob. 29EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 31EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 32EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 33EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 34EAPCh. 30 - At t=0 s, the current in the circuit in FIGURE...Ch. 30 - The switch in FIGURE EX3O.36 has been open for a...Ch. 30 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 38EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 40EAPCh. 30 - A 10cm10cm square loop lies in the xy-plane. The...Ch. 30 - A spherical balloon with a volume of L is in a mT...Ch. 30 - Prob. 43EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 30 - FIGURE P30.46 shows a 4.0-cm-diameter loop with...Ch. 30 - Prob. 47EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 48EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 49EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 50EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 51EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 52EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 53EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 54EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 55EAPCh. 30 - Your camping buddy has an idea for a light to go...Ch. 30 - 57. The -wide, zero-resistance slide wire shown...Ch. 30 - ]58. You’ve decided to make the magnetic...Ch. 30 - FIGURE P30.59 shows a U-shaped conducting rail...Ch. 30 - Prob. 60EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 61EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 62EAPCh. 30 - Equation 30.26 is an expression for the induced...Ch. 30 - Prob. 64EAPCh. 30 - One possible concern with MRI (see Exercise 28) is...Ch. 30 - FIGURE P30.66 shows the current through a 10mH...Ch. 30 - Prob. 67EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 68EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 69EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 70EAPCh. 30 - An LC circuit is built with a inductor and an...Ch. 30 - Prob. 72EAPCh. 30 - For your final exam in electronics, you’re asked...Ch. 30 - The inductor in FIGURE P30.74 is a -cm-long, -cm-...Ch. 30 - The capacitor in FIGURE P30.75 is initially...Ch. 30 - The switch in FIGURE P30.76 has been open for a...Ch. 30 - 77. The switch in FIGURE P30.77 has been open for...Ch. 30 - Prob. 78EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 79EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 80EAPCh. 30 - In recent years it has been possible to buy a 1.0F...Ch. 30 - Prob. 82EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 83EAPCh. 30 - Prob. 84EAPCh. 30 - A 2.0 -cm-diameter solenoid is wrapped with 1000...Ch. 30 - High-frequency signals are often transmitted along...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardA rectangular current loop (a = 15.0 cm, b = 34.0 cm) is located a distance d = 10.0 cm near a long, straight wire that carries a current (Iw) of 17.0 A (see the drawing). The current in the loop is IL = 21.0 A. Determine the magnitude of the net magnetic force that acts on the loop. Solve in N. a b IL Iwarrow_forward
- Two long, straight wires are separated by distance, d = 22.0 cm. The wires carry currents of I1 = 7.50 A and I2 = 5.50 A in opposite directions, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point (B). Let r₁ = 12.0 cm, r2 = 7.00 cm, and r3 = 13.0 cm. Solve in T. 12 d A √3arrow_forwardI tried to solve this question, and I had an "expert" answer it and they got it wrong. I cannot answer this questionarrow_forwardEddie Hall is the current world record holder in the deadlift, a powerlifting maneuver in which a weighted barbell is lifted from the ground to waist height, then dropped. The figure below shows a side view of the initial and final positions of the deadlift. a 0 = 55.0° Fift h22.5 cm i hy = 88.0 cm b iarrow_forward
- solve for (_) Narrow_forwardTwo boxes of fruit on a frictionless horizontal surface are connected by a light string as in the figure below, where m₁ = 11 kg and m₂ = 25 kg. A force of F = 80 N is applied to the 25-kg box. mq m1 Applies T Peaches i (a) Determine the acceleration of each box and the tension in the string. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s² N (b) Repeat the problem for the case where the coefficient of kinetic friction between each box and the surface is 0.10. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s2 Narrow_forwardAll correct but t1 and t2 from part Aarrow_forward
- Three long, straight wires are mounted on the vertices of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. The wires carry currents of I₁ = 3.50 A, I2 = 5.50 A, and I3 = 8.50 A. Each side of the triangle has a length of 34.0 cm, and the point (A) is located half way between (11) and (12) along one of the sides. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at point (A). Solve in Teslas (T). I₁arrow_forwardNumber There are four charges, each with a magnitude of 2.38 μC. Two are positive and two are negative. The charges are fixed to the corners of a 0.132-m square, one to a corner, in such a way that the net force on any charge is directed toward the center of the square. Find the magnitude of the net electrostatic force experienced by any charge. ips que Mi Units estic re harrow_forwardTwo long, straight wires are separated by distance, d = 22.0 cm. The wires carry currents of I1 = 7.50 A and I2 = 5.50 A in opposite directions, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point (B). Let r₁ = 12.0 cm, r2 = 7.00 cm, and r3 = 13.0 cm. Solve in T. 12 d A √3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What is Electromagnetic Induction? | Faraday's Laws and Lenz Law | iKen | iKen Edu | iKen App; Author: Iken Edu;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3HyORmBip-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY