
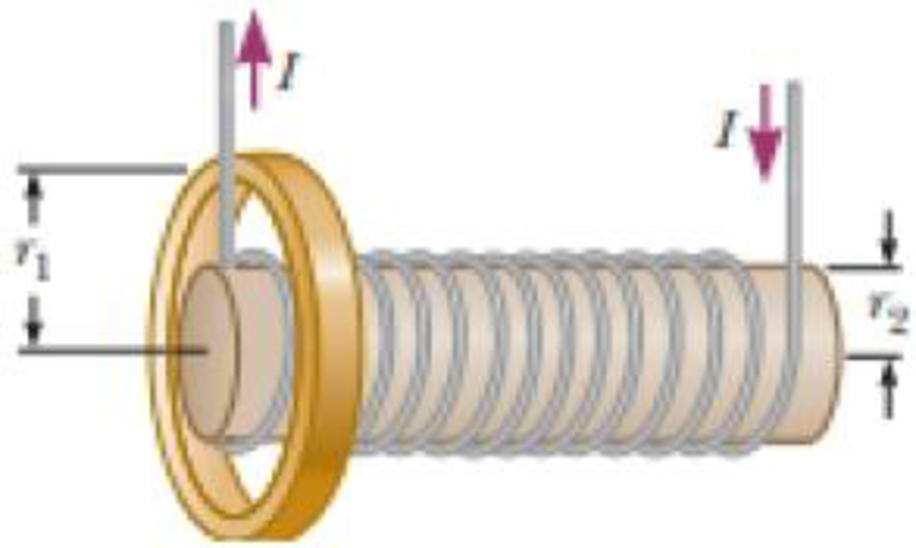
An aluminum ring of radius r1 = 5.00 cm and resistance 3.00 × 10−4 Ω is placed around one end of a long air-core solenoid with 1 000 turns per meter and radius r2 = 3.00 cm as shown in Figure P30.5. Assume the axial component of the field produced by the solenoid is one-half as strong over the area of the end of the solenoid as at the center of the solenoid. Also assume the solenoid produces negligible field outside its cross-sectional area. The current in the solenoid is increasing at a rate of 270 A/s. (a) What is the induced current in the ring? At the center of the ring, what are (b) the magnitude and (c) the direction of the magnetic field produced by the induced current in the ring?
Figure P30.5 Problems 5 and 6.
(a)
The induced current in the ring.
Answer to Problem 5P
The induced current in the ring is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: Radius of aluminum ring is
The magnetic field due to solenoid can be given as,
Here,
The area of the coil can be given as,
Here,
Substitute
The emf generated in the coil can be given as,
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
As the ring is placed around one end and also the field produced by the end of the solenoid is half at the centre of the solenoid.
Then, emf induced in the ring can be given as,
Here,
Substitute
The current induced in the ring can be given as,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the current induced in the ring is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the current induced in the ring is
(b)
The magnitude of the magnetic field at the centre of the ring.
Answer to Problem 5P
The magnitude of the magnetic field at the centre of the ring is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: Radius of aluminum ring is
The magnetic field at the center of the ring can be given as,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the magnitude of the magnetic field is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the magnetic field at the center of ring is
(c)
The direction of magnetic field at the center of the ring.
Answer to Problem 5P
The direction of magnetic field at the center of the ring is towards the left.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: Radius of aluminum ring is
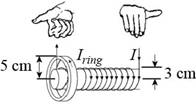
Figure (1)
The solenoid’s field points to the right through the ring as shown in the figure (I). So, to oppose the increasing field, the direction of magnetic field at the center of the ring will be towards the left.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the direction of magnetic field at the center of the ring will be towards towards the left.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Bundle: Physics For Scientists And Engineers With Modern Physics, 10th + Webassign Printed Access Card For Serway/jewett's Physics For Scientists And Engineers, 10th, Multi-term
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
- What is the resistance (in (2) of a 27.5 m long piece of 17 gauge copper wire having a 1.150 mm diameter? 0.445 ΧΩarrow_forwardFind the ratio of the diameter of silver to iron wire, if they have the same resistance per unit length (as they might in household wiring). d. Ag dFe = 2.47 ×arrow_forwardFind the ratio of the diameter of silver to iron wire, if they have the same resistance per unit length (as they might in household wiring). d Ag = 2.51 dFe ×arrow_forward
- Show that the units 1 v2/Q = 1 W, as implied by the equation P = V²/R. Starting with the equation P = V²/R, we can get an expression for a watt in terms of voltage and resistance. The units for voltage, V, are equivalent to [? v2 v2 A, are equivalent to J/C ✓ X . Therefore, 1 = 1 = 1 A V1 J/s Ω V-A X = 1 W. . The units for resistance, Q, are equivalent to ? The units for current,arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





