
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
9th Edition
ISBN: 8220100461262
Author: SERWAY
Publisher: Cengage Learning US
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 30, Problem 30.9CQ
The quantity ∫
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A charge of -3.99 μC is fixed in place. From a horizontal distance of 0.0423 m, a
particle of mass 7.31 x 103 kg and charge -9.76 µC is fired with an initial speed
of 84.1 m/s directly toward the fixed charge. How far does the particle travel
before its speed is zero?
a)
What is the minimum tension in N that the cable must be able to support without breaking? Assume the cable is massless.
T =
b)
If the cable can only support a tension of 10,000 N what is the highest mass the ball can have in kg?
mm =
Curve Fitter
CURVE FITTER
Open
Update Fit
Save
New
Exclusion Rules
Select Validation Data
Polynomial Exponential Logarithmic
Auto
Fourier
Fit
Fit
Duplicate Data
Manual
FILE
DATA
FIT TYPE
FIT
Harmonic Motion X
us
0.45
mi
ce
0.4
0.35
0.3
0.25
0.2
Residuals Plot
Contour Plot
Plot Prediction Bounds None
VISUALIZATION
Colormap Export
PREFERENCES EXPORT
Fit Options
COA Fourier
Equation
Fit Plot
x vs. t
-Harmonic Motion
a0+ a1*cos(x*w) +
b1*sin(x*w)
Number of terms
Center and scale
1
▸ Advanced Options
Read about fit options
Results
Value
Lower
Upper
0.15
a0
0.1586
0.1551
0.1620
a1
0.0163
0.0115
0.0211
0.1
b1
0.0011
-0.0093
0.0115
W
1.0473
0.9880
1.1066
2
8
10
t
12
14
16
18
20
Goodness of Fit
Value
Table of Fits
SSE
0.2671
Fit State Fit name
Data
Harmonic Motion x vs. t
Fit type
fourier1
R-square
0.13345
SSE
DFE
0.26712
296
Adj R-sq
0.12467
RMSE
0.030041
# Coeff
Valic
R-square
0.1335
4
DFE
296.0000
Adj R-sq
0.1247
RMSE
0.0300
Chapter 30 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
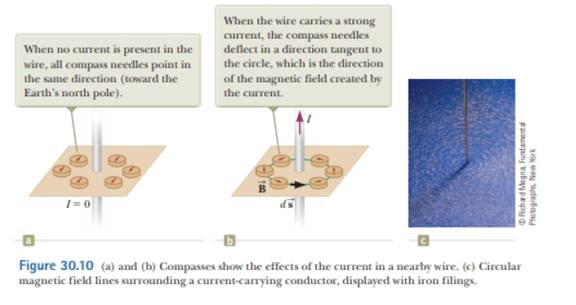
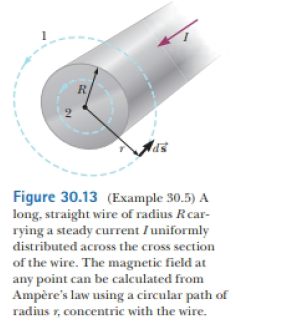
Ch. 30 - Consider the magnetic field due to the current in...Ch. 30 - A loose spiral spring carrying no current is hung...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.3QQCh. 30 - Prob. 30.4QQCh. 30 - Consider a solenoid that is very long compared...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.1OQCh. 30 - In Figure 30.7, assume I1 = 2.00 A ami I2 = 6.00...Ch. 30 - Answer each question yes or no. (a) Is it possible...Ch. 30 - Two long, parallel wires each carry the same...Ch. 30 - Two long, straight wires cross each other at a...
Ch. 30 - A long, vertical, metallic wire carries downward...Ch. 30 - Suppose you are facing a tall makeup mirror on a...Ch. 30 - A long, straight wire carries a current I (Fig....Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.9OQCh. 30 - Consider the two parallel wires carrying currents...Ch. 30 - What creates a magnetic Hold? More than one answer...Ch. 30 - A long solenoid with closely spaced turns carries...Ch. 30 - A uniform magnetic field is directed along the x...Ch. 30 - Rank the magnitudes of the following magnetic...Ch. 30 - Solenoid A has length L and N turns, solenoid B...Ch. 30 - Is the magnetic field created by a current loop...Ch. 30 - One pole of a magnet attracts a nail. Will the...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.3CQCh. 30 - A hollow copper tube carries a current along its...Ch. 30 - Imagine you have a compass whose needle can rotate...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.6CQCh. 30 - A magnet attracts a piece of iron. The iron can...Ch. 30 - Why does hitting a magnet with a hammer cause the...Ch. 30 - The quantity B ds in Amperes law is called...Ch. 30 - Figure CQ30.10 shows four permanent magnets, each...Ch. 30 - Explain why two parallel wires carrying currents...Ch. 30 - Consider a magnetic field that is uniform in...Ch. 30 - Review. In studies of the possibility of migrating...Ch. 30 - In each of parts (a) through (c) of Figure P30.2....Ch. 30 - Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field at a...Ch. 30 - Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field at a...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.5PCh. 30 - In Niels Bohrs 1913 model of the hydrogen atom, an...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.7PCh. 30 - A conductor consists of a circular loop of radius...Ch. 30 - Two long, straight, parallel wires carry currents...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.10PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.11PCh. 30 - Consider a flat, circular current loop of radius R...Ch. 30 - A current path shaped as shown in Figure P30.13...Ch. 30 - One long wire carries current 30.0 A to the left...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.15PCh. 30 - In a long, .straight, vertical lightning stroke,...Ch. 30 - Determine the magnetic field (in terms of I, a,...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.18PCh. 30 - Determine the magnetic field (in terms of I, a,...Ch. 30 - Two long, parallel wires carry currents of I1 =...Ch. 30 - Two long, parallel conductors, separated by 10.0...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.22PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.23PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.24PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.25PCh. 30 - In Figure P30.25, the current in the long,...Ch. 30 - Two long, parallel wires are attracted to each...Ch. 30 - Why is the following situation impossible? Two...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.29PCh. 30 - Niobium metal becomes a superconductor when cooled...Ch. 30 - Figure P30.31 Is a cross-sectional view of a...Ch. 30 - The magnetic coils of a tokamak fusion reactor are...Ch. 30 - A long, straight wire lies on a horizontal table...Ch. 30 - An infinite sheet of current lying in the yz plane...Ch. 30 - The magnetic field 40.0 cm away from a long,...Ch. 30 - A packed bundle of 100 long, straight, insulated...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.37PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.38PCh. 30 - Prob. 30.39PCh. 30 - A certain superconducting magnet in the form of a...Ch. 30 - A long solenoid that has 1 000 turns uniformly...Ch. 30 - You are given a certain volume of copper from...Ch. 30 - A single-turn square loop of wire, 2.00 cm on each...Ch. 30 - A solenoid 10.0 cm in diameter and 75.0 cm long is...Ch. 30 - It is desired to construct a solenoid that will...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.46PCh. 30 - A cube of edge length l=2.50 cm is positioned as...Ch. 30 - A solenoid of radius r = 1.25 cm and length =...Ch. 30 - The magnetic moment of the Earth is approximately...Ch. 30 - At saturation, when nearly all the atoms have...Ch. 30 - A 30.0-turn solenoid of length 6.00 cm produces a...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.52APCh. 30 - Suppose you install a compass on the center of a...Ch. 30 - Why is the following situation impossible? The...Ch. 30 - A nonconducting ring of radius 10.0 cm is...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.56APCh. 30 - Prob. 30.57APCh. 30 - A circular coil of five turns and a diameter of...Ch. 30 - A very large parallel-plate capacitor has uniform...Ch. 30 - Two circular coils of radius R, each with N turns,...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.61APCh. 30 - Two circular loops are parallel, coaxial, and...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.63APCh. 30 - Prob. 30.64APCh. 30 - As seen in previous chapters, any object with...Ch. 30 - Review. Rail guns have been suggested for...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.67APCh. 30 - An infinitely long, straight wire carrying a...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.69CPCh. 30 - We have seen that a long solenoid produces a...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.71CPCh. 30 - Prob. 30.72CPCh. 30 - A wire carrying a current I is bent into the shape...Ch. 30 - Prob. 30.74CPCh. 30 - Prob. 30.75CPCh. 30 - Prob. 30.76CPCh. 30 - The magnitude of the force on a magnetic dipole ...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What point on the spring or different masses should be the place to measure the displacement of the spring? For instance, should you measure to the bottom of the hanging masses?arrow_forwardLet's assume that the brightness of a field-emission electron gun is given by β = 4iB π² d²α² a) Assuming a gun brightness of 5x108 A/(cm²sr), if we want to have an electron beam with a semi-convergence angle of 5 milliradian and a probe current of 1 nA, What will be the effective source size? (5 points) b) For the same electron gun, plot the dependence of the probe current on the parameter (dpa) for α = 2, 5, and 10 milliradian, respectively. Hint: use nm as the unit for the electron probe size and display the three plots on the same graph. (10 points)arrow_forwardi need step by step clear answers with the free body diagram clearlyarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardReview the data in Data Table 1 and examine the standard deviations and 95% Margin of Error calculations from Analysis Questions 3 and 4 for the Acceleration of the 1st Based on this information, explain whether Newton’s Second Law of Motion, Equation 1, was verified for your 1st Angle. Equation: SF=ma Please help with explaining the information I collected from a lab and how it relates to the equation and Newton's Second Law. This will help with additional tables in the lab. Thanks!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the problem step by step with explanations along side each step stating what's been done correctly please. Thank you!! ( preferably type out everything)arrow_forward
- Kirchoff's Laws. A circuit contains 3 known resistors, 2 known batteries, and 3 unknown currents as shown. Assume the current flows through the circuit as shown (this is our initial guess, the actual currents may be reverse). Use the sign convention that a potential drop is negative and a potential gain is positive. E₂ = 8V R₁₁ = 50 R₂ = 80 b с w 11 www 12 13 E₁ = 6V R3 = 20 a) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop abefa in the clockwise direction starting at point a. (2 pt). b) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop bcdeb in the clockwise direction starting at point b. (2 pt). c) Apply Kirchoff's Junction Rule at junction b (1 pt). d) Solve the above 3 equations for the unknown currents I1, 12, and 13 and specify the direction of the current around each loop. (5 pts) I1 = A 12 = A 13 = A Direction of current around loop abef Direction of current around loop bcde (CW or CCW) (CW or CCW)arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward4.) The diagram shows the electric field lines of a positively charged conducting sphere of radius R and charge Q. A B Points A and B are located on the same field line. A proton is placed at A and released from rest. The magnitude of the work done by the electric field in moving the proton from A to B is 1.7×10-16 J. Point A is at a distance of 5.0×10-2m from the centre of the sphere. Point B is at a distance of 1.0×10-1 m from the centre of the sphere. (a) Explain why the electric potential decreases from A to B. [2] (b) Draw, on the axes, the variation of electric potential V with distance r from the centre of the sphere. R [2] (c(i)) Calculate the electric potential difference between points A and B. [1] (c(ii)) Determine the charge Q of the sphere. [2] (d) The concept of potential is also used in the context of gravitational fields. Suggest why scientists developed a common terminology to describe different types of fields. [1]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What is Electromagnetic Induction? | Faraday's Laws and Lenz Law | iKen | iKen Edu | iKen App; Author: Iken Edu;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3HyORmBip-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY