
Concept explainers
In a long, .straight, vertical lightning stroke, electrons move downward and positive ions move upward and constitute a current of magnitude 20.0 kA. At a location 50.0 m east of the middle of the stroke, a free electron drifts through the air toward the west with a speed of 300 m/s. (a) Make a sketch showing the various vectors involved. Ignore the effect of the Earth's magnetic field. (b) Find the vector force the lightning stroke exerts on the electron. (c) Find the radius of the electron’s path. (d) Is it a good approximation to model the electron as moving in a uniform field? Explain your answer. (e) If it does not collide with any obstacles, how many revolutions will the electron complete during the 60.0-µs duration of the lightning stroke?
(a)
To draw: The various vectors involved to represent the lightning stroke of the electron and the positive ions.
Answer to Problem 30.16P
The various vectors involved to represent the lightning stroke of the electron and the positive ions as shown below,
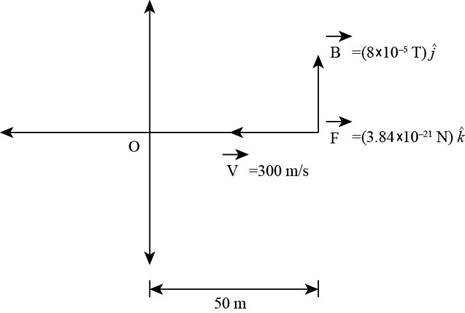
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The electrons move downward and the positive ions move upwards. The magnitude of the uniform current is
According to the Ampere’s right hand thumb rule, the index finger represents the direction of the velocity vector
Write the expression for the magnetic field.
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression for the direction of the magnetic field according to the ampere’s law of the magnetic field.
Write the expression for the velocity vector pointed towards the west.
Write the expression for the force vector on the electron,
Here,
Substitute
From the result of the force vector, field vector and velocity vector the as shown below,
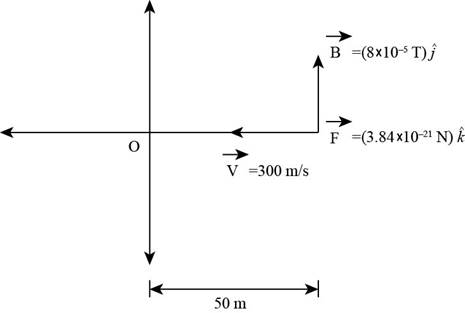
Figure (1)
(b)
The vector force lightning stroke exert on the electron.
Answer to Problem 30.16P
The vector force lightning stroke exert on the electron is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The electrons move downward and the positive ions move upwards. The magnitude of the uniform current is
From the part (a), the vector force on the electron.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the vector force lightning stroke exert on the electron is
(c)
The radius of the electron path.
Answer to Problem 30.16P
The radius of the electron path is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The electrons move downward and the positive ions move upwards. The magnitude of the uniform current is
Write the expression for the radius of the electron path.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the radius of the electron path is
(d)
Whether it is a good approximation to model the electron as moving in a uniform field.
Answer to Problem 30.16P
The electron was not moving in a uniform field cause of the magnetic field is varies from the location of the lightning stroke.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The electrons move downward and the positive ions move upwards. The magnitude of the uniform current is
From the figure (1) of the part (a), the magnitude of the magnetic field is varies with the distance of the light stroke towards the positive
Conclusion:
Therefore, the electron was not moving in a uniform field cause of the magnetic field is varies from the location of the lightning stroke.
(e)
The number of the revolutions will the electron complete during the
Answer to Problem 30.16P
The number of the revolutions will the electron complete during
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The electrons move downward and the positive ions move upwards. The magnitude of the uniform current is
From the part (c) the radius of the electron path,
Write the expression for the number of the revolution complete by the electron.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the number of the revolutions will the electron complete during
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update, Hybrid Edition (with Enhanced WebAssign Multi-Term LOE Printed Access Card for Physics)
- 3. As a woman, who's eyes are h = 1.5 m above the ground, looks down the road sees a tree with height H = 9.0 m. Below the tree is what appears to be a reflection of the tree. The observation of this apparent reflection gives the illusion of water on the roadway. This effect is commonly called a mirage. Use the results of questions 1 and 2 and the principle of ray reversibility to analyze the diagram below. Assume that light leaving the top of the tree bends toward the horizontal until it just grazes ground level. After that, the ray bends upward eventually reaching the woman's eyes. The woman interprets this incoming light as if it came from an image of the tree. Determine the size, H', of the image. (Answer 8.8 m) please show all work step by steparrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardPlease solvearrow_forward
- Please solvearrow_forwardA piece of silicon semiconductor has length L=0.01cm and cross-section in a square shape with an area of A=5×10−4cm2 . The semiconductor is doped with 1012cm−3 Phosphorus atoms and 1017cm−3 Boron atoms. An external electric field E=1.5×104N/C is applied to the silicon piece along the length direction, through the cross section. What is the total current in the silicon at T=300K? Assume the mobility of silicon is 1400cm2V−1s−1 for electrons and 450cm2V−1s−1 for holes, respectively. Assume the intrinsic carrier concentration in silicon is 1010cm−3 . Give your answer in mA, rounded to 3 significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.arrow_forwardAn impurity with a charge of 2e is placed in a three-dimensional metal. Assume that the Friedel sum rule holds for this system, and only the scattering phase shifts from the electrons contribute to this sum (we don't need to consider ion phase shifts). This metal has a spherical Fermi surface with Fermi wave vector kF . The only degeneracy for the electrons at the Fermi surface is spin (two-fold) and angular momentum ( 2l+1 for each angular momentum l ). Ignore scattering for l>2 and assume that the scattering doesn't depend on the spin degree of freedom. Denote the scattering phase shift at the Fermi wave vector in the l -th angular momentum channel as δl(kF) . If δ0(kF)=11π31 , and δ1(kF)=π29 , what is δ2(kF)? Round your answer to three significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.arrow_forward
- A pilot with a mass of 75 kg is flying an airplane at a true airspeed of 55m/s in air that is still relative to the ground. The pilot enters a coordinated turn of constant bank angle and constant altitude, and the pilot experiences an effective weight of 1471.5N normal to the wings of the plane. What is the rate of turn (in degrees per second) for the aircraft? Round your answer to three significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.arrow_forwardImagine you are out for a stroll on a sunny day when you encounter a lake. Unpolarized light from the sun is reflected off the lake into your eyes. However, you notice when you put on your vertically polarized sunglasses, the light reflected off the lake no longer reaches your eyes. What is the angle between the unpolarized light and the surface of the water, in degrees, measured from the horizontal? You may assume the index of refraction of air is nair=1 and the index of refraction of water is nwater=1.33 . Round your answer to three significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.arrow_forwardRed, yellow, green, and blue light with wavelengths of λred=700 nm , λyellow=580 nm , λgreen=520 nm , and λblue=475 nm are directed at a slit that is 20 μm wide at normal incidence. The light hits a screen 1 m behind the slit. Which color of light will have an interference minimum closest to a point 10 cm away from its central maxima? You may assume the small angle approximation sinθ≈tanθ≈θ for angles smaller than 10∘ . Just enter the wavelength of that color in nm, nothing else.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





