
Fox and McDonald's Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781118912652
Author: Philip J. Pritchard, John W. Mitchell
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 72P
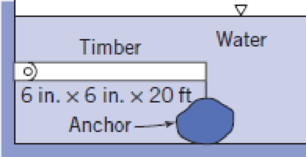
The timber weighs 40 lb/ft3 and is held in a horizontal position by the concrete (150 lb/ft3) anchor. Calculate the minimum total weight which the anchor may have.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
1) In each of the following scenarios, based on the plane of impact (shown with an (n, t)) and the
motion of mass 1, draw the direction of motion of mass 2 after the impact. Note that in all
scenarios, mass 2 is initially at rest. What can you say about the nature of the motion of mass 2
regardless of the scenario?
m1
15
<+
m2
2)
y
"L
χ
m1
m2
m1
בז
m2
F
8. In the following check to see if the set S is a vector subspace of the corresponding Rn. If
it is not, explain why not. If it is, then find a basis and the dimension.
X1
(a) S
=
X2
{[2], n ≤ n } c
X1 X2
CR²
X1
(b) S
X2
=
X3
X4
x1 + x2 x3 = 0
2) Suppose that two unequal masses m₁ and m₂ are moving with initial velocities V₁ and V₂,
respectively. The masses hit each other and have a coefficient of restitution e. After the impact,
mass 1 and 2 head to their respective gaps at angles a and ẞ, respectively. Derive expressions
for each of the angles in terms of the initial velocities and the coefficient of restitution.
m1
m2
8
m1
↑
บา
m2
ñ
В
Chapter 3 Solutions
Fox and McDonald's Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
Ch. 3 - Because the pressure falls, water boils at a lower...Ch. 3 - Ear popping is an unpleasant phenomenon sometimes...Ch. 3 - When you are on a mountain face and boil water,...Ch. 3 - Your pressure gauge indicates that the pressure in...Ch. 3 - A 125-mL cube of solid oak is held submerged by a...Ch. 3 - The tube shown is filled with mercury at 20C....Ch. 3 - Calculate the absolute and gage pressure in an...Ch. 3 - An open vessel contains carbon tetrachloride to a...Ch. 3 - A hollow metal cube with sides 100 mm floats at...Ch. 3 - Compressed nitrogen (140 lbm) is stored in a...
Ch. 3 - If at the surface of a liquid the specific weight...Ch. 3 - In the deep ocean the compressibility of seawater...Ch. 3 - Assuming the bulk modulus is constant for sea...Ch. 3 - An inverted cylindrical container is lowered...Ch. 3 - A water tank filled with water to a depth of 16 ft...Ch. 3 - A partitioned tank as shown contains water and...Ch. 3 - Consider the two-fluid manometer shown. Calculate...Ch. 3 - The manometer shown contains water and kerosene....Ch. 3 - Determine the gage pressure in kPa at point a, if...Ch. 3 - With the manometer reading as shown, calculate px....Ch. 3 - Calculate px py for this inverted U-tube...Ch. 3 - An inclined gauge having a tube of 3-mm bore, laid...Ch. 3 - Water flows downward along a pipe that is inclined...Ch. 3 - A reservoir manometer has vertical tubes of...Ch. 3 - A rectangular tank, open to the atmosphere, is...Ch. 3 - The sketch shows a sectional view through a...Ch. 3 - The manometer reading is 6 in. when the funnel is...Ch. 3 - A reservoir manometer is calibrated for use with a...Ch. 3 - The inclined-tube manometer shown has D = 96 mm...Ch. 3 - The inclined-tube manometer shown has D = 76 mm...Ch. 3 - A barometer accidentally contains 6.5 inches of...Ch. 3 - A water column stands 50 mm high in a 2.5-mm...Ch. 3 - Consider a small-diameter open-ended tube inserted...Ch. 3 - Compare the height due to capillary action of...Ch. 3 - If atmospheric pressure at the ground is 101.3 kPa...Ch. 3 - If the temperature in the atmosphere is assumed to...Ch. 3 - A hydropneumatic elevator consists of a...Ch. 3 - Semicircular plane gate AB is hinged along B and...Ch. 3 - A circular gate 3 m in diameter has its center 2.5...Ch. 3 - For the situation shown, find the air pressure in...Ch. 3 - What is the pressure at A? Draw a free body...Ch. 3 - A plane gate of uniform thickness holds back a...Ch. 3 - A rectangular gate (width w = 2 m) is hinged as...Ch. 3 - Gates in the Poe Lock at Sault Ste. Marie,...Ch. 3 - Calculate the minimum force P necessary to hold a...Ch. 3 - Calculate magnitude and location of the resultant...Ch. 3 - Calculate magnitude and location of the resultant...Ch. 3 - A window in the shape of an isosceles triangle and...Ch. 3 - A large open tank contains water and is connected...Ch. 3 - The circular access port in the side of a water...Ch. 3 - The gate AOC shown is 6 ft wide and is hinged...Ch. 3 - The gate shown is hinged at H. The gate is 3 m...Ch. 3 - For the dam shown, what is the vertical force of...Ch. 3 - The parabolic gate shown is 2 m wide and pivoted...Ch. 3 - An open tank is filled with water to the depth...Ch. 3 - A dam is to be constructed using the cross-section...Ch. 3 - The quarter cylinder AB is 10 ft long. Calculate...Ch. 3 - Calculate the magnitude, direction (horizontal and...Ch. 3 - A hemispherical shell 1.2 m in diameter is...Ch. 3 - A cylindrical weir has a diameter of 3 m and a...Ch. 3 - If you throw an anchor out of your canoe but the...Ch. 3 - A hydrometer is a specific gravity indicator, the...Ch. 3 - A cylindrical can 76 mm in diameter and 152 mm...Ch. 3 - If the 10-ft-long box is floating on the oil-water...Ch. 3 - The timber weighs 40 lb/ft3 and is held in a...Ch. 3 - Find the specific weight of the sphere shown if...Ch. 3 - The fat-to-muscle ratio of a person may be...Ch. 3 - An open tank is filled to the top with water. A...Ch. 3 - If the timber weighs 670 N, calculate its angle of...Ch. 3 - The barge shown weighs 40 tons and carries a cargo...Ch. 3 - Quantify the experiment performed by Archimedes to...Ch. 3 - Hot-air ballooning is a popular sport. According...Ch. 3 - It is desired to use a hot air balloon with a...Ch. 3 - The opening in the bottom of the tank is square...Ch. 3 - A balloon has a weight (including crew but not...Ch. 3 - A helium balloon is to lift a payload to an...Ch. 3 - The stem of a glass hydrometer used to measure...Ch. 3 - A sphere of radius R is partially immersed to...Ch. 3 - A sphere of 1-in.-radius made from material of...Ch. 3 - You are in the Bermuda Triangle when you see a...Ch. 3 - Three steel balls (each about half an inch in...Ch. 3 - A proposed ocean salvage scheme involves pumping...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Write an if statement that prints the message The number is valid if the variable temperature is within the ran...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
A picture is taken of a man performing a pole vault, and the minimum radius of curvature of the pole is estimat...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Figure 2-26 shows a grade report that is mailed to students at the end of each semester. Prepare an ERD reflect...
Modern Database Management
The current source in the circuit shown generates the current pulse
Find (a) v (0); (b) the instant of time gr...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Describe the purpose of the access key attribute and how it supports accessibility.
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
This part of a function definition is comprised of one or more statements that are executed when the function i...
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The fallowing question is from a reeds book on applied heat i am studying. Although the answer is provided, im struggling to understand the whole answer and the formulas and the steps theyre using. Also where some ov the values such as Hg and Hf come from in part i for example. Please explain step per step in detail thanks In an NH, refrigerator, the ammonia leaves the evaporatorand enters the cornpressor as dry saturated vapour at 2.68 bar,it leaves the compressor and enters the condenser at 8.57 bar with50" of superheat. it is condensed at constant pressure and leavesthe condenser as saturated liquid. If the rate of flow of the refrigerantthrough the circuit is 0.45 kglmin calculate (i) the compressorpower, (ii) the heat rejected to the condenser cooling water in kJ/s,an (iii) the refrigerating effect in kJ/s. From tables page 12, NH,:2.68 bar, hg= 1430.58.57 bar, hf = 275.1 h supht 50" = 1597.2Mass flow of refrigerant--- - - 0.0075 kgls 60Enthalpy gain per kg of refrigerant in…arrow_forwardstate the formulas for calculating work done by gasarrow_forwardExercises Find the solution of the following Differential Equations 1) y" + y = 3x² 3) "+2y+3y=27x 5) y"+y=6sin(x) 7) y"+4y+4y = 18 cosh(x) 9) (4)-5y"+4y = 10 cos(x) 11) y"+y=x²+x 13) y"-2y+y=e* 15) y+2y"-y'-2y=1-4x³ 2) y"+2y' + y = x² 4) "+y=-30 sin(4x) 6) y"+4y+3y=sin(x)+2 cos(x) 8) y"-2y+2y= 2e* cos(x) 10) y+y-2y=3e* 12) y"-y=e* 14) y"+y+y=x+4x³ +12x² 16) y"-2y+2y=2e* cos(x)arrow_forward
- The state of stress at a point is σ = -4.00 kpsi, σy = 16.00 kpsi, σ = -14.00 kpsi, Try = 11.00 kpsi, Tyz = 8.000 kpsi, and T = -14.00 kpsi. Determine the principal stresses. The principal normal stress σ₁ is determined to be [ The principal normal stress σ2 is determined to be [ The principal normal stress σ3 is determined to be kpsi. kpsi. The principal shear stress 71/2 is determined to be [ The principal shear stress 7½ is determined to be [ The principal shear stress T₁/, is determined to be [ kpsi. kpsi. kpsi. kpsi.arrow_forwardRepeat Problem 28, except using a shaft that is rotatingand transmitting a torque of 150 N * m from the left bearing to the middle of the shaft. Also, there is a profile keyseat at the middle under the load. (I want to understand this problem)arrow_forwardProb 2. The material distorts into the dashed position shown. Determine the average normal strains &x, Ey and the shear strain Yxy at A, and the average normal strain along line BE. 50 mm B 200 mm 15 mm 30 mm D ΕΙ 50 mm x A 150 mm Farrow_forward
- Prob 3. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the shear strain, Yxy, at A. Prob 4. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the average normal strain & along the x axis. Prob 5. The triangular plate is fixed at its base, and its apex A is given a horizontal displacement of 5 mm. Determine the average normal strain &x along the x' axis. x' 45° 800 mm 45° 45% 800 mm 5 mmarrow_forwardAn airplane lands on the straight runaway, originally travelling at 110 ft/s when s = 0. If it is subjected to the decelerations shown, determine the time t' needed to stop the plane and construct the s -t graph for the motion. draw a graph and show all work step by steparrow_forwarddny dn-1y dn-1u dn-24 +a1 + + Any = bi +b₂- + +bnu. dtn dtn-1 dtn-1 dtn-2 a) Let be a root of the characteristic equation 1 sn+a1sn- + +an = : 0. Show that if u(t) = 0, the differential equation has the solution y(t) = e\t. b) Let к be a zero of the polynomial b(s) = b₁s-1+b2sn−2+ Show that if the input is u(t) equation that is identically zero. = .. +bn. ekt, then there is a solution to the differentialarrow_forward
- B 60 ft WAB AB 30% : The crane's telescopic boom rotates with the angular velocity w = 0.06 rad/s and angular acceleration a = 0.07 rad/s². At the same instant, the boom is extending with a constant speed of 0.8 ft/s, measured relative to the boom. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of point B at this instant.arrow_forwardThe motion of peg P is constrained by the lemniscate curved slot in OB and by the slotted arm OA. (Figure 1) If OA rotates counterclockwise with a constant angular velocity of 0 = 3 rad/s, determine the magnitude of the velocity of peg P at 0 = 30°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of peg P at 0 = 30°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 0 (4 cos 2 0)m² B Aarrow_forward5: The structure shown was designed to support a30-kN load. It consists of a boom AB with a 30 x 50-mmrectangular cross section and a rod BC with a 20-mm-diametercircular cross section. The boom and the rod are connected bya pin at B and are supported by pins and brackets at A and C,respectively.1. Calculate the normal stress in boom AB and rod BC,indicate if in tension or compression.2. Calculate the shear stress of pins at A, B and C.3. Calculate the bearing stresses at A in member AB,and in the bracket.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Solids: Lesson 53 - Slope and Deflection of Beams Intro; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I7lTq68JRmY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY