
Concept explainers
1.
Journalize the given transactions.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the given transactions:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| a | Cash (+A) | $1,390 | |
| Receivables (+A) | $24,704 | ||
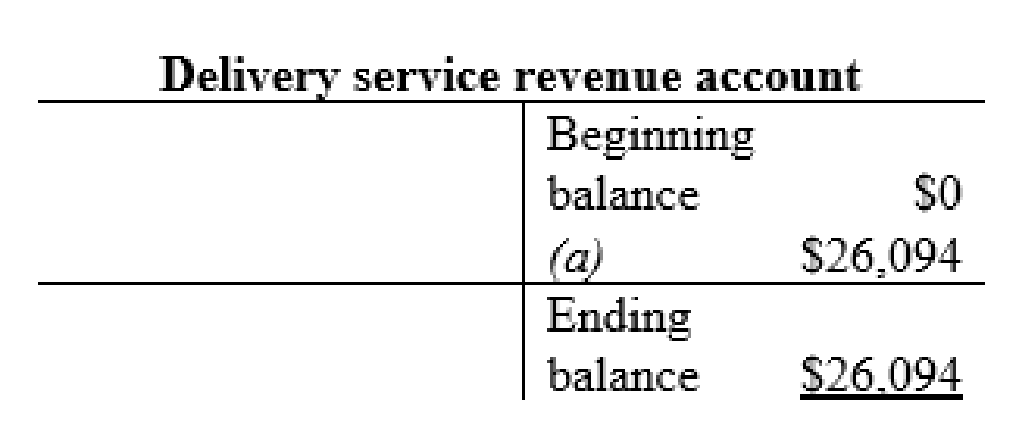
| Delivery Service revenue (+SE, +R) | $26,094 | ||
| (To record the sales) | |||
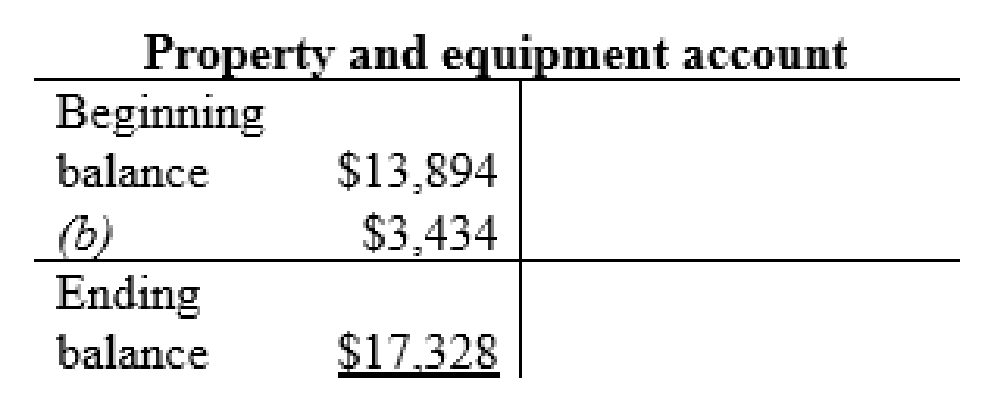
| b | Property and equipment (+A) | $3,434 | |
| Long-term notes payable (+L) | $3,434 | ||
| (To record the long-term notes payable) | |||
| c | Rent expense (+E) (-SE) | $3,136 | |
| Prepaid rent (+A) | $4,728 | ||
| Cash (-A) | $7,864 | ||
| (To record the rent expense and prepaid rent) | |||
| d | Repairs expense (+E) (-SE) | $864 | |
| Cash (-A) | $864 | ||
| (To record the expenses paid) | |||
| e | Cash (+A) | $24,285 | |
| Receivable (-A) | $24,285 | ||
| (To record the receivables collected) | |||
| f | Long-term notes payable (-L) | $150 | |
| Cash (-A) | $150 | ||
| (To record the payment of long-term notes payable) | |||
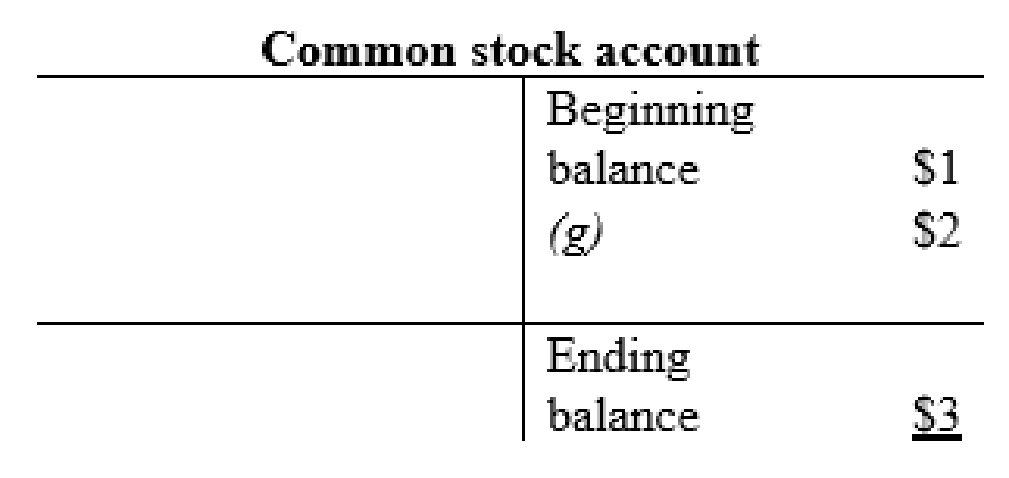
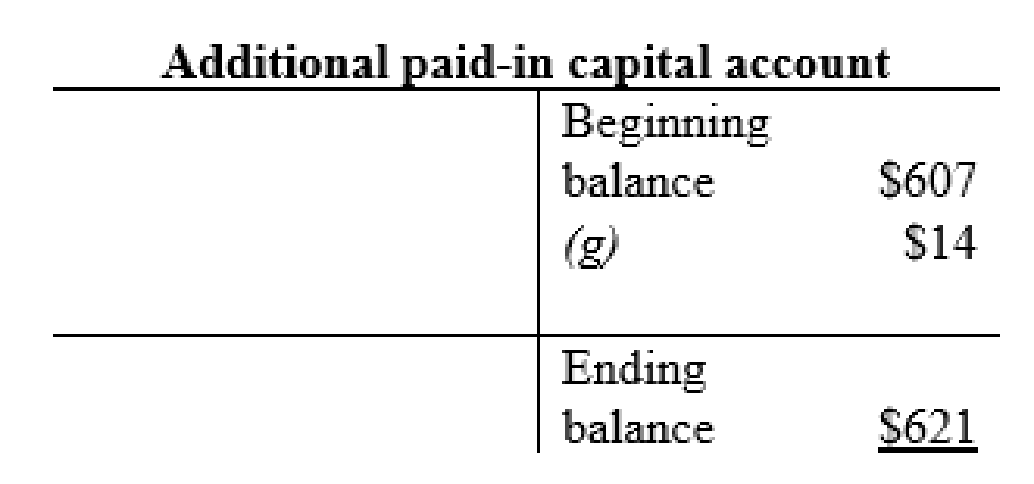
| g | Cash (+A) | $16 | |
| Common Stock (+SE) | $2 | ||
| Additional paid-in-capital (+SE) | $14 | ||
| (To record the receipt of stock) | |||
| h | Wages (+E) (-SE) | $9,276 | |
| Cash (-A) | $9,276 | ||
| (To record the wages paid) | |||
| i | Spare parts, supplies, and fuel (+A) | $6,564 | |
| Cash (-A) | $6,564 | ||
| (To record the sales revenues) | |||
| j | Spare parts, supplies, and fuel expense (+E) (-SE) | $6,450 | |
| Spare parts, supplies, and fuel (-A) | $6,450 | ||
| (To record the sales revenues) | |||
| k | Accounts payable (-L) | $784 | |
| Cash (-A) | $784 | ||
| (To record the sales revenues) | |||
| l | No entry | ||
Table (1)
2
Prepare the T- account and enter the transaction into their respective accounts for calculating the ending balance.
2
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the T-accounts:
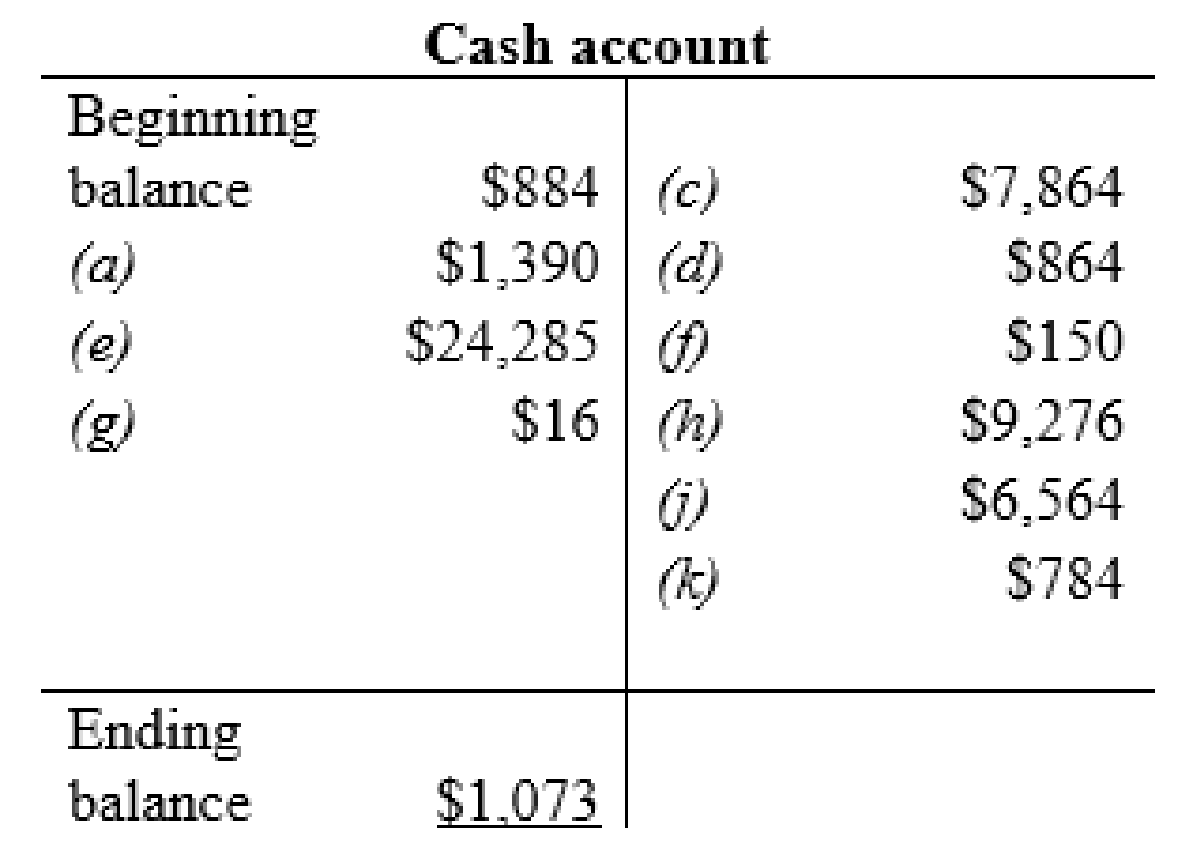
Cash account:
Receivables account:
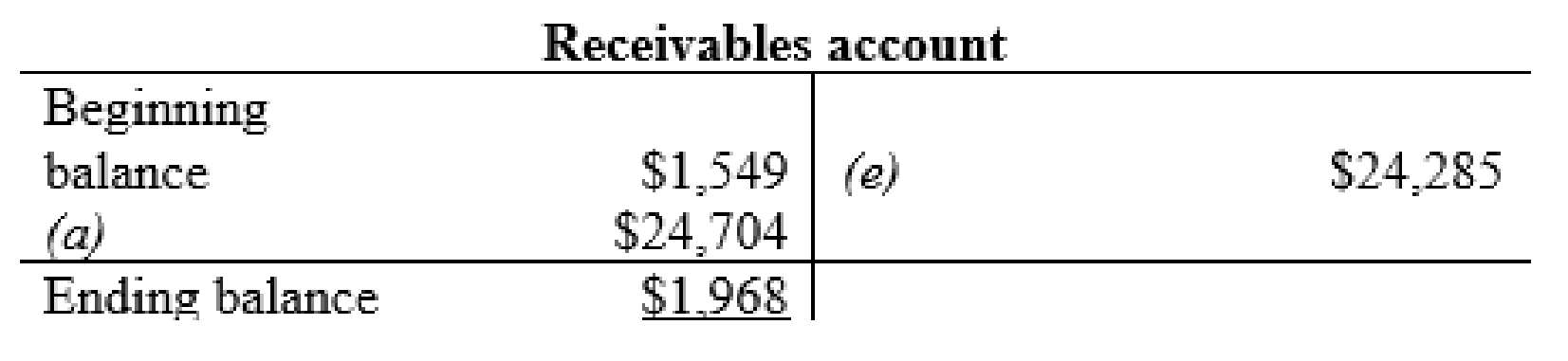
Spare parts, supplies and fuel account:
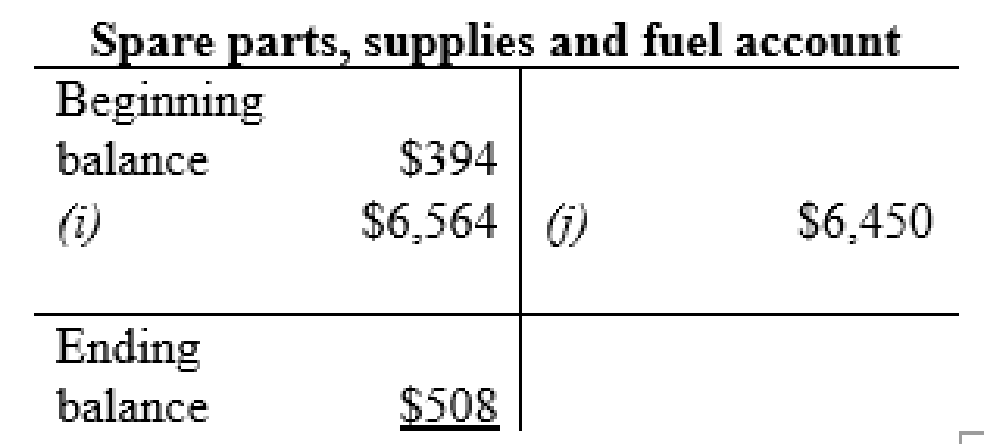
Prepaid expenses account:
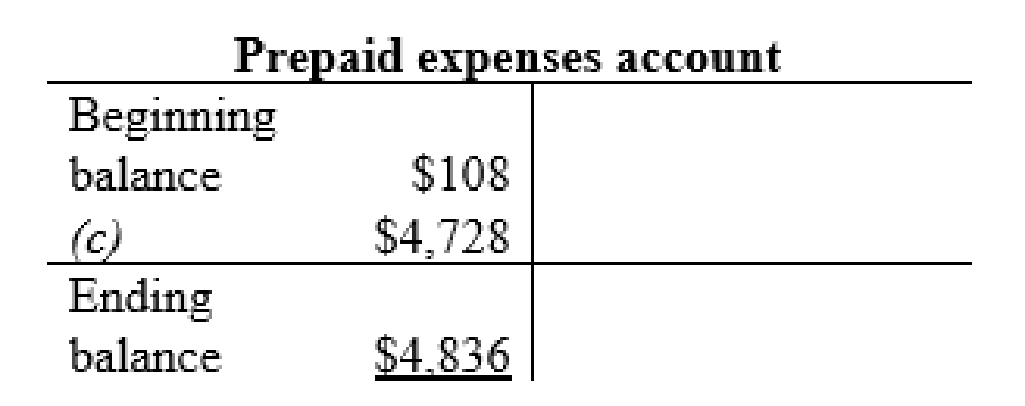
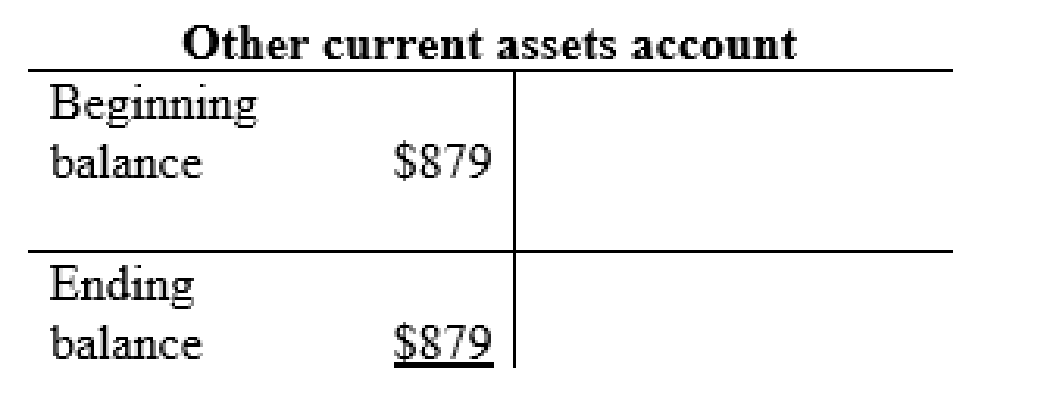
Other current asset account:
Property and equipment account:
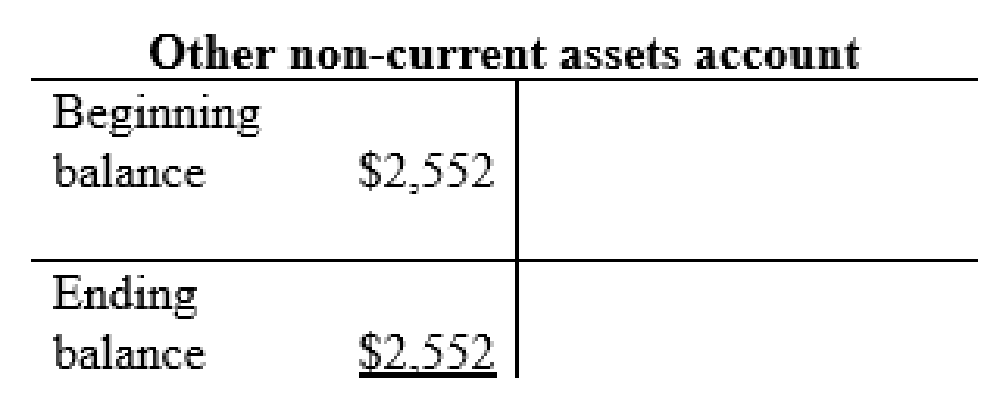
Other non-current asset account:
Accounts payable account:
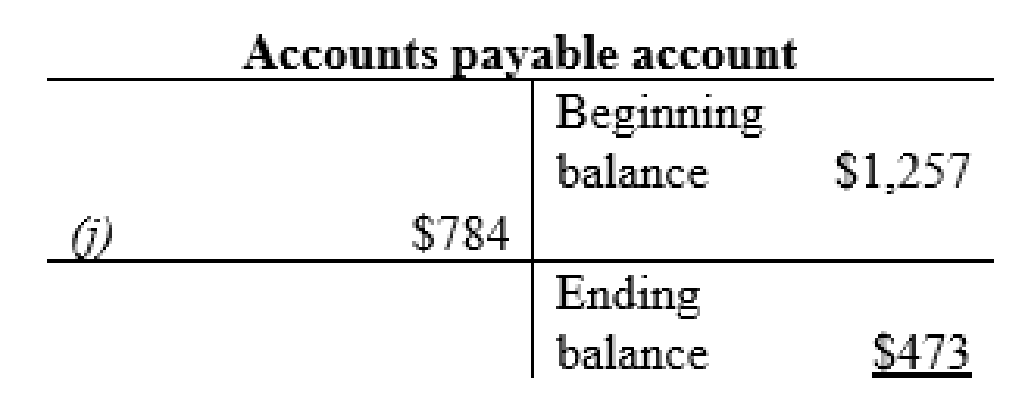
Accrued expenses payable account:
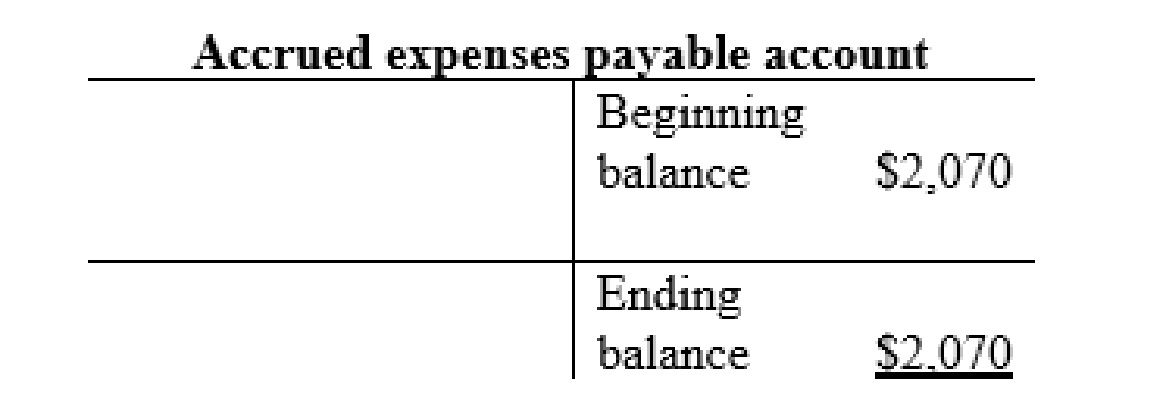
Other current liabilities account:
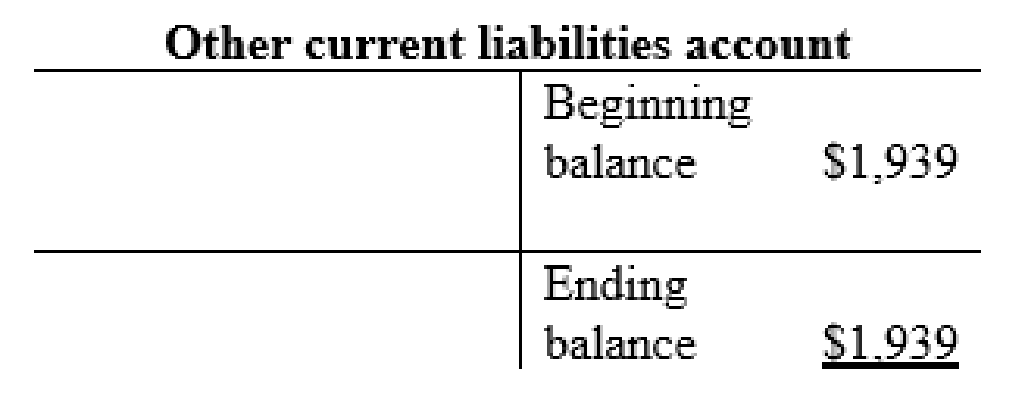
Long-term note payable account:
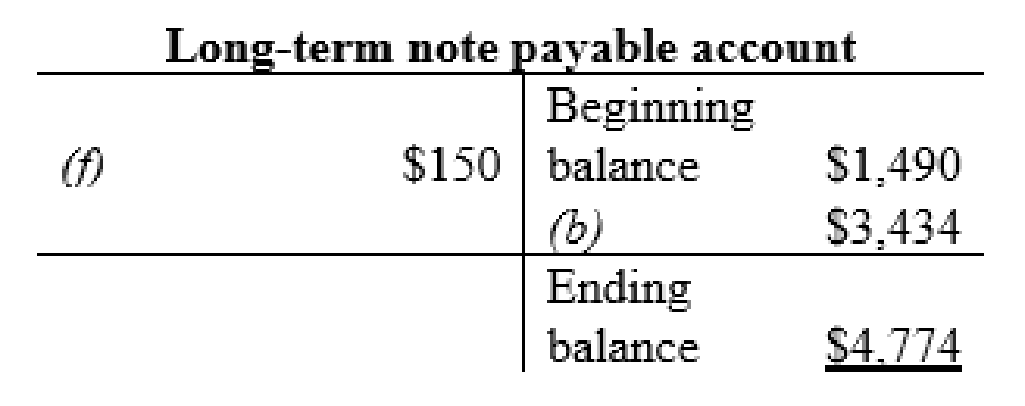
Other non-current liabilities account:
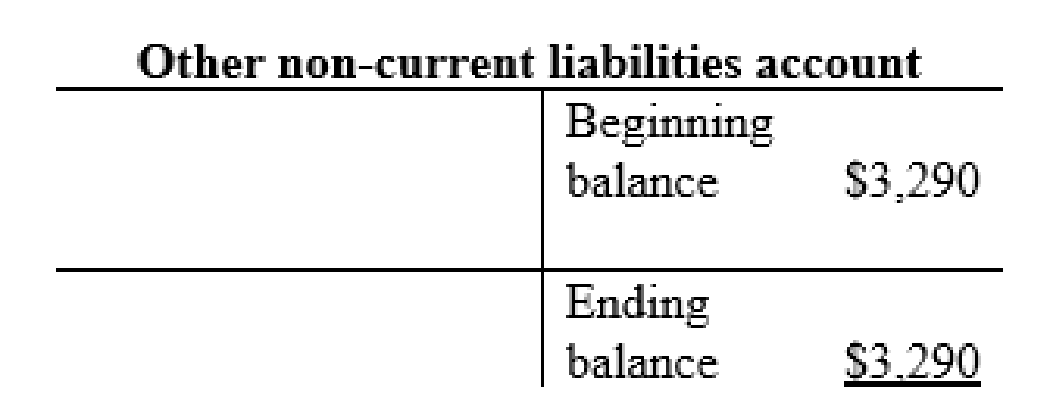
Common stock account:
Additional paid-in capital account:
Delivery service revenue account:
Aircraft rental expense account:
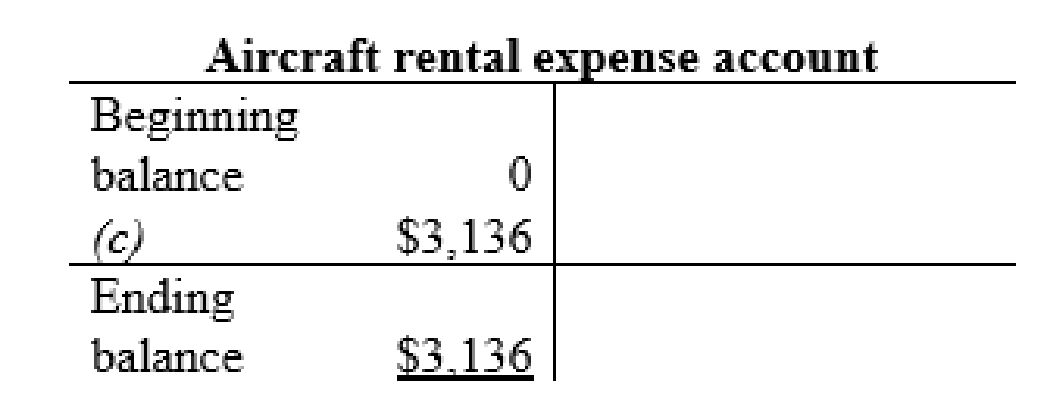
Maintenance and repair expense account:
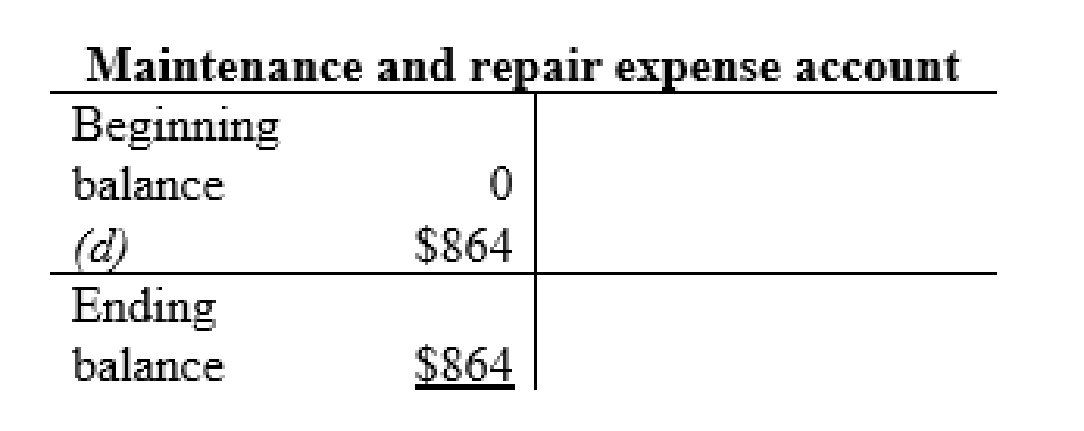
Wage expense account:
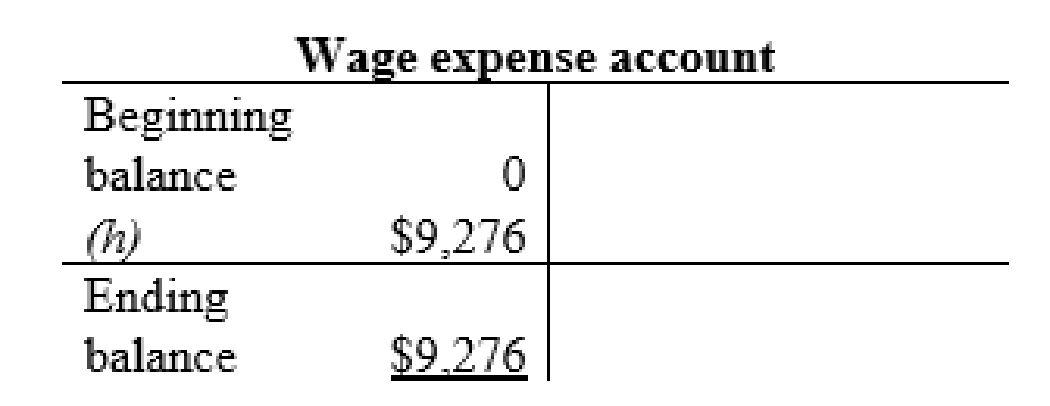
Fuel expense account:
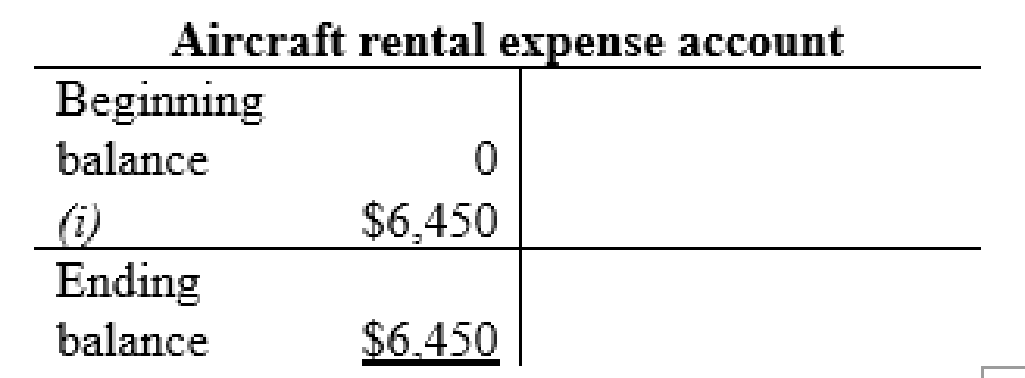
Thus, the t-accounts are prepared and the ending balances are calculated.
3.
Prepare an income statement for the month May.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an income statement:
| Company F | ||
| Income statement (Unadjusted) | ||
| For the year ended May 31 (in millions) | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues: | ||
| Delivery service revenue | 26,094 | |
| Total revenues (A) | 26,094 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Rental expense | 3,136 | |
| Fuel expense | 9,276 | |
| Wage expense | 6,450 | |
| Repair expense | 864 | |
| Total expenses (B) | 19,726 | |
| Net Income | $6,368 | |
Table (2)
Hence, the net income of Company F is $6,368 million.
4.
Compute the net profit margin ratio and based on the result give suggestion to the company.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the net profit margin ratio:
Hence, the net profit margin ratio is 0.24.
Suggestion:
- By evaluating the net profit margin ratio, the company has earned $0.24 in net income for every $ 1 in the sales revenue.
- To know the better result about the company, net profit margin ratio should be calculated to identify the way in which the management is generating its revenue and controlling the various expenses.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- The Foundational 15 (Static) [LO6-2, LO6-3, LO6-4, LO6-5, LO6-6) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $120 and $80, respectively. Each product uses only one type of raw material that costs $6 per pound. The company has the capacity to annually produce 100,000 units of each product. Its average cost per unit for each product at this level of activity are given below: Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $120 and $80, respectively. Each product uses only one type of raw material that costs $6 per pound. The company has the capacity to annually produce 100,000 units of each product. Its average cost per unit for each product at this level of activity are given below: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Traceable fixed manufacturing overhead Variable selling expenses Common fixed expenses Total cost per unit $100 The…arrow_forwardwhat was the cost of merchandise purchased during the year?arrow_forwardNext year, a business estimates that it will sell 30,000 units at a selling price of $15 per unit. Variable costs per unit are 40% of the selling price, and the business estimates that it will make a profit of $100,000. Calculate the fixed costs of the business for next year.arrow_forward
- General Accounting Question please answerarrow_forwardThe manager of Kancha Supermarket needs to verify today's register accuracy. The store started with $500 float, processed customer payments of $5,840, issued refunds worth $320, and paid an urgent supplier bill of $280 from the register. During closing, the register shows $5,440. Determine the discrepancy from expected balance.arrow_forwardI want answerarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





