
Concept explainers
1.
Journalize the given transactions.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the given transactions:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| a | Cash (+A) | $1,390 | |
| Receivables (+A) | $24,704 | ||
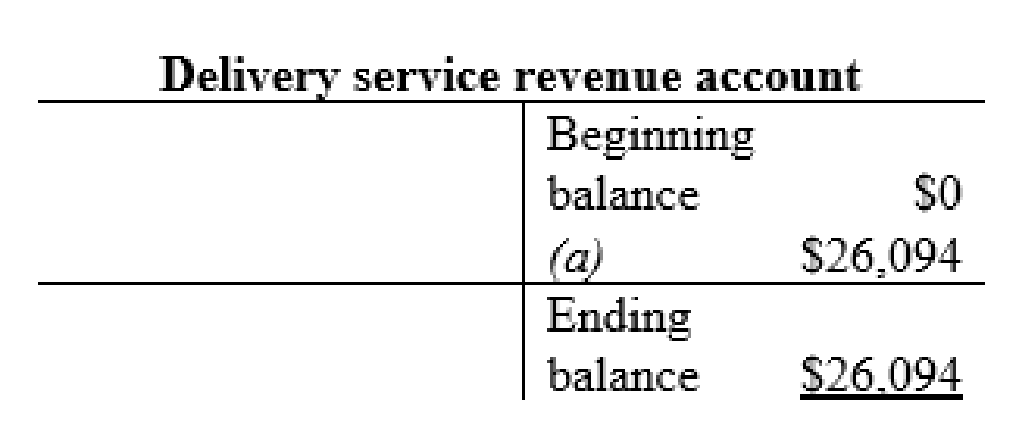
| Delivery Service revenue (+SE, +R) | $26,094 | ||
| (To record the sales) | |||
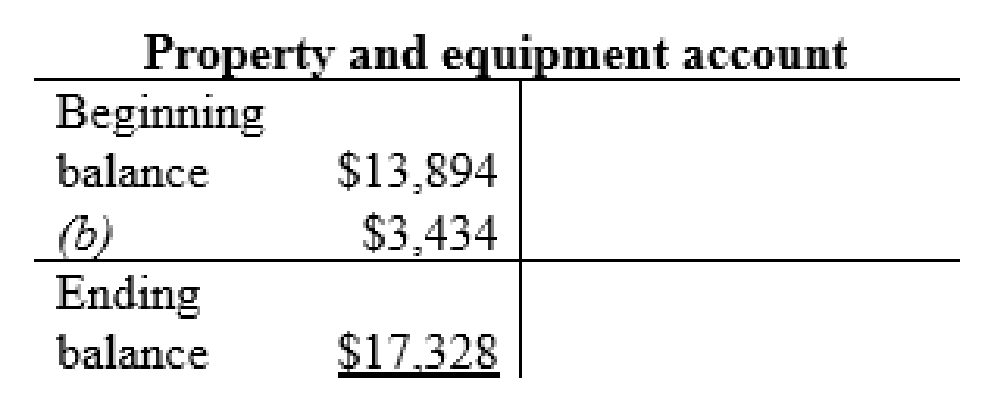
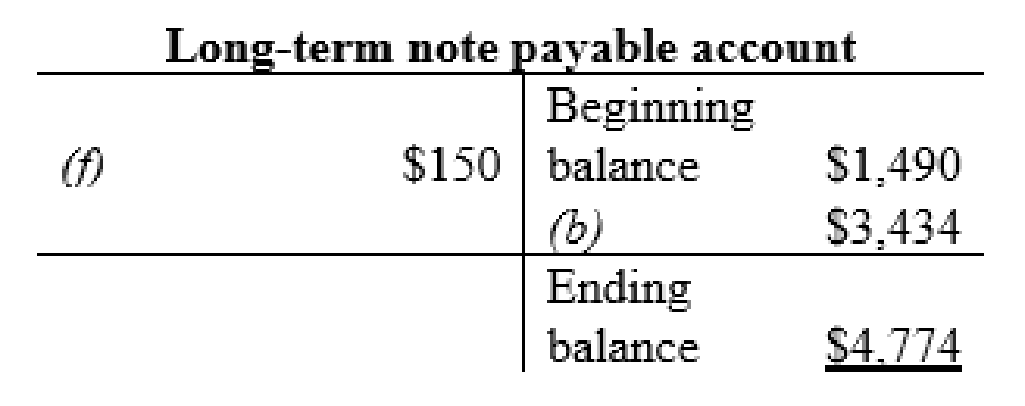
| b | Property and equipment (+A) | $3,434 | |
| Long-term notes payable (+L) | $3,434 | ||
| (To record the long-term notes payable) | |||
| c | Rent expense (+E) (-SE) | $3,136 | |
| Prepaid rent (+A) | $4,728 | ||
| Cash (-A) | $7,864 | ||
| (To record the rent expense and prepaid rent) | |||
| d | Repairs expense (+E) (-SE) | $864 | |
| Cash (-A) | $864 | ||
| (To record the expenses paid) | |||
| e | Cash (+A) | $24,285 | |
| Receivable (-A) | $24,285 | ||
| (To record the receivables collected) | |||
| f | Long-term notes payable (-L) | $150 | |
| Cash (-A) | $150 | ||
| (To record the payment of long-term notes payable) | |||
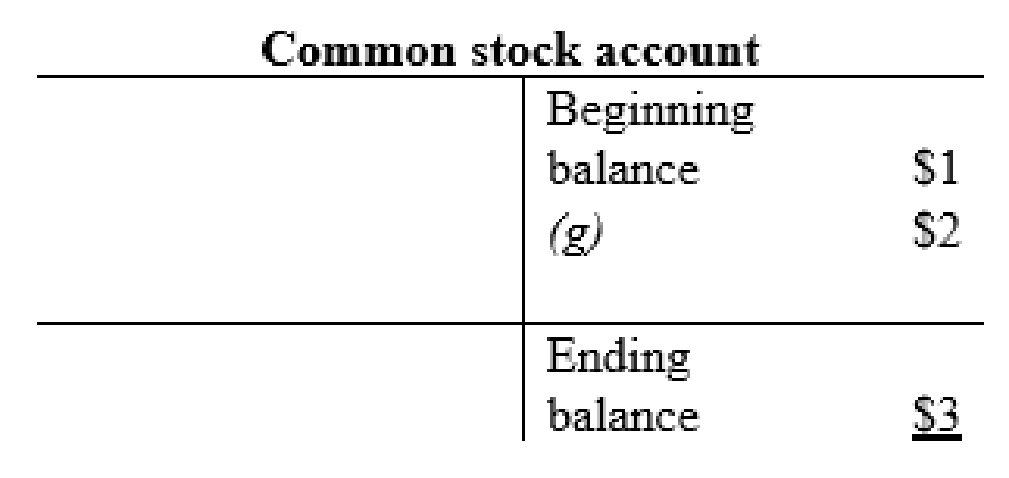
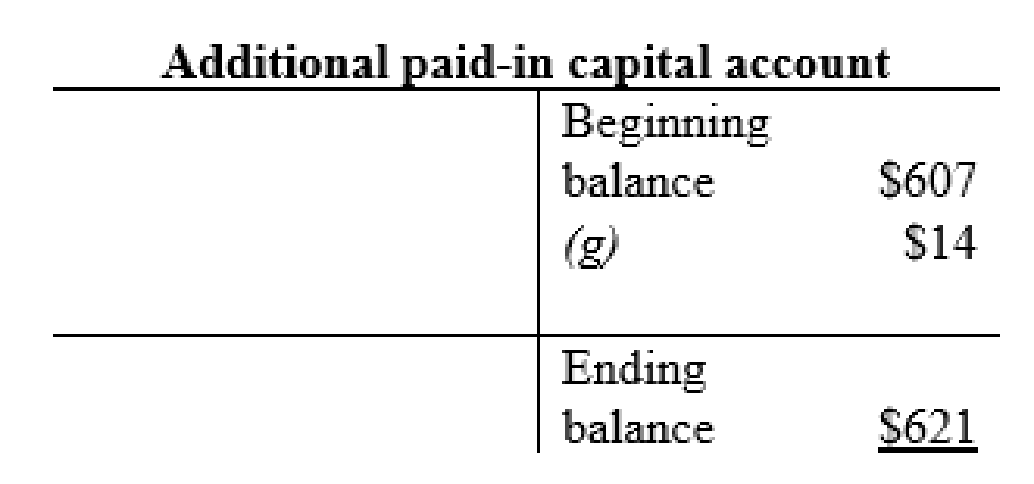
| g | Cash (+A) | $16 | |
| Common Stock (+SE) | $2 | ||
| Additional paid-in-capital (+SE) | $14 | ||
| (To record the receipt of stock) | |||
| h | Wages (+E) (-SE) | $9,276 | |
| Cash (-A) | $9,276 | ||
| (To record the wages paid) | |||
| i | Spare parts, supplies, and fuel (+A) | $6,564 | |
| Cash (-A) | $6,564 | ||
| (To record the sales revenues) | |||
| j | Spare parts, supplies, and fuel expense (+E) (-SE) | $6,450 | |
| Spare parts, supplies, and fuel (-A) | $6,450 | ||
| (To record the sales revenues) | |||
| k | Accounts payable (-L) | $784 | |
| Cash (-A) | $784 | ||
| (To record the sales revenues) | |||
| l | No entry | ||
Table (1)
2
Prepare the T- account and enter the transaction into their respective accounts for calculating the ending balance.
2
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the T-accounts:
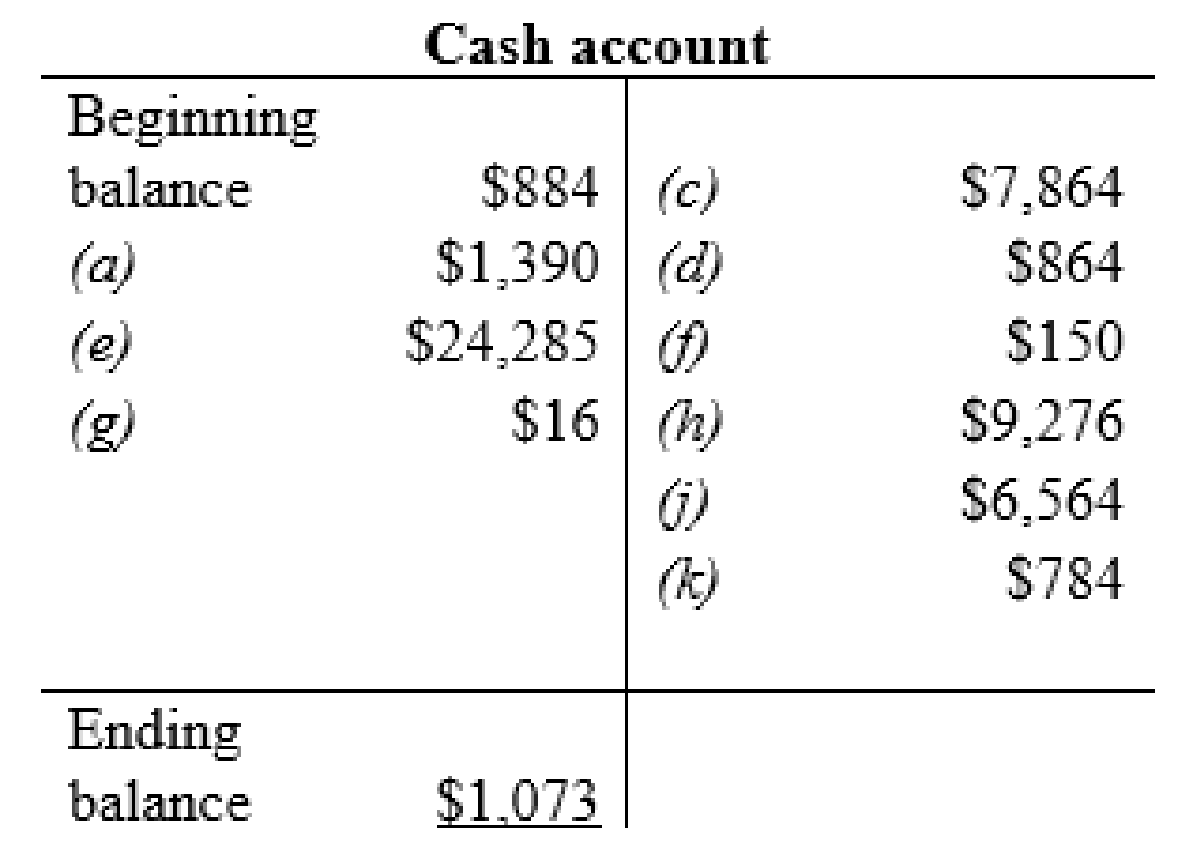
Cash account:
Receivables account:
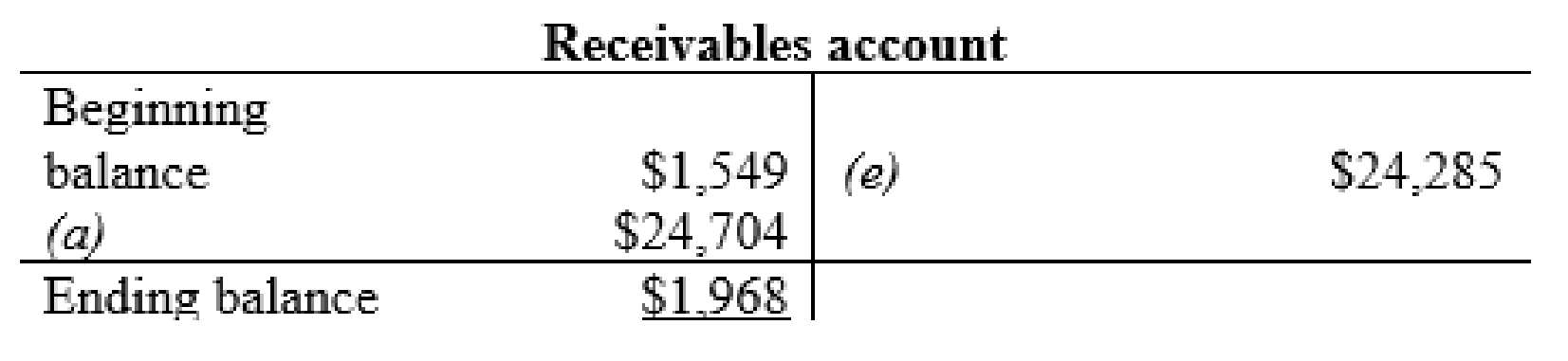
Spare parts, supplies and fuel account:
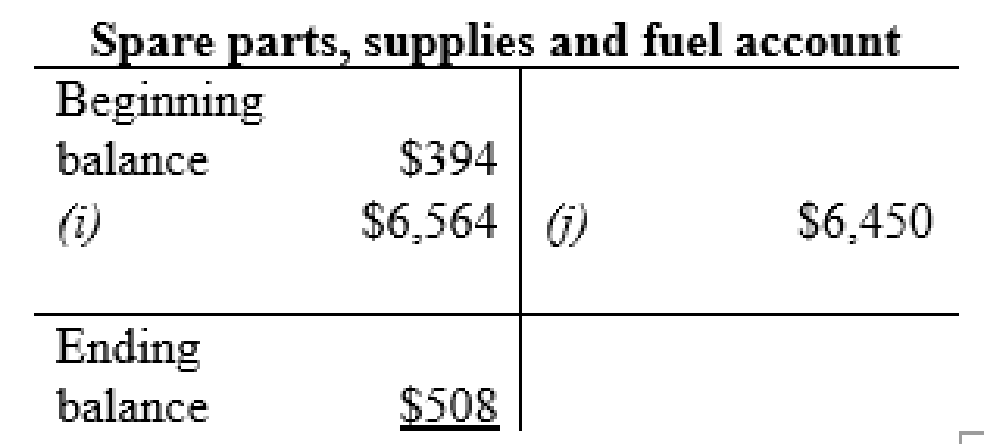
Prepaid expenses account:
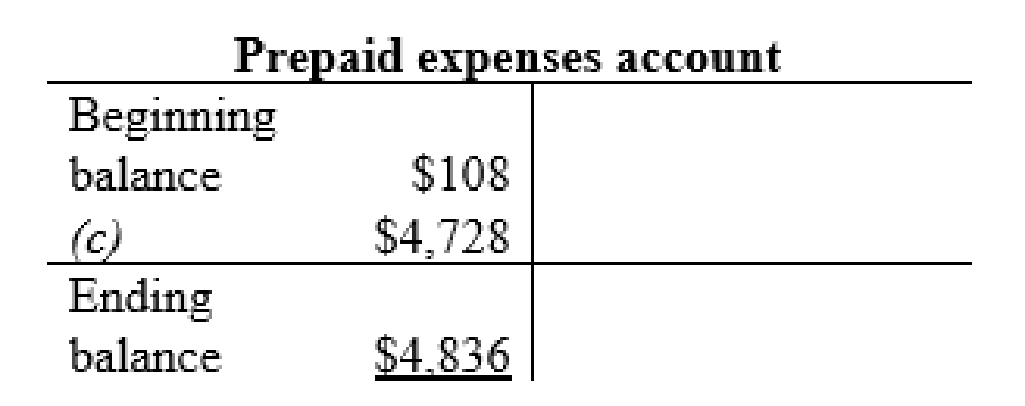
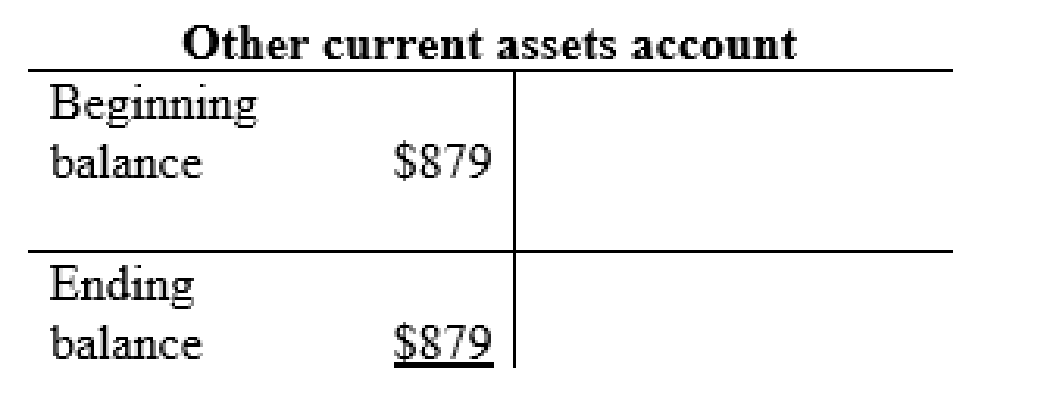
Other current asset account:
Property and equipment account:
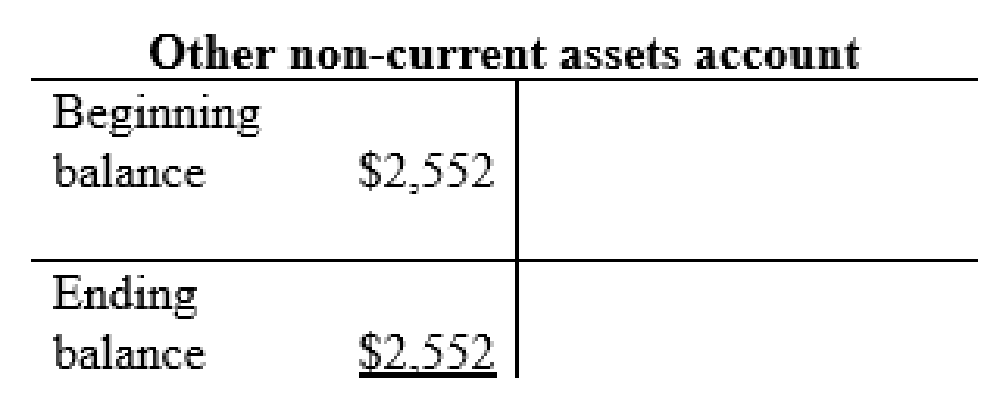
Other non-current asset account:
Accounts payable account:
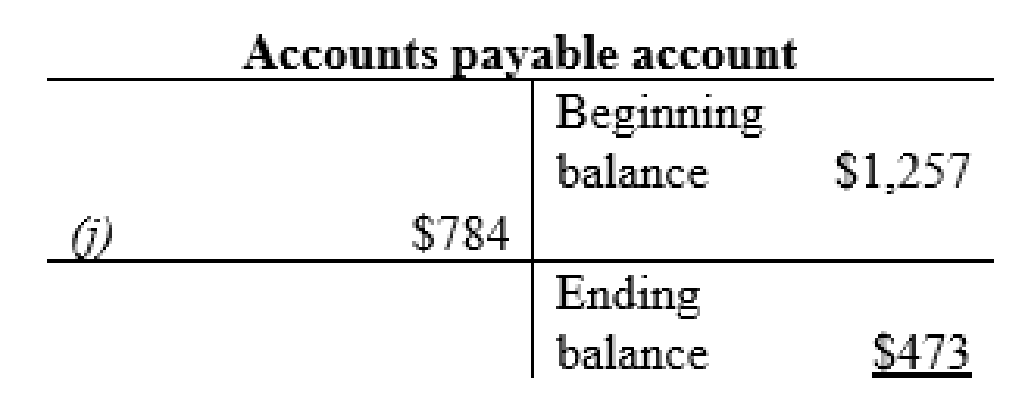
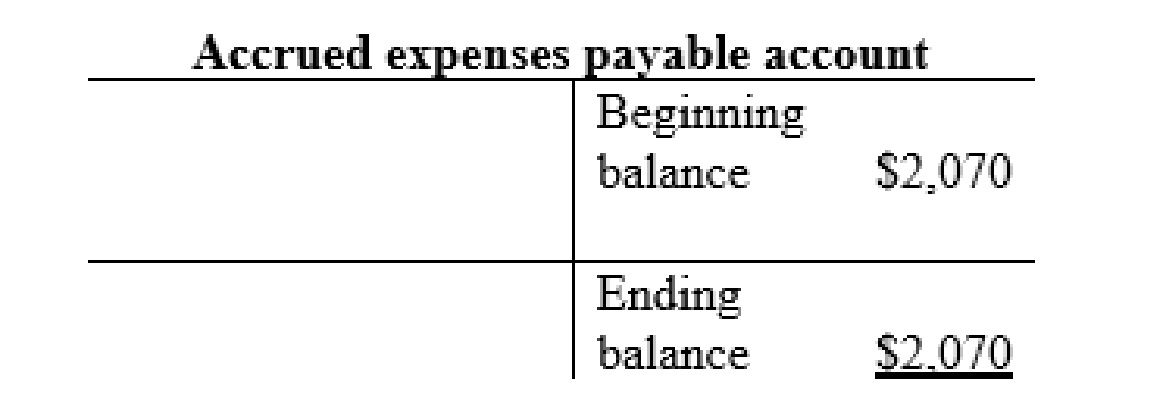
Accrued expenses payable account:
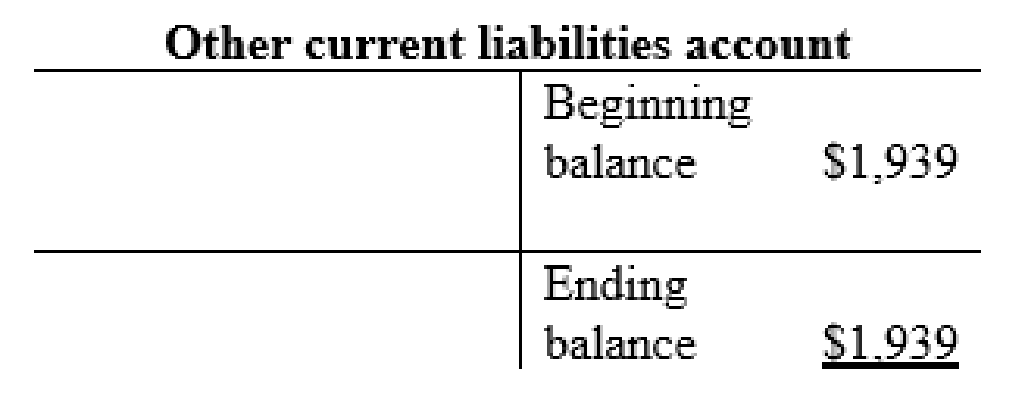
Other current liabilities account:
Long-term note payable account:
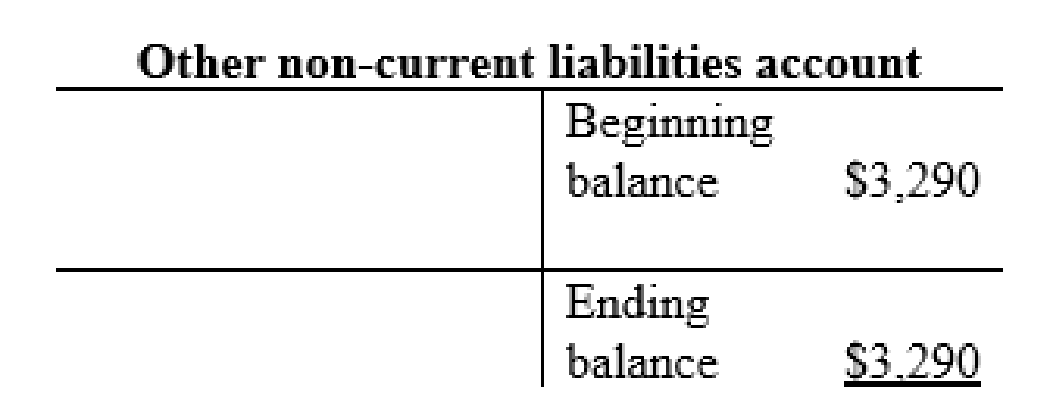
Other non-current liabilities account:
Common stock account:
Additional paid-in capital account:
Delivery service revenue account:
Aircraft rental expense account:
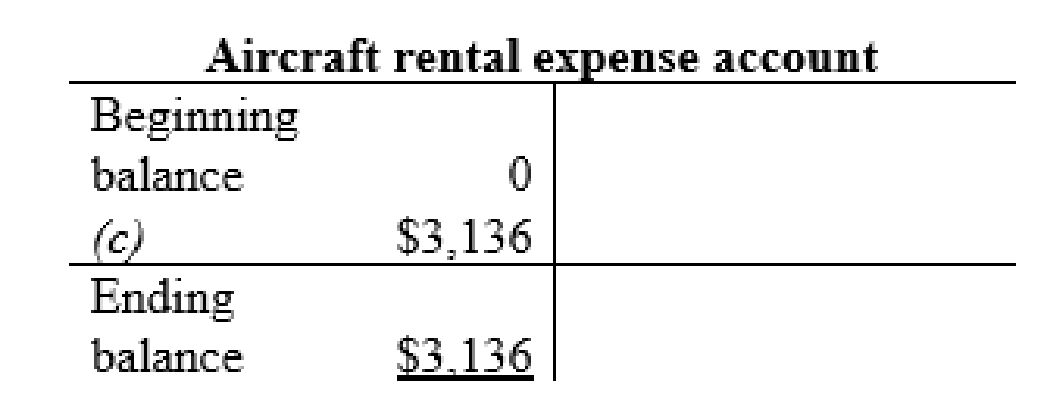
Maintenance and repair expense account:
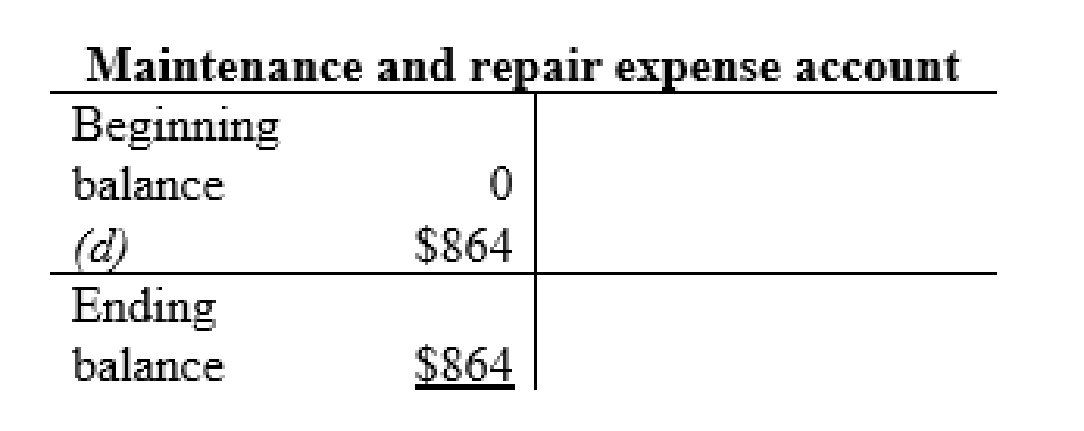
Wage expense account:
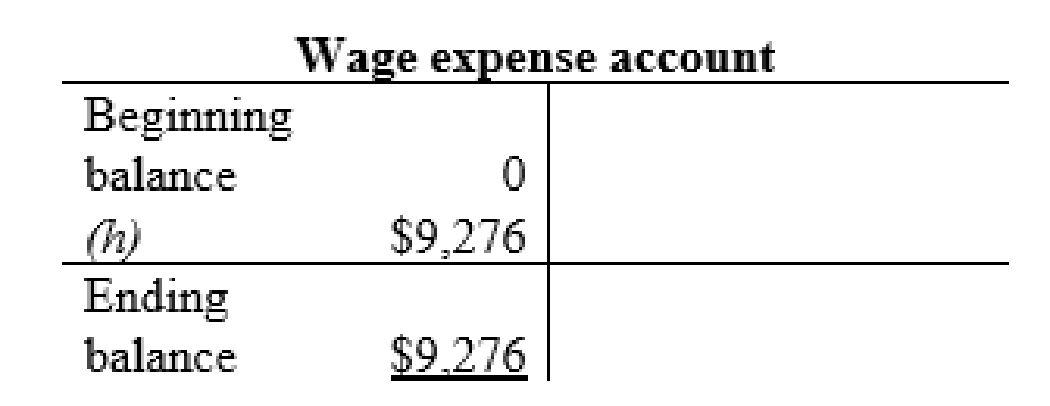
Fuel expense account:
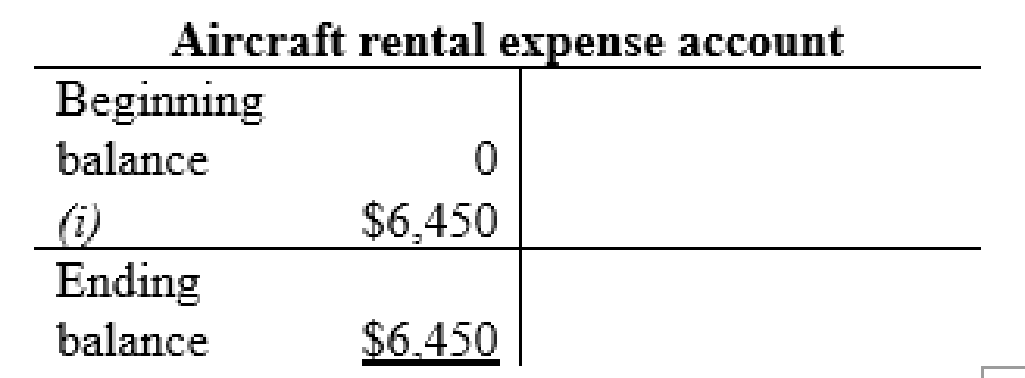
Thus, the t-accounts are prepared and the ending balances are calculated.
3.
Prepare an income statement for the month May.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an income statement:
| Company F | ||
| Income statement (Unadjusted) | ||
| For the year ended May 31 (in millions) | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues: | ||
| Delivery service revenue | 26,094 | |
| Total revenues (A) | 26,094 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Rental expense | 3,136 | |
| Fuel expense | 9,276 | |
| Wage expense | 6,450 | |
| Repair expense | 864 | |
| Total expenses (B) | 19,726 | |
| Net Income | $6,368 | |
Table (2)
Hence, the net income of Company F is $6,368 million.
4.
Compute the net profit margin ratio and based on the result give suggestion to the company.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the net profit margin ratio:
Hence, the net profit margin ratio is 0.24.
Suggestion:
- By evaluating the net profit margin ratio, the company has earned $0.24 in net income for every $ 1 in the sales revenue.
- To know the better result about the company, net profit margin ratio should be calculated to identify the way in which the management is generating its revenue and controlling the various expenses.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
- Please solve this question General accounting and step by step explanationarrow_forwardThe overhead assigned to each unit of product A would bearrow_forwardRK Co. sells snowboards. Each snowboard requires direct materials for $140, direct labor for $55, and variable overhead of $64. The company expects fixed overhead costs of $673,000 and fixed selling and administrative costs of $160,000 for the next year. It expects to produce and sell 11,900 snowboards in the next year. What will be the selling price per unit if RK uses a mark-up of 17% of the total cost? Answerarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





