
1.
Journalize the given transactions.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the given transactions:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
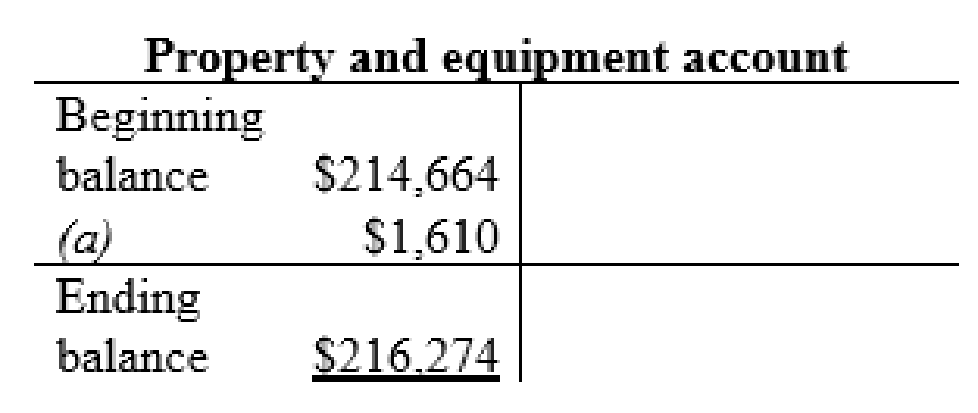
| a | Property and equipment (+A) | $1,610 | |
| Long-term notes payable (+L) | $1,610 | ||
| (To record the long-term notes payable) | |||
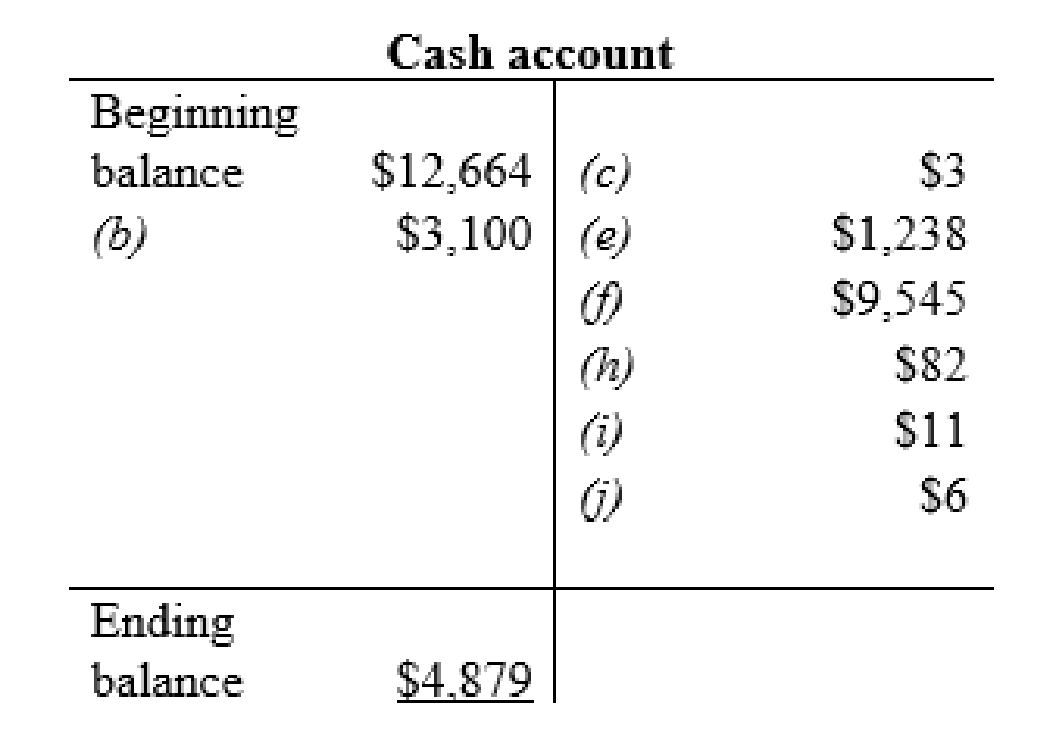
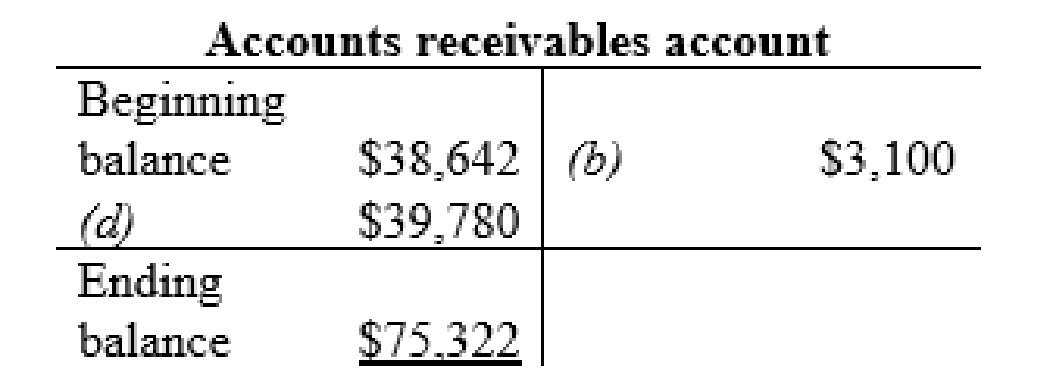
| b | Cash (+A) | $3,100 | |
| Accounts receivable (-A) | $3,100 | ||
| (To record the receivables collected) | |||
| c | Utilities expense (+E) (-SE) | $3 | |
| Cash (-A) | $3 | ||
| (To record the expenses paid) | |||
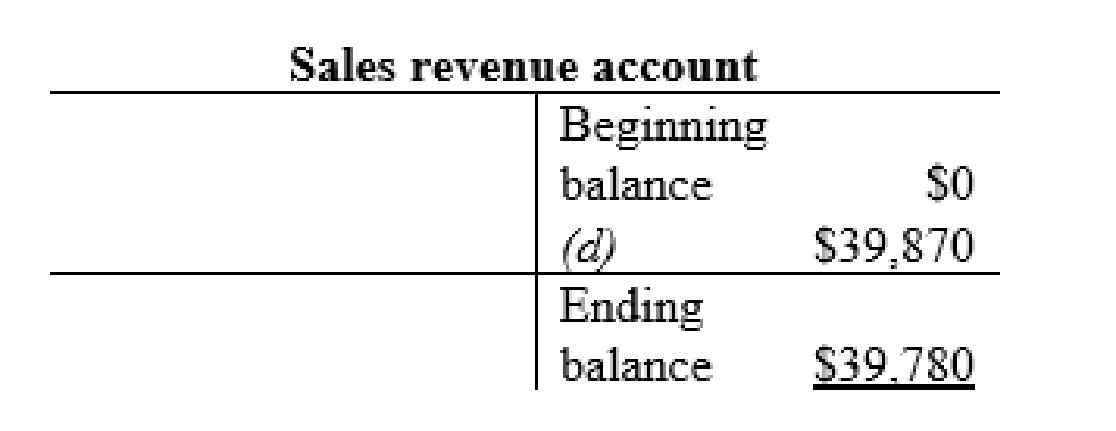
| d | Accounts receivable (+A) | $39,780 | |
| Sales Revenue (+SE, +R) | $39,780 | ||
| (To record the expenses paid) | |||
| Cost of Sales (+E) (-SE) | $5,984 | ||
| Inventory (-A) | $5,984 | ||
| (To record the cost involved in sales) | |||
| e | Wages (+E) (-SE) | $1,238 | |
| Cash (-A) | $1,238 | ||
| (To record the wages paid) | |||
| f | Income tax payable (-L) | $9,545 | |
| Cash (-A) | $9,545 | ||
| (To record the income taxes paid) | |||
| g | Inventory (+A) | $23 | |
| Accounts payable (+L) | $23 | ||
| (To record the inventory purchased on account) | |||
| h | Prepaid expenses (+A) | $82 | |
| Cash (-A) | $82 | ||
| (To record the expenses paid in advance) | |||
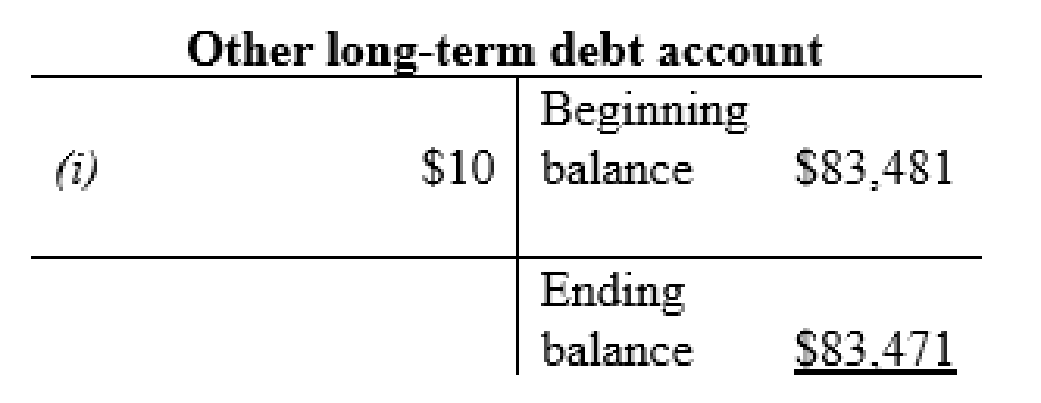
| i | Other long-term debt (-L) | $10 | |
| Interest expense | $1 | ||
| Cash (-A) | $11 | ||
| (To record the debt paid off) | |||
| j | Other assets and intangibles (+A) | $6 | |
| Cash (-A) | $6 | ||
| (To record the purchase of other assets and intangibles) | |||
Table (1)
2
Prepare the T- account and enter the transaction into their respective accounts for calculating the ending balance.
2
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the T-accounts:
Cash account:
Short-term investments account:
Accounts receivables account:
Inventories account:

Prepaid expenses account:
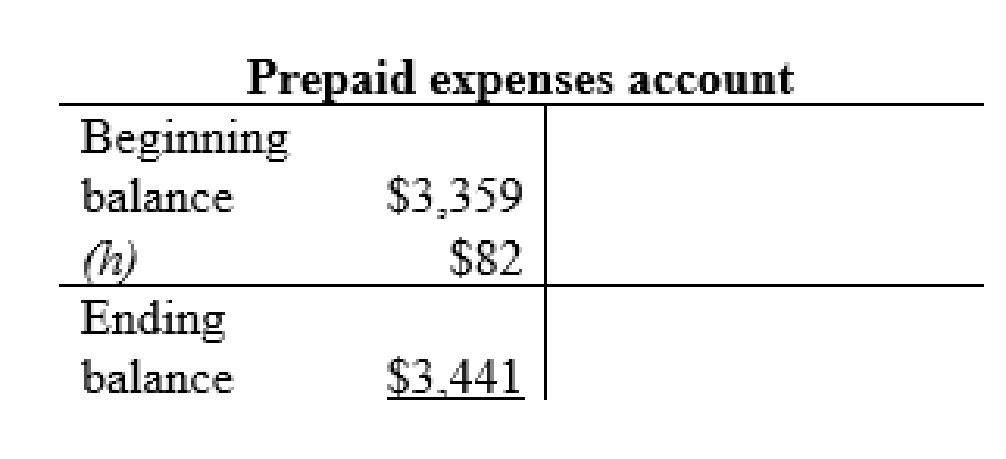
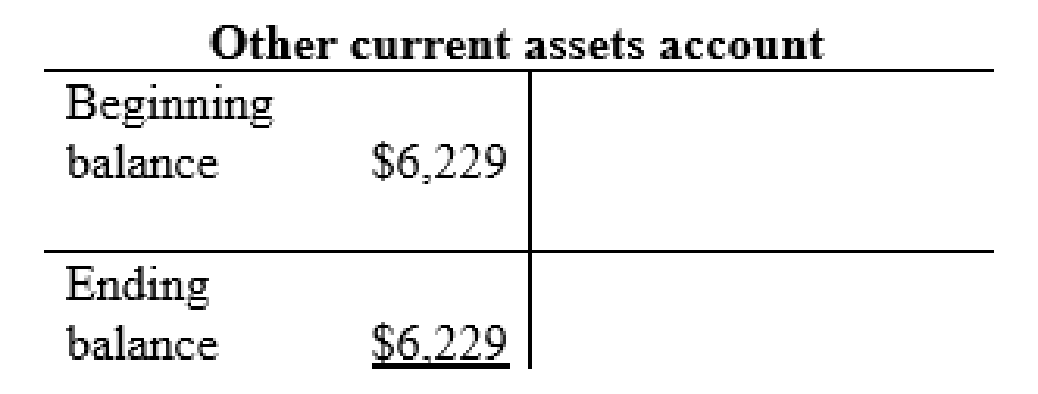
Other current assets account:
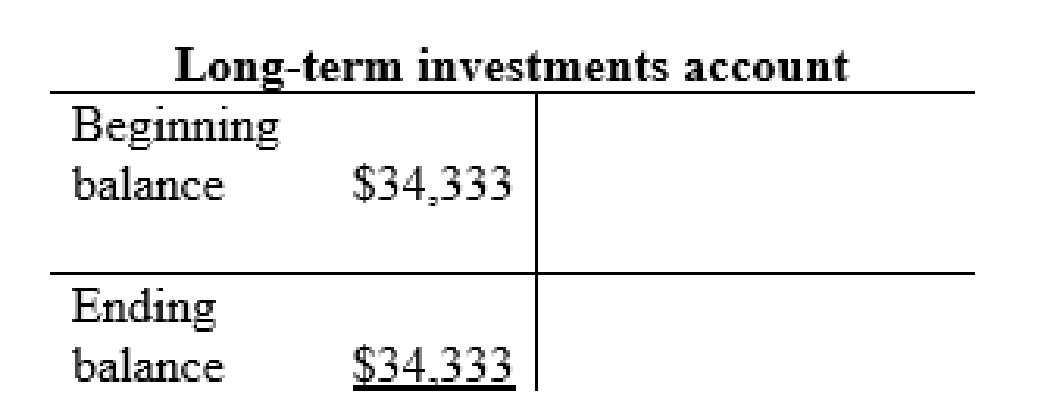
Long-term investments account:
Other assets and intangibles account:
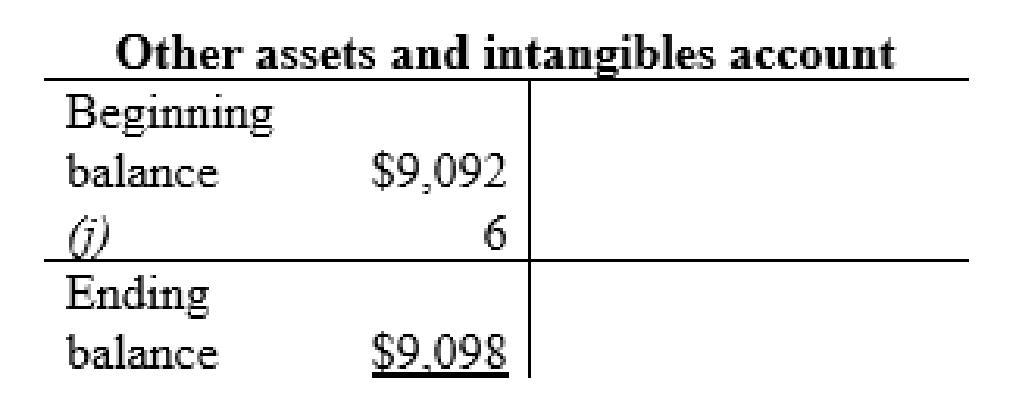
Property and equipment account:
Short-term notes payable account:
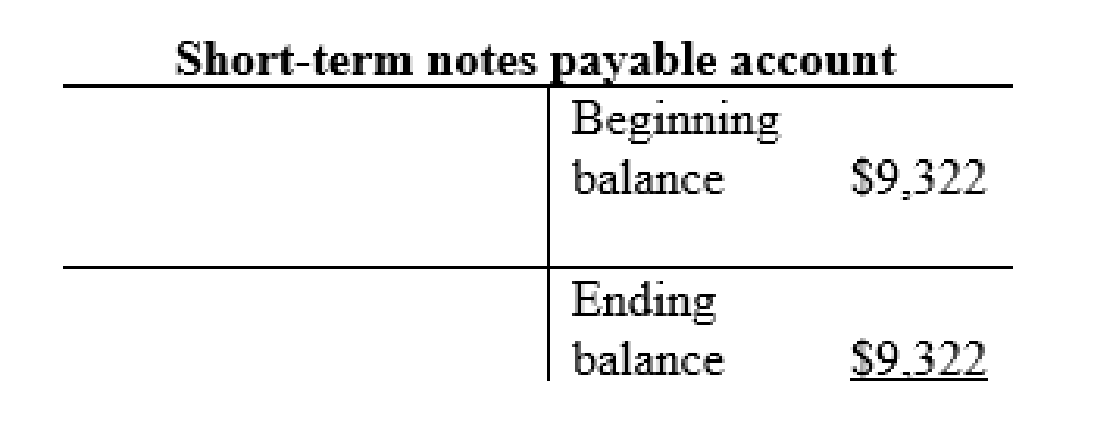
Accounts payable account:
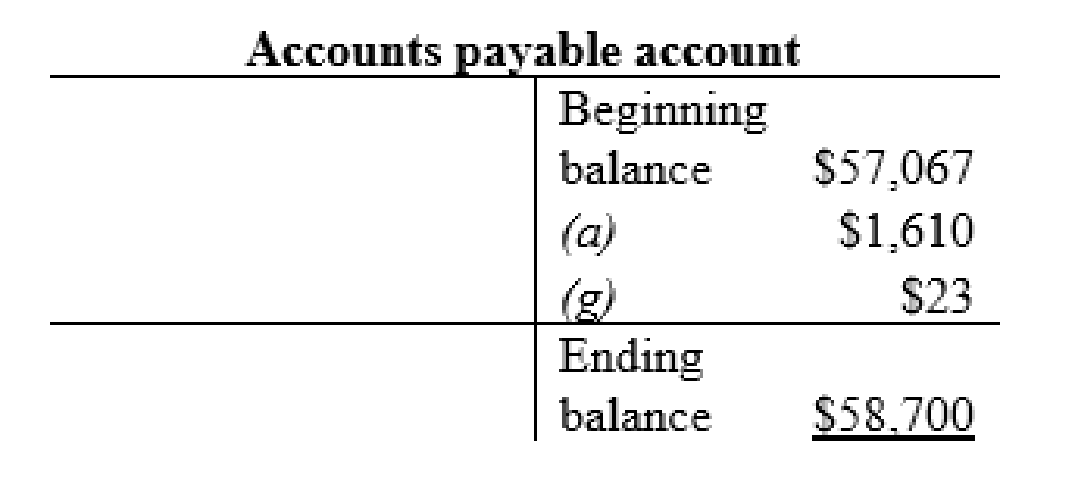
Income taxes payable account:
Long-term note payable account:
Other long-term debt account:
Common stock account:
Sales revenue account:
Cost of sales account:
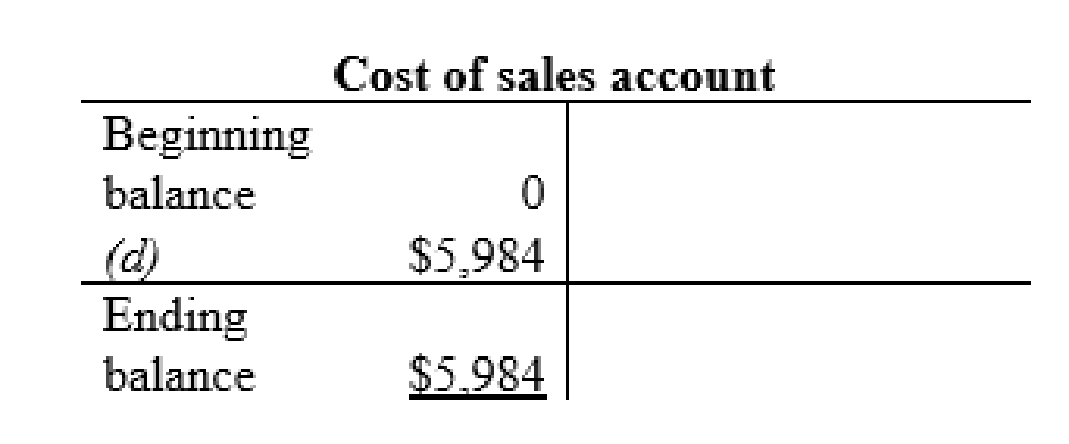
Utilities expense account:
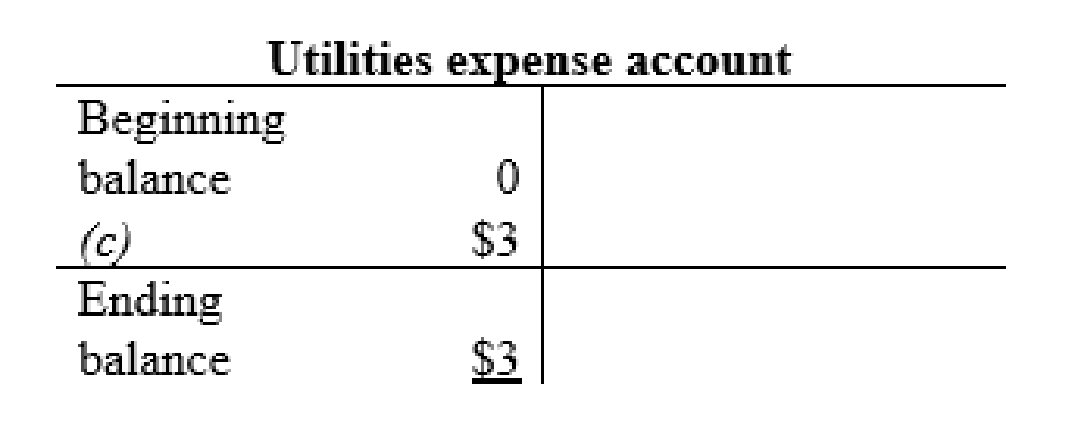
Interest expense account:
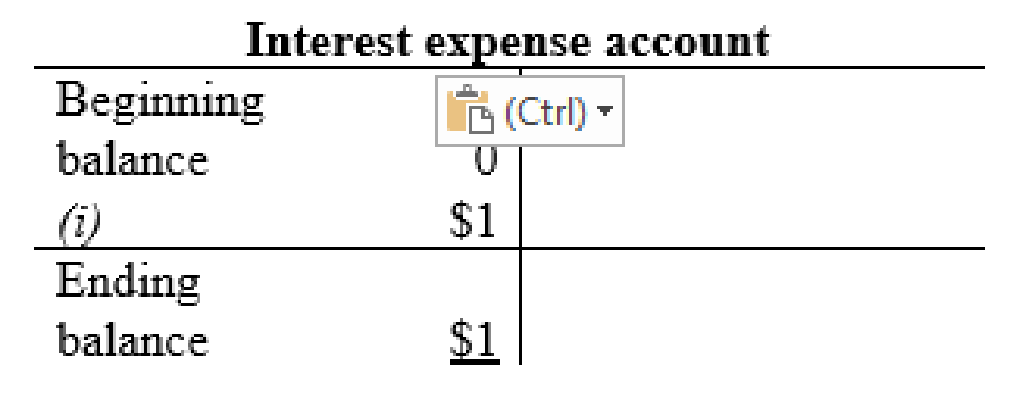
Wage expense account:
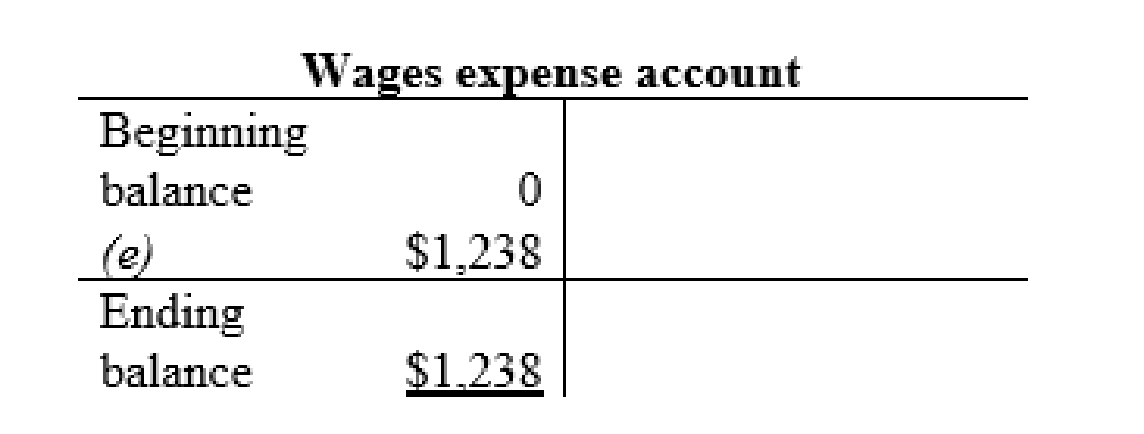
Thus, the t-accounts are prepared and the ending balances are calculated.
3.
Prepare an income statement for the month of January.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an income statement:
| Corporation EM | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the month ended 31st January | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues: | ||
| Sales revenue | 39,780 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Cost of sales | 5,984 | |
| Wage expense | 1,238 | |
| Utilities expense | 3 | |
| Total costs and expenses | 7,225 | |
| Operating income | 32,555 | |
| Less: Other expense | ||
| Interest expense | 1 | |
| Net Income | $32,554 | |
Table (2)
Hence, the net income of Company E is $32,554.
4.
Compute the net profit margin ratio and based on the result give suggestion to the company.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the net profit margin ratio:
Hence, the net profit margin ratio is 0.82.
- By evaluating the net profit margin ratio, the company has earned $0.82 in net income for every $ 1 in the sales revenue.
- To know the better result about the company, net profit margin ratio should be calculated to identify the way in which the management is generating its revenue and controlling the various expenses.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
- Assume the following information: Direct Materials $40 per unit Direct Labor $20 per unit Total Estimated Manufacturing Overhead $8,400,000 Manufacturing overhead is allocated based on estimated direct-labor hours. Each unit of product requires 1 direct labor hour. If 441,000 units were produced, how much overhead was applied to work in process? (Note: Overhead per unit is based on supervisor's preferred estimate of 420,000 hours.arrow_forwardSapphire Industries uses a job order costing system. During one month, Sapphire purchased $245,000 of raw materials on credit; issued materials to production of $278,000 of which $18,000 were indirect. Sapphire incurred a factory payroll of $196,000, of which $32,000 was indirect labor. Sapphire uses a predetermined overhead rate of 175% of direct labor cost. The total manufacturing costs added during the period are___.arrow_forwardDriftwood Furniture Company implemented a new quality control system. Product approval requires: material inspection (40% weighting), structural testing (30% weighting), and finish quality (30% weighting). If a product scored 76 on material inspection, 82 on structural testing, and 68 on finish quality, your task is to identify the weighted quality score.arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this general accounting question using valid accounting techniques?arrow_forwardI need assistance with this general accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forward
- Is the estimated variable delivery cost component per shipment? General accountingarrow_forwardClark Company manufactures a product with a standard direct labor cost of two hours at $16.87 per hour. During July, 2,232 units were produced using 4,267 hours at $15.96 per hour. What is the labor quantity variance?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forward
- A local bakery sells 12,000 loaves of sourdough bread each year. The loaves are ordered from an outside supplier, and it takes 4 days for each shipment of loaves to arrive. Ordering costs are estimated at $18 per order. Carrying costs are $6 per loaf per year. Assume that the bakery is open 300 days a year. What is the maximum inventory of loaves held in a given ordering cycle? Provide Answerarrow_forwardHello tutor solve this question and accounting questionarrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question using the right approach.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





