
1.
Journalize the given transactions.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the given transactions:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| a | Cash (+A) | $9,500 | |
| Consulting fees revenue (+R) (+SE) | $9,500 | ||
| (To record the fees earned) | |||
| b | Cash (+A) | $1,200 | |
| Common stock (+SE) | $10 | ||
| Additional paid-in capital (+SE) | $1,190 | ||
| (To record the purchase of building) | |||
| c | Office equipment (+A) | $640 | |
| Cash (-A) | $160 | ||
| Short-term notes payable (+L) | $480 | ||
| (To record the purchase of equipment on account) | |||
| d | Cash (+A) | $890 | |
| Unearned revenue (+L) | $890 | ||
| (To record the unearned revenue) | |||
| e | Supplies (+A) | $470 | |
| Accounts payable (-L) | $470 | ||
| (To record the purchase of supplies on account) | |||
| f | Utilities expense (+E) (-SE) | $1,800 | |
| Cash (-A) | $1,800 | ||
| (To record the utilities expense) | |||
| g | $1,620 | ||
| Consulting fees revenue (+R) (+SE) | $1,620 | ||
| (To record the fees earned) | |||
| h | Cash (+A) | $2,980 | |
| Accounts receivable (-A) | $2,980 | ||
| (To record the cash receivable from customer) | |||
| i | Salaries expense (+E) (-SE) | $6,210 | |
| Cash (-A) | $5,300 | ||
| Salaries payable (+L) | $910 | ||
| (To record the payment of cash for accounts payable) | |||
| j | Short term investments (+A) | $1,230 | |
| Prepaid expenses (+A) | $800 | ||
| Cash (-A) | $2,030 | ||
| (To record the cash receivable from customer) | |||
| k | Cash (+A) | $10 | |
| Interest revenue (+R) (-SE) | $10 | ||
| (To record the interest revenue) |
Table (1)
2
Prepare the T- account and enter the transaction into their respective accounts for calculating the ending balance.
2
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the T-accounts:
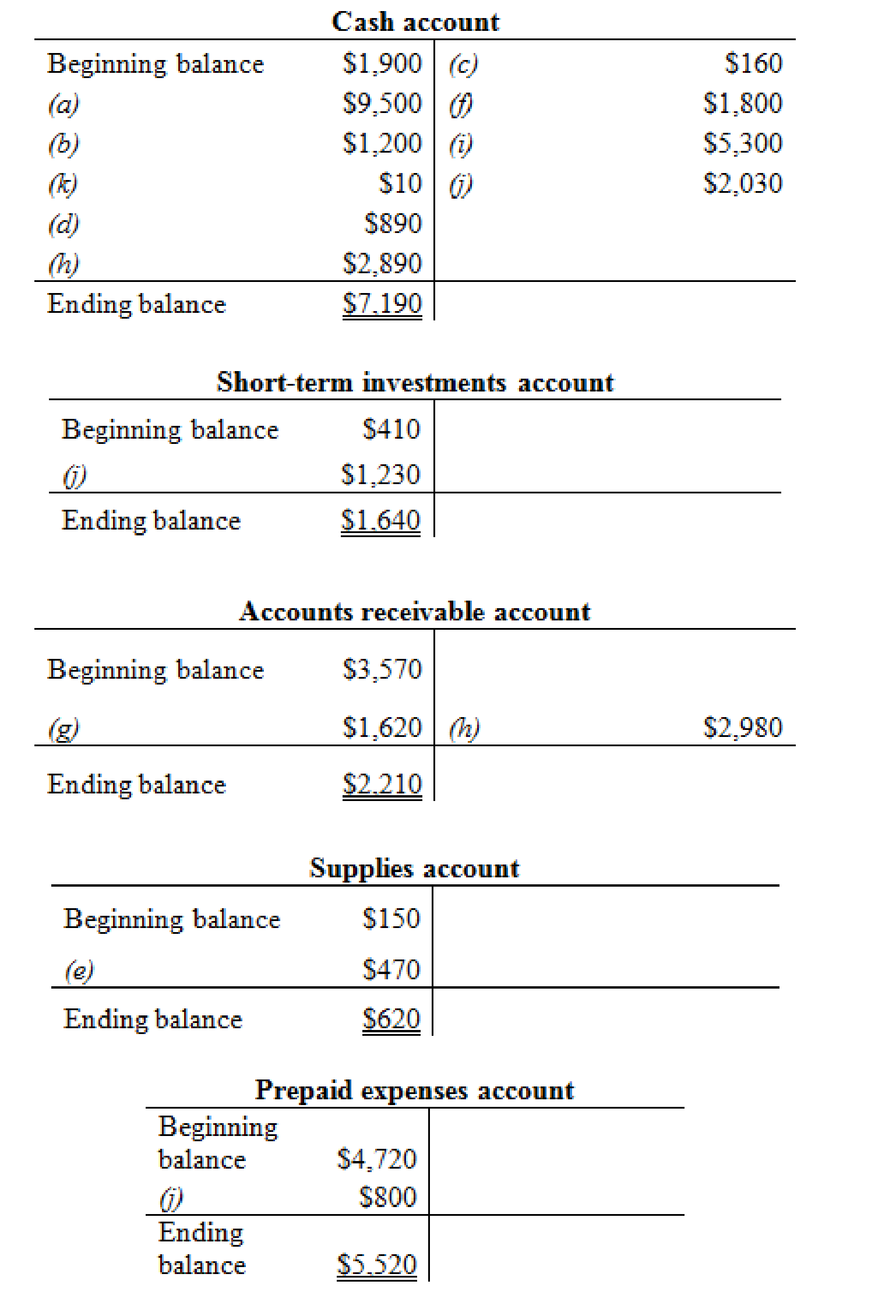
Figure (1)
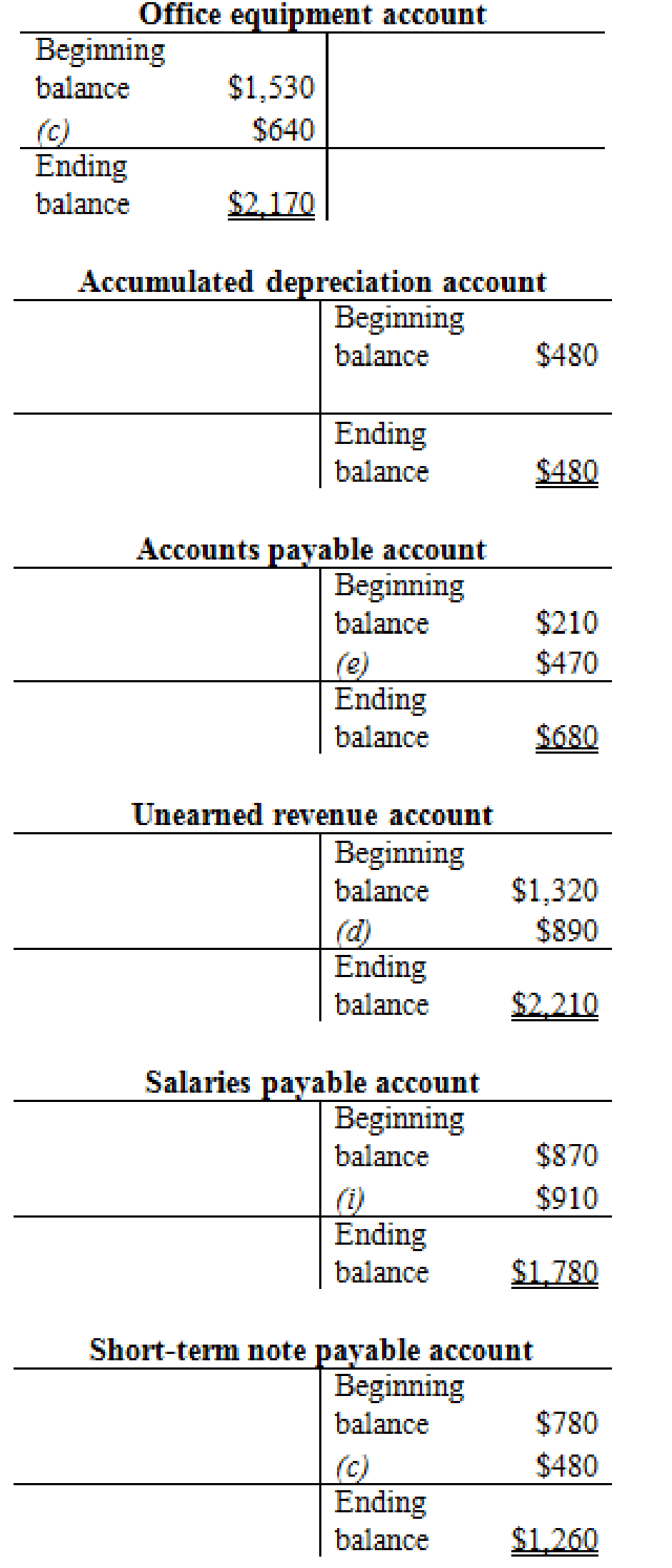
Figure (2)
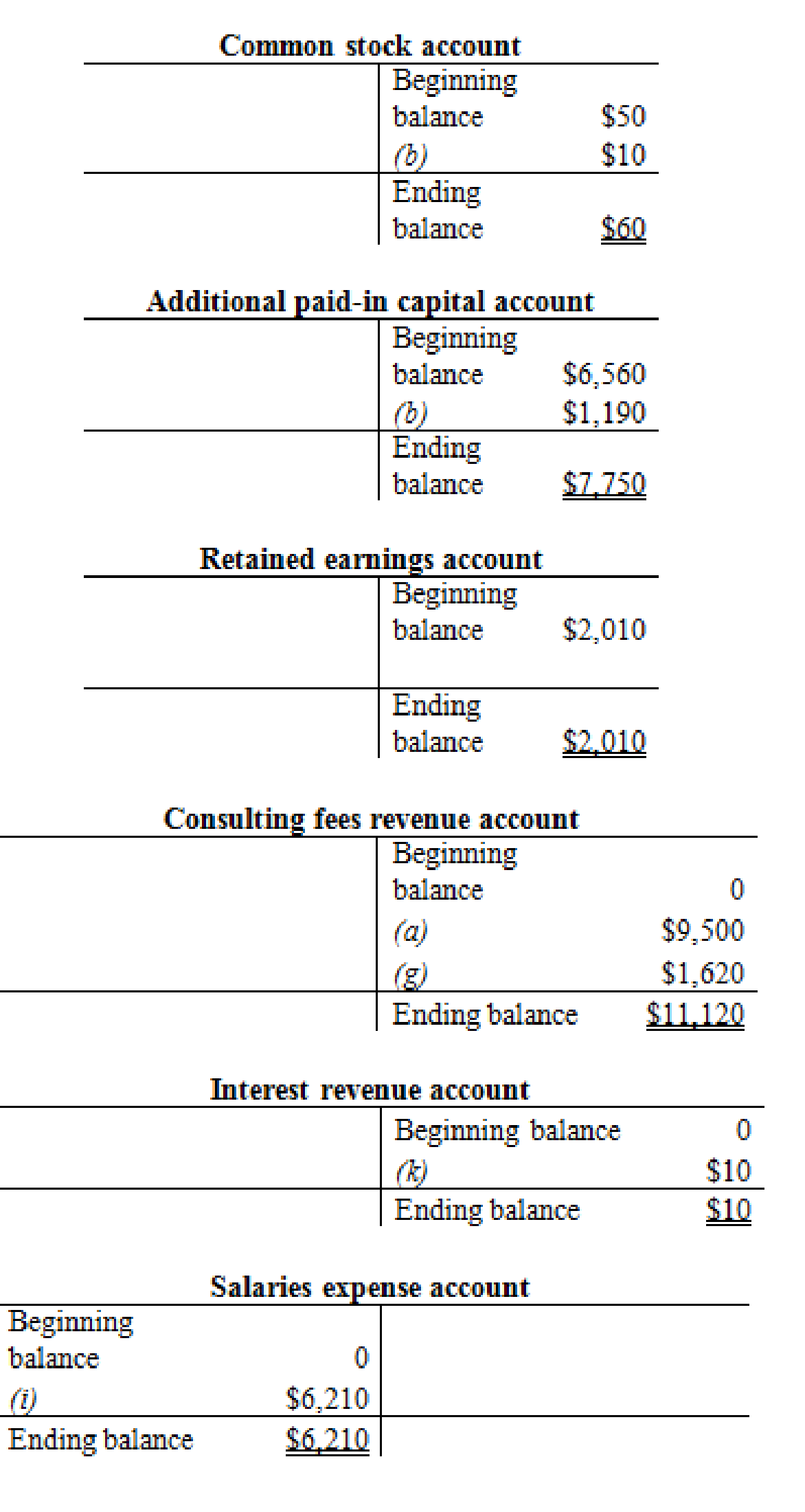
Figure (3)
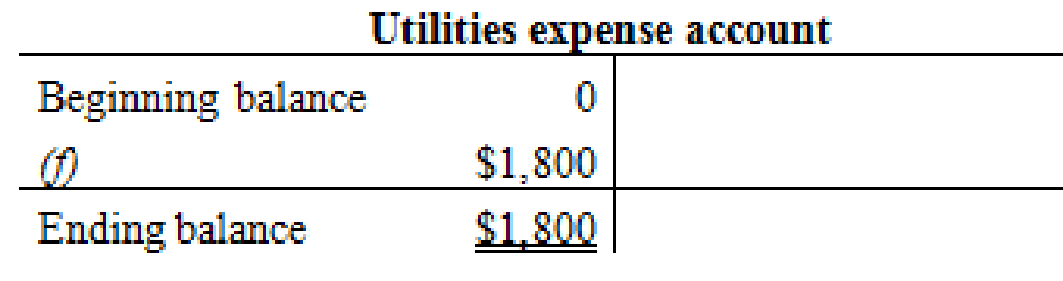
Figure (4)
Thus, the T-accounts are prepared and the ending balances are calculated.
3.
Ascertain the amount for the given equations at the end of the January.
3.
Explanation of Solution
For the equationRevenues−Expenses=Net income:
Revenue−Expenses=Net income$11,130−$8,010=$3,120
For the equationAssets=Liabilities+Stockholders' equity:
Assets=Liabilities+Stockholders' equity$18,870=$5,930+$12,940
Working note (1):
Calculate the revenues:
Revenues=Consulting fees revenue+Interest revenue=$11,120+$10=$11,130
Working note (2):
Calculate the expenses:
Expenses=Salaries expenses+Utilities expenses=$6,210+$1,800=$8,010
Working note (3):
Calculate the net income:
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues | (1) 11,130 | |
| Less: Expenses | (2) 8,010 | |
| Net income | $3,120 |
Table (2)
4.
Calculate the net income under cash basis of accounting and explain the reason in which manner the net income differs from accrual basis of accounting.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the net income under cash basis accounting:
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash receipts | (4) 14,580 | |
| Less: Cash payments | (5) 9,290 | |
| Net income | $5,290 |
Table (3)
Net income of Incorporation C under cash basis of accounting is $5,290.
Working note (4):
Calculate the cash receipts:
Cash receipts=(Consulting fees revenue)+(Common stock issued)+(Consulting fees revenue)+(Accounts receivable)+(Interest revenue)=$9,500+$1,200+$890+$2,980+$10=$14,580
Working note (5):
Calculate the cash payments:
Cash payments=(Short-term notes payable)+(Utilities expenses)+(Salaries expenses)+(Purchase of short-term invenstment)=$160+$1,800+$5,300+$2,030=$19,760
- According to the cash basis of accounting, the net income is $5,290 which higher than the accrual basis of accounting.
- The recording of the expenses and revenues differ from the accrual basis of accounting.
- Hence, the net income is different for the accrual basis of accounting and cash basis of accounting.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
- Answer? Financial accounting questionarrow_forwardGerald Books Ltd. currently has $720,000 in accounts receivable and generated $5,600,000 in sales (all on credit) during the year that just ended. The firm's days sales outstanding (DSO) is how many days? Use 365 days as the length of a year in all calculations. Gerald Books Ltd.'s CFO is unhappy with its DSO and wants to improve collections next year. Sales are expected to grow by 10% next year, and the CFO wants to lower the DSO to the industry average of 28 days. How much accounts receivable is the firm expected to carry next year?arrow_forwardWing Apparel Store had a balance in the Accountsarrow_forward
- Gerald Books Ltd. currently has $720,000 in accounts receivable and generated $5,600,000 in sales (all on credit) during the year that just ended. The firm's days sales outstanding (DSO) is how many days? Use 365 days as the length of a year in all calculations. Gerald Books Ltd.'s CFO is unhappy with its DSO and wants to improve collections next year. Sales are expected to grow by 10% next year, and the CFO wants to lower the DSO to the industry average of 28 days. How much accounts receivable is the firm expected to carry next year? provide answerarrow_forwardGive me Answerarrow_forwardCash conversion cyclearrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





