
Concept explainers
Suppose the string in the figure in Question 48 breaks and the stone slows in its upward motion.
a. Draw a force vector diagram of the stone when it reaches the top of its path.
b. Is the net force on the stone zero at the top?
(a)
To draw: A force vector diagram of the stone when it reaches the top of its path.
Answer to Problem 49A
After reaching the top, no tension force will be applied to it. But, only gravity will act upon it.
The force vector diagram is shown in Figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
For a stable equilibrium, all the forces will balance each other.
As shown in the vector diagram below, both tension and force of gravity are acting upon the stone at starting. As the stone goes up with the external force, the tension in the force decreases, and the force of gravity which is constant supersedes. Once it is reached at the top, tension force disappears but only gravity applies.
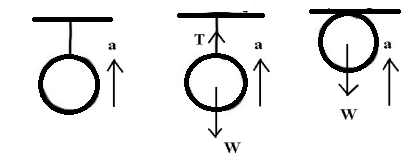
Figure 1
Conclusion:
Thus, after reaching the top, no tension force will be applied to it. But, only gravity will act upon it. The force diagram is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
To identify: Whether the net force on the stone at the top is zero or not.
Answer to Problem 49A
After reaching the top, only the gravitational force will act upon the stone. Thus, the net force will not be zero.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
For a stable equilibrium, all the forces will balance each other.
Gravitational force on any object acts downwards and it is constant with for a mass. Tension in the force is acting upwards or towards the string. When it reaches the top of the string then the tension will not act upon the stone. Thus, only gravitational force will act downwards as shown in Figure 1. The net force is shown after reaching at the top in the third figure. The only force that acts upon the stone is gravitational force downwards. Thus, the net force will not be zero.
Conclusion:
After reaching the top, only gravitational force will act upon the stone. Thus, the net force will not be zero.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Conceptual Physics: The High School Physics Program
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
- please answer this asap!!!!arrow_forwardRT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





