PHYS 212 FOR SCI+ENG W/MAST PHYS >ICP<
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781323834831
Author: Knight
Publisher: PEARSON C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 41EAP
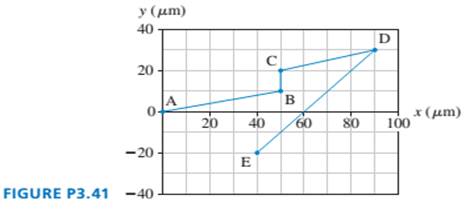
The bacterium E. coli is a single-cell organism that lives in the gut of healthy animals, including humans. When grown in a uniform medium in the laboratory, these bacteria swim along zig-zag paths at a constant speed of 20 µm/s. FIGURE P3.41 shows the trajectory of an E. coli as moves from point A to point E. What are the magnitude and direction of the bacterium’s average velocity for the entire trip?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In an electron gun, electrons are accelerated through a region with an electric field of magnitude 1.5 × 104 N/C for a distance of 2.5 cm. If the electrons start from rest, how fast are they moving after traversing the gun?
Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!
Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!
Chapter 3 Solutions
PHYS 212 FOR SCI+ENG W/MAST PHYS >ICP<
Ch. 3 - Can the magnitude of the displacement vector be...Ch. 3 - If C=A+B, can C = A + B? Can C>A + B? For each,...Ch. 3 - If C=A+B can C = 0? Can C< O? For each, show how...Ch. 3 - Is it possible to add a scalar to a vector? If so,...Ch. 3 - How would you define the zero vector ?Ch. 3 - Can a vector have a component equal to zero and...Ch. 3 - Can a vector have zero magnitude if one of its...Ch. 3 - Suppose two vectors have unequal magnitudes. Can...Ch. 3 - Are the following statements true or false?...Ch. 3 - I. Trace the vectors in FIGURE EX3.1 onto your...
Ch. 3 - Trace the vectors in FIGURE EX3.2 onto your paper....Ch. 3 - a. What are the x- and v-components of vector E...Ch. 3 - A velocity vector 40° below the positive x-axis...Ch. 3 - A position vector in the first quadrant has an...Ch. 3 - Draw each of the following vectors. Then find its...Ch. 3 - Draw each of the following vectors. Then find its...Ch. 3 - Let C = (3.15 m, 15° above the negative x-axis)...Ch. 3 - A runner is training for an upcoming marathon by...Ch. 3 - Draw each of the following vectors, label an angle...Ch. 3 - Draw each of the following vectors, label an angle...Ch. 3 - Let a. Write Vector Cin component form. b. Draw a...Ch. 3 - a. Write vector Cin component form. b. Draw a...Ch. 3 - a. Write vector Din component form. b. Draw a...Ch. 3 - Let A = 4î - 2j, B = -3î + 5j, and E = 2 A + 3 B...Ch. 3 - Let A = 41 - 2j, B = -3î + 5j, and F = A -4 B . a....Ch. 3 - 17. Let = 2î + 3? and = 2î — 2?. Find the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 18EAPCh. 3 - 19. What are the x– and y- components of the...Ch. 3 - 20. For the three vectors shown Figure EX3.20, + +...Ch. 3 - Prob. 21EAPCh. 3 - 22. Let = (3.0 m, 20° south of east), = (2.0 m,...Ch. 3 - The position of a particle as a function of time...Ch. 3 - a. What is the angle between vectors E and F in...Ch. 3 - FIGURE P3.25 shows vectors A and B . Find vector C...Ch. 3 - Prob. 26EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 27EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 28EAPCh. 3 - The minute hand on a watch is 2.0 cm in length....Ch. 3 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 3 - Ruth sets out to visit her friend Ward, who lives...Ch. 3 - A cannon tilted upward at 30° fires a cannonball...Ch. 3 - Prob. 33EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 34EAPCh. 3 - A pine cone falls straight down from a pine tree...Ch. 3 - Prob. 36EAPCh. 3 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 3 - Your neighbor Paul has rented a truck with a...Ch. 3 - Tom is climbing a 3.0-m-long ladder that leans...Ch. 3 - The treasure map in FIGURE P3.40 gives the...Ch. 3 - The bacterium E. coli is a single-cell organism...Ch. 3 - A flock of ducks is trying to migrate south for...Ch. 3 - FIGURE P3.43 shows three ropes tied together in a...Ch. 3 - I Four forces are exerted on the object shown in...Ch. 3 - FIGURE P3.45 shows four electric charges located...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a) Use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit in Fig. P4.14. b) How much power does the 40 V voltage source deliver to the circuit? Figure P4.14 302 202 w w + + + 40 V V1 80 Ω 02 ΣΑΩ 28 A V3 + w w 102 202arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardYou're on an interplanetary mission, in an orbit around the Sun. Suppose you make a maneuver that brings your perihelion in closer to the Sun but leaves your aphelion unchanged. Then you must have Question 2 options: sped up at perihelion sped up at aphelion slowed down at perihelion slowed down at aphelionarrow_forward
- The force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE DO NOT USE LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- The force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward་ The position of a particle is described by r = (300e 0.5t) mm and 0 = (0.3t²) rad, where t is in seconds. Part A Determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer Part B ? Units Determine the magnitude of the particle's acceleration at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. a = Value A ? Unitsarrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Kinematics Part 3: Projectile Motion; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aY8z2qO44WA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY