
(a)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- A covalent bond is formed between two atoms whose difference in electronegativity is less than 1.9, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
The octet rule states that atoms of various elements enter chemical combination so as to attain a configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so by either transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons.
A covalent bond is formed by sharing of same number of electrons between two atoms to complete their octet. Atoms taking part in covalent bond formation may share one, two or three electron pairs thus forming single, double and triple bond respectively.
Answer to Problem 39P
A covalent bond is formed between two atoms whose difference in electronegativity is less than 1.9. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The electronegativity difference between the atoms determine that whether the bond formed will be covalent or ionic.
If the atoms have equal electronegativity value, then a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale, if exceeded, the bond becomes ionic in nature.
For example: For hydrogen gas: The electronegativity of both the hydrogen is 2.2, therefore a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
For hydrogen chloride:
Electronegativity of Hydrogen = 2.2.
Electronegativity of Chlorine = 3.1.
Electronegativity difference = 0.9.
Therefore, a polar covalent bond is formed.
For sodium chloride:
Electronegativity of Sodium = 1.0.
Electronegativity of Chlorine = 3.1.
Electronegativity difference = 2.1.
Therefore, an ionic bond is formed.
Thus, a covalent bond is formed between two atoms whose difference in electronegativity is less than 1.9.
(b)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- If the difference in electronegativity between two atoms is zero (they have identical electronegativities), then the two atoms will not form a covalent bond, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
A covalent bond is formed by sharing of same number of electrons between two atoms to complete their octet. Atoms taking part in covalent bond formation may share one, two or three electron pairs thus forming single, double and triple bond respectively.
If the difference in electronegativity between two atoms is zero (they have identical electronegativities), then the two atoms will form a covalent bond. Thus, the statement is false.
The electronegativity difference between the atoms determine that whether the bond formed will be covalent or ionic.
If the atoms have equal electronegativity value, then a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale, if exceeded, the bond becomes ionic in nature.
For example: For hydrogen gas: The electronegativity of both the hydrogen is 2.2, therefore a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
(c)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- A covalent bond is formed by sharing two electrons is called a double bond, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
A covalent bond is formed by sharing of same number of electrons between two atoms to complete their octet. Atoms taking part in covalent bond formation may share one, two or three electron pairs thus forming single, double and triple bond respectively.
A covalent bond is formed by sharing two electrons is called a double bond. Thus, the statement is true.
Atoms taking part in covalent bond formation may share one, two or three electron pairs thus, forming single, double and triple bond respectively.
An oxygen atom is formed when an atom of oxygen shares a pair of atoms each.
(d)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement - In the hydrogen molecule
Concept Introduction:
The octet rule states that atoms of various elements enter into chemical combination so as to attain a configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so by either transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons.
In the hydrogen molecule
A covalent bond is formed by sharing of same number of electrons between two atoms to complete their octet. Atoms taking part in covalent bond formation may share one, two or three electron pairs thus forming single, double and triple bond respectively. Hydrogen has only one electron in their valence shell, it shares it with another electron of the other Hydrogen atom to form a single covalent bond.
Sharing of 1 pair of electrons forms a single bond.
(e)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement in the molecule
Concept Introduction:
The octet rule states that atoms of various elements enter chemical combination so as to attain a configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so by either transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons. The logic of 8 electrons is that the noble gases have 8 electrons in their outermost shell and are stable. So, to attain stability noble gas configuration is acquired either by sharing, donating or accepting electrons.
In the molecule
The electronic configuration of the elements is according to the distribution of the electrons in the shells of the atoms.
These shells are K, L, M, n and so on.
K can accommodate a maximum of 2 electrons.
L can accommodate a maximum of 8 electrons.
M can accommodate a maximum of 18 electrons.
N can accommodate a maximum of 32 electrons.
The element with electronic configuration 2 is Helium, therefore each hydrogen attains electronic configuration of Helium.
The element with electronic configuration 2,8 is Neon, therefore each Carbon attains electronic configuration of Neon.
(f)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement, in a polar covalent bond, the more electronegative atom has a partial negative charge
Concept Introduction:
If the atoms have same electronegativity or they are of same atom, then a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale.
In a polar covalent bond, the more electronegative atom has a partial negative charge
The electronegativity difference between the atoms determine that whether the bond formed will be covalent or ionic.
Electronegativity of Hydrogen = 2.2.
Electronegativity of Chlorine = 3.1.
Electronegativity difference = 0.9.
Therefore, a polar covalent bond is formed, the shared paired of electrons are more towards the electronegative chlorine atom and it will get a partial negative charge and hydrogen being electropositive in nature get a partial negative charge.
(g)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement - These bonds are arranged in order of increasing polarity.
Concept Introduction:
If the atoms have same electronegativity or they are of same atom, then a non polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale.
The bonds are arranged in order of increasing polarity as follows:
Thus, the statement is true.
If the atoms have same electronegativity or they are of same atom, then a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale.
More the electronegativity difference, more polar is the bond. Since, the order of electronegativity is as follows:
Therefore, bonds in order of increasing polarity.
(h)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- These bonds are arranged in order of increasing polarity.
Concept Introduction:
If the atoms have same electronegativity or they are of same atom, then a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale.
These bonds are arranged in order of increasing polarity.
Thus, the statement is false.
Electronegativity of hydrogen -2.2.
Electronegativity of Fluorine- 3.9.
Electronegativity of Chlorine-3.1.
Electronegativity of Bromine-2.9.
More the electronegativity difference, more polar is the bond.
Therefore, bonds in order of increasing polarity is as follows:
(i)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement, a polar bond has a dipole with the negative end located at the more electronegative atom., is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
If the atoms have same electronegativity or they are of same atom, then a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale.
A polar bond has a dipole with the negative end located at the more electronegative atom. Thus, the statement is true.
Electronegativity of Hydrogen = 2.2.
Electronegativity of Chlorine = 3.1.
Electronegativity difference = 0.9.
Therefore, a polar covalent bond is formed, and dipole is shown as follows:
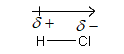
A polar bond has a dipole with the negative end located at the more electronegative atom which is shown by the arrow.
(j)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement, in a single bond, two atoms share one pair of electrons; in a double bond, they share two pairs of electrons; and in a triple bond, they share three pair of electrons., is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
The octet rule states that atoms of various elements enter chemical combination so as to attain a configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so by either transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons.
In a single bond, two atoms share one pair of electrons; in a double bond, they share two pairs of electrons; and in a triple bond, they share three pair of electrons. Thus, the statement is true.
A covalent bond is formed by sharing of same number of electrons between two atoms to complete their octet. Atoms taking part in covalent bond formation may share one, two or three electron pairs thus forming single, double and triple bond respectively.
Atoms taking part in covalent bond formation may share one, two or three electron pairs thus forming single, double and triple bond respectively.
(k)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- The Lewis structure for ethane,
Concept Introduction:
Lewis concept states that atoms of various elements enter chemical combination so as to attain the configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so either by transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons.
The Lewis structure for ethane,
From the structure of ethane.

Total single bonds= 7.
Non-bonding electrons left with carbon = 0.
Non-bonding electrons left with Hydrogen= 0.
Therefore, total electron counts in valence shell-
The Lewis structure for ethane,
(l)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement -
The Lewis structure for formaldehyde,
Concept Introduction:
Lewis concept states that atoms of various elements enter chemical combination so as to attain the configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so either by transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons.
The Lewis structure for formaldehyde,
From the structure of Formaldehyde-
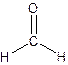
Total single bonds= 2.
Total double bonds=1.
Non-bonding electrons left with carbon = 0.
Non-bonding electrons left with Hydrogen= 0.
Non-bonding electrons left with Oxygen= 4.
Therefore, total electron counts in valence shell-
(m)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement -
The Lewis structure for ammonium ion,
Concept Introduction:
Lewis concept states that atoms of various elements enter chemical combination so as to attain the configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so either by transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons.
The Lewis structure for ammonium ion,
From the structure of Ammonium ion-
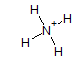
Total single bonds= 4.
Total double bonds=0.
Charge =+1.
Non-bonding electrons left with Nitrogen = 1.
Non-bonding electrons left with Hydrogen= 0.
Therefore, total electron counts I valence shell-
(n)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement-Atoms of third-period elements can hold more than eight electrons in their valence shells, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:.
Atoms of third-period elements can hold more than eight electrons in their valence shells.
According to the Lewis model of bonding, atoms bond together in such a way that each atom participating in the bond acquires an outer-shell electron configuration matching that of the noble gas nearest to it in atomic number.
The electronic configuration of the elements is according to the distribution of the electrons in the shells of the atoms.
These shells are K, L, M, n and so on.
K can accommodate a maximum of 2 electrons.
L can accommodate a maximum of 8 electrons.
M can accommodate a maximum of 18 electrons.
N can accommodate a maximum of 32 electrons.
The element with electronic configuration 2 is Helium.
The element with electronic configuration 2,8 is Neon.
The element with electronic configuration 2,8,18 is Argon and so on.
Since, these configurations corresponds to noble gas configurations on attaining these configurations an atom of an element becomes stable.
Atoms of elements upto 2nd period have can have only 8 electrons in their valence shell due to the presence of only s and p orbitals, whereas atoms of higher periods have d, f orbitals also which can occupy more electrons.
Answer to Problem 39P
If the difference in electronegativity between two atoms is zero (they have identical electronegativities), then the two atoms will form a covalent bond. Thus, the statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
The electronegativity difference between the atoms determine that whether the bond formed will be covalent or ionic.
If the atoms have equal electronegativity value, then a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale, if exceeded, the bond becomes ionic in nature.
For example: For hydrogen gas: The electronegativity of both the hydrogen is 2.2, therefore a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
(c)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- A covalent bond is formed by sharing two electrons is called a double bond, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
A covalent bond is formed by sharing of same number of electrons between two atoms to complete their octet. Atoms taking part in covalent bond formation may share one, two or three electron pairs thus forming single, double and triple bond respectively.
Answer to Problem 39P
A covalent bond is formed by sharing two electrons is called a double bond. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Atoms taking part in covalent bond formation may share one, two or three electron pairs thus, forming single, double and triple bond respectively.
An oxygen atom is formed when an atom of oxygen shares a pair of atoms each.
(d)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement - In the hydrogen molecule
Concept Introduction:
The octet rule states that atoms of various elements enter into chemical combination so as to attain a configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so by either transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons.
Answer to Problem 39P
In the hydrogen molecule
Explanation of Solution
A covalent bond is formed by sharing of same number of electrons between two atoms to complete their octet. Atoms taking part in covalent bond formation may share one, two or three electron pairs thus forming single, double and triple bond respectively. Hydrogen has only one electron in their valence shell, it shares it with another electron of the other Hydrogen atom to form a single covalent bond.
Sharing of 1 pair of electrons forms a single bond.
(e)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement in the molecule
Concept Introduction:
The octet rule states that atoms of various elements enter chemical combination so as to attain a configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so by either transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons. The logic of 8 electrons is that the noble gases have 8 electrons in their outermost shell and are stable. So, to attain stability noble gas configuration is acquired either by sharing, donating or accepting electrons.
Answer to Problem 39P
In the molecule
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of the elements is according to the distribution of the electrons in the shells of the atoms.
These shells are K, L, M, n and so on.
K can accommodate a maximum of 2 electrons.
L can accommodate a maximum of 8 electrons.
M can accommodate a maximum of 18 electrons.
N can accommodate a maximum of 32 electrons.
The element with electronic configuration 2 is Helium, therefore each hydrogen attains electronic configuration of Helium.
The element with electronic configuration 2,8 is Neon, therefore each Carbon attains electronic configuration of Neon.
(f)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement, in a polar covalent bond, the more electronegative atom has a partial negative charge
Concept Introduction:
If the atoms have same electronegativity or they are of same atom, then a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale.
Answer to Problem 39P
In a polar covalent bond, the more electronegative atom has a partial negative charge
Explanation of Solution
The electronegativity difference between the atoms determine that whether the bond formed will be covalent or ionic.
Electronegativity of Hydrogen = 2.2.
Electronegativity of Chlorine = 3.1.
Electronegativity difference = 0.9.
Therefore, a polar covalent bond is formed, the shared paired of electrons are more towards the electronegative chlorine atom and it will get a partial negative charge and hydrogen being electropositive in nature get a partial negative charge.
(g)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement - These bonds are arranged in order of increasing polarity.
Concept Introduction:
If the atoms have same electronegativity or they are of same atom, then a non polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale.
Answer to Problem 39P
The bonds are arranged in order of increasing polarity as follows:
Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
If the atoms have same electronegativity or they are of same atom, then a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale.
More the electronegativity difference, more polar is the bond. Since, the order of electronegativity is as follows:
Therefore, bonds in order of increasing polarity.
(h)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- These bonds are arranged in order of increasing polarity.
Concept Introduction:
If the atoms have same electronegativity or they are of same atom, then a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale.
Answer to Problem 39P
These bonds are arranged in order of increasing polarity.
Thus, the statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Electronegativity of hydrogen -2.2.
Electronegativity of Fluorine- 3.9.
Electronegativity of Chlorine-3.1.
Electronegativity of Bromine-2.9.
More the electronegativity difference, more polar is the bond.
Therefore, bonds in order of increasing polarity is as follows:
(i)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement, a polar bond has a dipole with the negative end located at the more electronegative atom., is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
If the atoms have same electronegativity or they are of same atom, then a non-polar covalent bond is formed.
But if there is an electronegativity difference between the atoms forming a bond, the bond formed is a polar bond. This difference should not exceed 1.9 on Pauling scale.
Answer to Problem 39P
A polar bond has a dipole with the negative end located at the more electronegative atom. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Electronegativity of Hydrogen = 2.2.
Electronegativity of Chlorine = 3.1.
Electronegativity difference = 0.9.
Therefore, a polar covalent bond is formed, and dipole is shown as follows:
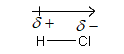
A polar bond has a dipole with the negative end located at the more electronegative atom which is shown by the arrow.
(j)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement, in a single bond, two atoms share one pair of electrons; in a double bond, they share two pairs of electrons; and in a triple bond, they share three pair of electrons., is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
The octet rule states that atoms of various elements enter chemical combination so as to attain a configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so by either transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons.
Answer to Problem 39P
In a single bond, two atoms share one pair of electrons; in a double bond, they share two pairs of electrons; and in a triple bond, they share three pair of electrons. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
A covalent bond is formed by sharing of same number of electrons between two atoms to complete their octet. Atoms taking part in covalent bond formation may share one, two or three electron pairs thus forming single, double and triple bond respectively.
Atoms taking part in covalent bond formation may share one, two or three electron pairs thus forming single, double and triple bond respectively.
(k)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement- The Lewis structure for ethane,
Concept Introduction:
Lewis concept states that atoms of various elements enter chemical combination so as to attain the configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so either by transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons.
Answer to Problem 39P
The Lewis structure for ethane,
Explanation of Solution
From the structure of ethane.

Total single bonds= 7.
Non-bonding electrons left with carbon = 0.
Non-bonding electrons left with Hydrogen= 0.
Therefore, total electron counts in valence shell-
The Lewis structure for ethane,
(l)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement -
The Lewis structure for formaldehyde,
Concept Introduction:
Lewis concept states that atoms of various elements enter chemical combination so as to attain the configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so either by transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons.
Answer to Problem 39P
The Lewis structure for formaldehyde,
Explanation of Solution
From the structure of Formaldehyde-
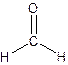
Total single bonds= 2.
Total double bonds=1.
Non-bonding electrons left with carbon = 0.
Non-bonding electrons left with Hydrogen= 0.
Non-bonding electrons left with Oxygen= 4.
Therefore, total electron counts in valence shell-
(m)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement -
The Lewis structure for ammonium ion,
Concept Introduction:
Lewis concept states that atoms of various elements enter chemical combination so as to attain the configuration of eight electrons in their outermost shell. They do so either by transference of electrons or by mutual sharing of electrons.
Answer to Problem 39P
The Lewis structure for ammonium ion,
Explanation of Solution
From the structure of Ammonium ion-

Total single bonds= 4.
Total double bonds=0.
Charge =+1.
Non-bonding electrons left with Nitrogen = 1.
Non-bonding electrons left with Hydrogen= 0.
Therefore, total electron counts I valence shell-
(n)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement-Atoms of third-period elements can hold more than eight electrons in their valence shells, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:.
Answer to Problem 39P
Atoms of third-period elements can hold more than eight electrons in their valence shells.
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of the elements is according to the distribution of the electrons in the shells of the atoms.
These shells are K, L, M, n and so on.
K can accommodate a maximum of 2 electrons.
L can accommodate a maximum of 8 electrons.
M can accommodate a maximum of 18 electrons.
N can accommodate a maximum of 32 electrons.
The element with electronic configuration 2 is Helium.
The element with electronic configuration 2,8 is Neon.
The element with electronic configuration 2,8,18 is Argon and so on.
Since, these configurations corresponds to noble gas configurations on attaining these configurations an atom of an element becomes stable.
Atoms of elements upto 2nd period have can have only 8 electrons in their valence shell due to the presence of only s and p orbitals, whereas atoms of higher periods have d, f orbitals also which can occupy more electrons.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
INTRO.TO GENERAL,ORGAN...-OWLV2 ACCESS
- presented by Morallen Lig Intermine the hand product for the given mution by adding atoms, bonds, nonhonding diarion panda скуль Step 3: Comp the draw the product Step 2: Agama workup Compithe 429 ملولةarrow_forwardReaction A 0,0arrow_forwardpresented by Morillon Leaning Predict the organic product for the min кусур HSC Adithane carved arnown to come than that to the condon slchroruis in acid in in aquishri with ноюarrow_forward
- 6.15PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Include any relevant stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Problem 1 of O H [PhзPCH2CH3]*C|¯ NaH Drawing > Q Atoms, Bonds and Draw or tap a nearrow_forward8:17 PM Sun Mar 30 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Probler Drawing Ato Bonds Clarrow_forwardpresented by Mr L How the coprion. (Il Done in no wraction, dew the starting redential) доarrow_forward
- 8:16 PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Proble 1. CH3MgBr 2. H3O+ F Drawingarrow_forwardо но оarrow_forwardName the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forward
- Macmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardProvide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning


