
Quinapril (trade name Accupril) is a drug used to treat hypertension and congestive heart
failure.
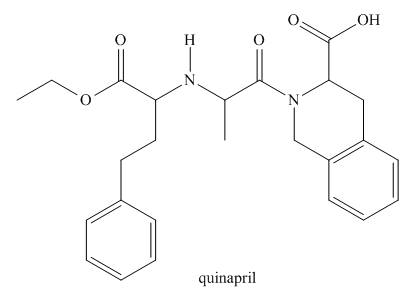
a. Identify the
b. Classify any alcohol, amide or
c. At which sites can quinapril hydrogen bond to water?
d. At which sites can quinapril hydrogen bond to acetone
e. Label the most acidic hydrogen atom.
f. Which site is most basic?
(a)
Interpretation: The functional groups present in the given compound, quinapril are to be identified.
Concept introduction: An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as functional groups. The functional group is the most reactive part present in the molecule. The main functional groups are
Answer to Problem 3.60P
The functional groups present in the given compound, quinapril are shown below.
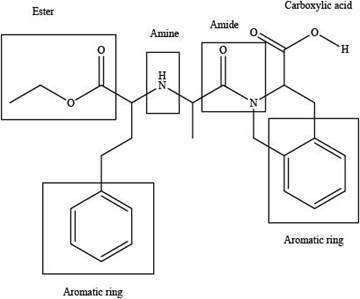
Explanation of Solution
The functional groups present in the given compound, quinapril are shown as,
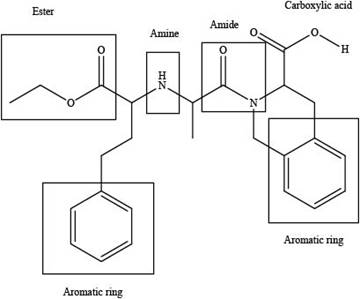
Figure 1
Thus, there are total four functional groups present in quinapril which are ester group, amine group, amide group and carboxylic group as highlighted above. There are two aromatic also present in the given compound, quinapril.
There are total four functional groups present in quinapril which are ester group, amine group, amide group and carboxylic group.
(b)
Interpretation: The alcohol, amine or amide groups present in the given compound, quinapril are to be classified as
Concept introduction: The amine, amide or alcoholic groups are identified as primary
Answer to Problem 3.60P
The classification of alcohol, amine or amide groups present in the given compound, quinapril as
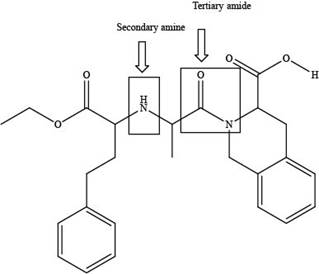
Explanation of Solution
The classification alcohol, amine or amide groups present in the given compound, quinapril are shown as,
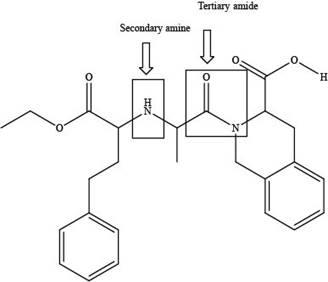
Figure 2
The given compound consists of one tertiary amide and one secondary amine as shown above.
The classification of alcohol, amine or amide groups present in the given compound, quinapril as
(c)
Interpretation: The site at which quinapril forms hydrogen bond with water is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The bonding that takes place between hydrogen atom and hetero atoms like oxygen, nitrogen and fluorine is known as hydrogen bonding. In case of water, hydrogen atom makes bond with each other. Hydrogen bonding is the strongest bonding among the intermolecular forces and covalent bonding.
Answer to Problem 3.60P
The site at which quinapril forms hydrogen bond with water is shown below.
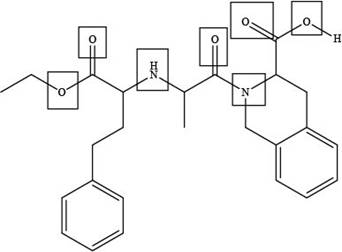
Explanation of Solution
The site at which quinapril forms hydrogen bond with water is shown as,

Figure 3
In the given compound, the sites where the electronegative atoms like, oxygen and nitrogen are present, there only hydrogen bond forms with water as highlighted above.
The site at which quinapril forms hydrogen bond with water is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The site at which quinapril forms hydrogen bond with acetone is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The bonding that takes place between hydrogen atom and hetero atoms like oxygen, nitrogen and fluorine is known as hydrogen bonding. In case of acetone, hydrogen atom makes bond with that electronegative atom which is attached to hydrogen atom only. Hydrogen bonding is the strongest bonding among the intermolecular forces and covalent bonding.
Answer to Problem 3.60P
The site at which quinapril forms hydrogen bond with acetone is shown below.
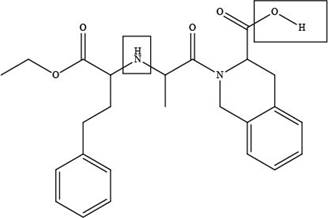
Explanation of Solution
The site at which quinapril forms hydrogen bond with acetone is shown as,

Figure 4
In the given compound, the sites where the electronegative atoms like, oxygen and nitrogen attached to other hydrogen atom are present, there only hydrogen bond forms with acetone as highlighted above.
The site at which quinapril forms hydrogen bond with acetone is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The most acidic hydrogen present in the given compound, quinapril is to be labeled.
Concept introduction: The most acidic hydrogen
Answer to Problem 3.60P
The labeling of the most acidic hydrogen present in the given compound, quinapril is shown below.
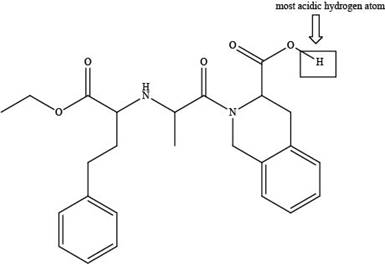
Explanation of Solution
The labeling of the most acidic hydrogen present in the given compound, quinapril is shown as,

Figure 5
The electronegativity increases while moving left to right in the period. Thus, oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen atom as it is located at the extreme right position. According to the structure of quinapril, hydrogen atom that is bonded with oxygen atom is the most acidic one because oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen atom. The higher electronegativity corresponds to the greater acidic character of hydrogen atom attached to the electronegative atom.
The labeling of the most acidic hydrogen present in the given compound, quinapril is shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The most basic site in the compound quinapril is to be labeled.
Concept introduction: According to Bronsted-Lowry theory, the species that easily tends to accept the proton is known as base and the species that easily donate the proton is known as acid. The high delocalization of electron pair corresponds to the high basic character of the atom.
Answer to Problem 3.60P
The labeling of the most basic site in the compound quinapril is shown below.
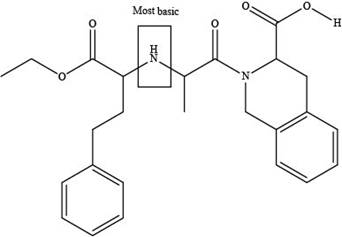
Explanation of Solution
The labeling of the most basic site in the compound quinapril is shown as,
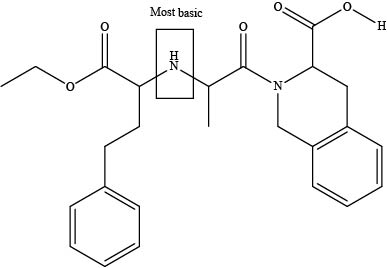
Figure 6
According to the structure of quinapril, the site at which amide group is present is the most basic site because in amides, the pair of electrons over nitrogen atom gets highly delocalized. Hence, the most basic site is present at tertiary amide.
The labeling of the most basic site in the compound quinapril is shown in Figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

