
Concept explainers
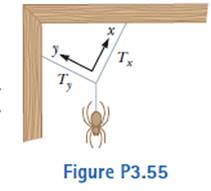
In Figure P3.55, a spider is resting after starting to spin its web. The gravitational force on the spider makes it exert a downward force of 0.150 N on the junction of the three strands of silk. The junction is supported by different tension forces in the two strands above it so that the resultant force on the junction is zero. The two sloping strands are perpendicular, and we have chosen the x and y directions to be along them. The tension Tx is 0.127 N. Find (a) the tension Ty, (b) the angle the x axis makes with the horizontal, and (c) the angle the y axis makes with the horizontal.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 3 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Concepts and Investigations
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
EBK INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- If the car in the previous problem increases its power output by 10% (by pressing the gas pedal farther down), at what rate will the car accelerate? Hint: Consider the net force. In the previous problem the power was 31.8kWarrow_forwardWhat power is required (at the wheels) for a 1400 kg automobile to climb a 4% grade at a constant speed 30 m/s while it is opposed by drag and rolling resistance forces totaling 500 N?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- As a box is lifted against gravity and placed on a shelf, how does the work done by the lifter compare with the work done by gravity? What is the net work done on the box? What does this imply about its change in kinetic energy? Use definitions and mathematics from this chapter to answer these questions.arrow_forwardAs I carry a box up a flight of stairs, am I doing positive work or negative work on the box? Provide a mathematical explanation.arrow_forwardAs a ball falls under the influence of gravity, does gravity do positive work or negative work? Provide a mathematical explanation.arrow_forward
- Under what circumstances is it bad to describe kinetic energy as k = 1/2mv^2arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardAir temperature of 37 °C increases swimming pool temperature of 2.55 °C. What is the fraction of the water in the pool must evaporate during this time to carry enough energy to keep the temperature of the pool constant? 4186 J/(kg°C) = specific heat of water 2,430,000 (2.43 x 106) J/kg = latent heat of vaporization for the water in the pool.arrow_forward
- The iceberg requires 7.4 x 1020 Joules of energy to melt it completely. It absorbs energy from the Sun at a constant average rate of 88 Watts/m2. The total surface area of iceberg exposed to the sunlight is 12 billion (1.2 x 1010) square meters. How long will it take for sunlight to melt the entire iceberg in yearsarrow_forward1.0 kg block of ice to melt in the kitchen. The temperature in the kitchen is 31 °C. The ice starts out at 0 °C and takes an hour to melt and reach the same temperature as the surrounding room (31 °C). How much heat does the 1.0 kg of ice/water absorb from the room as it melts and heats up to 31 °C in Joules absorbed? Latent heat of fusion for water/ice is 334,000 J/kg Specific heat of water is 4186 J/kg°Carrow_forward5.84 If the coefficient of static friction between a table and a uni- form, massive rope is μ, what fraction of the rope can hang over the edge of the table without the rope sliding? 5.97 Block A, with weight Figure P5.97 3w, slides down an inclined plane S of slope angle 36.9° at a constant speed while plank B, with weight w, rests on top of A. The plank is attached by a cord to the wall (Fig. P5.97). (a) Draw a diagram of all the forces acting on block A. (b) If the coefficient of kinetic friction is the same between A and B and between S and A, determine its value. 36.9° 1arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





