
Concept explainers
An air-traffic controller observes two aircraft on his radar screen. The first is at altitude 800 m, horizontal distance 19.2 km, and 25.0° south of west. The second aircraft is at altitude 1 100 m, horizontal distance 17.6 km, and 20.0° south of west. What is the distance between the two aircraft? (Place the x axis west, the y axis south, and the z axis vertical.)
The distance between the two aircraft.
Answer to Problem 3.54AP
The distance between the two aircraft is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The air traffic controller observes two aircraft on his radar screen. The first is at altitude
Consider the
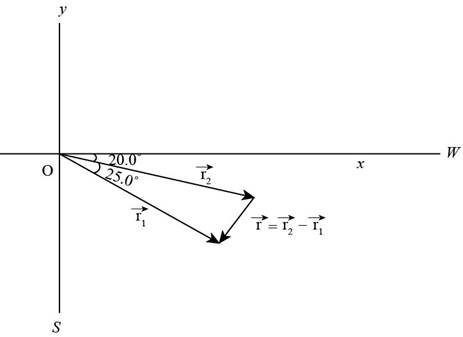
Figure (1)
The displacement vector of the first aircraft in the
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the displacement vector of the first aircraft in
The displacement vector of the first aircraft in the
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the displacement vector of the first aircraft in
The displacement vector of the first aircraft in the
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the displacement vector of the first aircraft in
The position vector of the first aircraft is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the position vector of the first aircraft is
The displacement vector of the second aircraft in the
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the displacement vector of the second aircraft in
The displacement vector of the second aircraft in the
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the displacement vector of the second aircraft in
The displacement vector of the second aircraft in the
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the displacement vector of the second aircraft in
The position vector of the second aircraft is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the position vector of the second aircraft is
The net distance vector between the two aircraft is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the net distance vector between the two aircraft is
The magnitude for the net distance vector between the two aircraft is,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the distance between the two aircraft is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
EBK INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
Loose Leaf For Integrated Principles Of Zoology
- Eddie Hall is the current world record holder in the deadlift, a powerlifting maneuver in which a weighted barbell is lifted from the ground to waist height, then dropped. The figure below shows a side view of the initial and final positions of the deadlift. a 0 = 55.0° Fift h22.5 cm i hy = 88.0 cm b iarrow_forwardsolve for (_) Narrow_forwardTwo boxes of fruit on a frictionless horizontal surface are connected by a light string as in the figure below, where m₁ = 11 kg and m₂ = 25 kg. A force of F = 80 N is applied to the 25-kg box. mq m1 Applies T Peaches i (a) Determine the acceleration of each box and the tension in the string. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s² N (b) Repeat the problem for the case where the coefficient of kinetic friction between each box and the surface is 0.10. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s2 Narrow_forward
- All correct but t1 and t2 from part Aarrow_forwardThree long, straight wires are mounted on the vertices of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. The wires carry currents of I₁ = 3.50 A, I2 = 5.50 A, and I3 = 8.50 A. Each side of the triangle has a length of 34.0 cm, and the point (A) is located half way between (11) and (12) along one of the sides. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at point (A). Solve in Teslas (T). I₁arrow_forwardNumber There are four charges, each with a magnitude of 2.38 μC. Two are positive and two are negative. The charges are fixed to the corners of a 0.132-m square, one to a corner, in such a way that the net force on any charge is directed toward the center of the square. Find the magnitude of the net electrostatic force experienced by any charge. ips que Mi Units estic re harrow_forward
- Two long, straight wires are separated by distance, d = 22.0 cm. The wires carry currents of I1 = 7.50 A and I2 = 5.50 A in opposite directions, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point (B). Let r₁ = 12.0 cm, r2 = 7.00 cm, and r3 = 13.0 cm. Solve in T. 12 d A √3arrow_forwardThank you in advance, image with question is attached below.arrow_forwardQuestion is attached, thank you.arrow_forward
- Two very small spheres are initially neutral and separated by a distance of 0.612 m. Suppose that 4.12 × 1013 electrons are removed from one sphere and placed on the other. (a) What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force that acts on each sphere? (b) Is the force attractive or repulsive?arrow_forwardEstimate the diameter of the Moon. During a total solar eclipse, the Moon passes in front of the Sun so that during “totality” their apparent sizes match and the Moon blocks light from the Sun shining on the Earth. a) What do you predict the size of the Moon would be if you were to use a pinhole in an aluminum holder, meter stick, and white paper screen to project light from the full Moon through a pinhole onto a screen that is one meter away from the pinhole? b) Describe in detail how you would use this apparatus and your knowledge of pinhole phenomena to estimate the diameter of the Moon. Assume that the distance between the Earth and the Moon is 250,000 miles.arrow_forwardThe following data was collected for a friction experiment in which an object was observed moving at constant speed over a surface. Graph the Applied Force versus the Normal Force and determine the coefficient of friction. Is this value the coefficient of kinetic friction or the coefficient of static friction? Justify your answer. Trial Normal Force Applied Force 1 4.13 1.44 2 6.41 1.68 3 8.94 2.82 4 11.34 3.94 5 13.82 5.05arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





