
Concept explainers
(a)
To determine: The structure and name of any eight isomers among the eighteen isomers of
Interpretation: The structure and name of any eight isomers among the eighteen isomers of alkane
Concept introduction: The rules for the naming of cycloalkanes are stated below.
- If two different cycloalkanes are present then the one with the more number of carbon atoms act as the parent chain.
- If the side chain has more number of carbon atoms then it act as the parent chain and the cyclic group becomes the substituent and is ended with the word”-yl”.
- The numbering is done in such a manner that the substituents groups occupy the lowest position.
- If different types of substituent groups are present then they are written in an alphabetical order.
- If a substituent is present more than one time then prefixes like di, tri, tetra are used depending on the number of times that particular substituent group appears in the given compound.
- If geometrical isomerism is possible in the given compound then cis and trans is used before the name of the compound.
(a)
Answer to Problem 3.33SP
The structure and name of any eight isomers among the eighteen isomers of alkane
Explanation of Solution
The isomers of given alkane
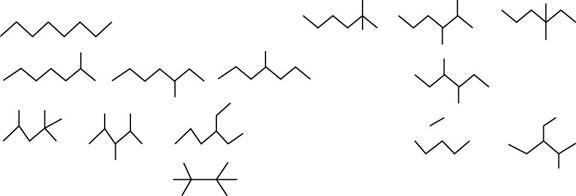
Figure 1
The randomly selected first isomer is shown below.
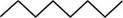
Figure 2
The name of the above compound is octane.
The randomly selected second isomer is shown below.
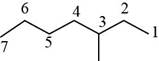
Figure 3
The name of the above compound is
The randomly selected third isomer is shown below.
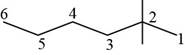
Figure 4
The name of the above compound is
The randomly selected fourth isomer is shown below.
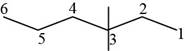
Figure 5
The name of the above compound is
The randomly selected fifth isomer is shown below.
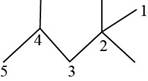
Figure 6
The name of the above compound is
The randomly selected sixth isomer is shown below.
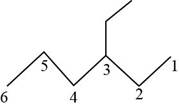
Figure 7
The name of the above compound is
The randomly selected seventh isomer is shown below.
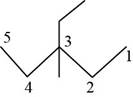
Figure 8
The name of the above compound is
The randomly selected seventh isomer is shown below.
Figure 9
The name of the above compound is
(b)
To determine: The structure and name of six isomeric cyclopentanes having molecular formula
Interpretation: The structure and name of six isomeric cyclopentanes having molecular formula
Concept introduction: The rules for the naming of cycloalkanes are stated below.
- If two different cycloalkanes are present then the one with the more number of carbon atoms act as the parent chain.
- If the side chain has more number of carbon atoms then it act as the parent chain and the cyclic group becomes the substituent and is ended with the word”-yl”.
- The numbering is done in such a manner that the substituents groups occupy the lowest position.
- If different types of substituent groups are present then they are written in an alphabetical order.
- If a substituent is present more than one time then prefixes like di, tri, tetra are used depending on the number of times that particular substituent group appears in the given compound.
- If geometrical isomerism is possible in the given compound then cis and trans is used before the name of the compound.
(b)
Answer to Problem 3.33SP
The structure and name of six isomeric cyclopentanes having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The isomers of given cyclopentane
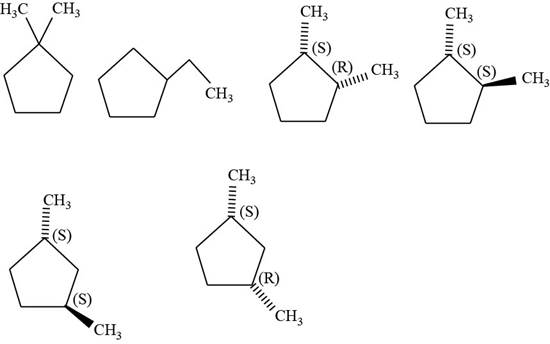
Figure 10
The first isomer is shown below.
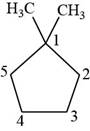
Figure 11
According to IUPAC rules numbering is started from the substituted carbon. Therefore, the name of the above compound is
The second isomer is shown below.
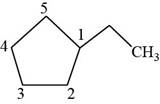
Figure 12
According to IUPAC rules numbering is started from the substituted carbon. Therefore, the name of the above compound is
The third isomer is shown below.
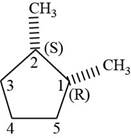
Figure 13
According to IUPAC rules numbering is started from the substituted carbon. Numbering is done in such a manner that the substituents occupy the least position. On the basis of priority of groups
The fourth isomer is shown below.
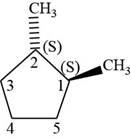
Figure 14
According to IUPAC rules numbering is started from the substituted carbon. Numbering is done in such a manner that the substituents occupy the least position. On the basis of priority of groups
The fifth isomer is shown below.
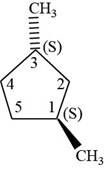
Figure 15
According to IUPAC rules numbering is started from the substituted carbon. Numbering is done in such a manner that the substituents occupy the least position. On the basis of priority of groups
The sixth isomer is shown below.
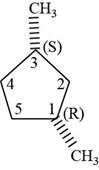
Figure 16
According to IUPAC rules numbering is started from the substituted carbon. Numbering is done in such a manner that the substituents occupy the least position. On the basis of priority of groups
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (9th Edition)
- Which of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O O OH OH 1. BH 2. H₂O₂, NaOH OH OHarrow_forward
- How many products are possible from the following reaction? Do not take into account stereoisomers. 01 04 03 O O O O 02 CH H₂SO4 heatarrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardChoose the major product of the reaction with correct regio- and stereochemistry. Br2 H₂O O "Br Br & O 'Br OH Br 吡 O OH OH Br "OH Brarrow_forward
- Select the major product of the following reaction. & Br (CH)CONa (CH₂),COH 0 OC(CH) O &arrow_forwardDraw the products of the hydrolysis reaction between the ester molecule and water. Determine the products of the following reaction.arrow_forwardWhat is the unsaturation number for compounds with the formula C₂H₁₂Cl₂? O õ õ o o 4 3arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





