
Concept explainers
The following set of data is from a sample of n = 5:
7 4 9 8 2
- Calculate the
mean ,median , andmode . - Calculate the
range , variance. standard deviation, and coefficient of variation. - Calculate the Z scores. Are there any outliers?
- Describe the shape of the data set.
(a)
To compute: The mean, median, and mode for the given data set.
Answer to Problem 3.1LB
Mean is 6, median is 7 for the given dataset.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Given data set is:
7,4,9,8, and 2.
Formula:
Calculation:
Mean could be calculated as for the given data set:
Median could be calculated as for the given data set:
Arrange the data in ascending ordered:
2,4,7,8, and 9.
Thus, Median is 7.
Mode:
There is no mode.
(b)
To conclude:
The range, variance, standard deviation, and coefficient of variation.
Answer to Problem 3.1LB
The is 7, variance is 11.33, standard deviation is 3.366 for the given data set.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
From the above given data set,
Calculation:
The range could be calculated as:
Formula:
The standard deviation
The standard deviation
(c)
To compute:
The Z-score, there is any outliers.
Answer to Problem 3.1LB
z scores are -1.18, -0.29, 0.89, -0.59, 0.59.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
from the above part,
Formula:
Calculation:
Z score can be calculated:
x =2,7,9,4,8
Thus,
Thus,
Z =-1.18, -0.29,0.89,-0.59,0.59
There is one value outlier 2 because 2 does not lie in the interval
(d)
To explain:
The shape of the data set.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
from the above given data set:
Graph:
The graph could be construct for the given data set as:
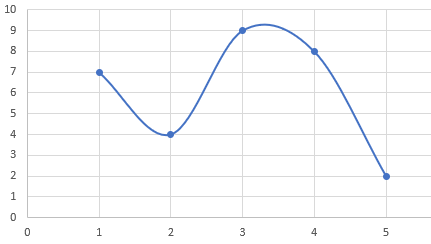
Interpretation:
Shape:
It seems that there would be two nods.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Pearson eText Business Statistics: First Course -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Precalculus: A Unit Circle Approach (3rd Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Beginning and Intermediate Algebra
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- 38. Possible values of X, the number of components in a system submitted for repair that must be replaced, are 1, 2, 3, and 4 with corresponding probabilities .15, .35, .35, and .15, respectively. a. Calculate E(X) and then E(5 - X).b. Would the repair facility be better off charging a flat fee of $75 or else the amount $[150/(5 - X)]? [Note: It is not generally true that E(c/Y) = c/E(Y).]arrow_forward74. The proportions of blood phenotypes in the U.S. popula- tion are as follows:A B AB O .40 .11 .04 .45 Assuming that the phenotypes of two randomly selected individuals are independent of one another, what is the probability that both phenotypes are O? What is the probability that the phenotypes of two randomly selected individuals match?arrow_forward53. A certain shop repairs both audio and video compo- nents. Let A denote the event that the next component brought in for repair is an audio component, and let B be the event that the next component is a compact disc player (so the event B is contained in A). Suppose that P(A) = .6 and P(B) = .05. What is P(BA)?arrow_forward
- 26. A certain system can experience three different types of defects. Let A;(i = 1,2,3) denote the event that the sys- tem has a defect of type i. Suppose thatP(A1) = .12 P(A) = .07 P(A) = .05P(A, U A2) = .13P(A, U A3) = .14P(A2 U A3) = .10P(A, A2 A3) = .011Rshelfa. What is the probability that the system does not havea type 1 defect?b. What is the probability that the system has both type 1 and type 2 defects?c. What is the probability that the system has both type 1 and type 2 defects but not a type 3 defect? d. What is the probability that the system has at most two of these defects?arrow_forwardThe following are suggested designs for group sequential studies. Using PROCSEQDESIGN, provide the following for the design O’Brien Fleming and Pocock.• The critical boundary values for each analysis of the data• The expected sample sizes at each interim analysisAssume the standardized Z score method for calculating boundaries.Investigators are evaluating the success rate of a novel drug for treating a certain type ofbacterial wound infection. Since no existing treatment exists, they have planned a one-armstudy. They wish to test whether the success rate of the drug is better than 50%, whichthey have defined as the null success rate. Preliminary testing has estimated the successrate of the drug at 55%. The investigators are eager to get the drug into production andwould like to plan for 9 interim analyses (10 analyzes in total) of the data. Assume thesignificance level is 5% and power is 90%.Besides, draw a combined boundary plot (OBF, POC, and HP)arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution for the attached image in detailed.arrow_forward
- 20 km, because GISS Worksheet 10 Jesse runs a small business selling and delivering mealie meal to the spaza shops. He charges a fixed rate of R80, 00 for delivery and then R15, 50 for each packet of mealle meal he delivers. The table below helps him to calculate what to charge his customers. 10 20 30 40 50 Packets of mealie meal (m) Total costs in Rands 80 235 390 545 700 855 (c) 10.1. Define the following terms: 10.1.1. Independent Variables 10.1.2. Dependent Variables 10.2. 10.3. 10.4. 10.5. Determine the independent and dependent variables. Are the variables in this scenario discrete or continuous values? Explain What shape do you expect the graph to be? Why? Draw a graph on the graph provided to represent the information in the table above. TOTAL COST OF PACKETS OF MEALIE MEAL 900 800 700 600 COST (R) 500 400 300 200 100 0 10 20 30 40 60 NUMBER OF PACKETS OF MEALIE MEALarrow_forwardLet X be a random variable with support SX = {−3, 0.5, 3, −2.5, 3.5}. Part ofits probability mass function (PMF) is given bypX(−3) = 0.15, pX(−2.5) = 0.3, pX(3) = 0.2, pX(3.5) = 0.15.(a) Find pX(0.5).(b) Find the cumulative distribution function (CDF), FX(x), of X.1(c) Sketch the graph of FX(x).arrow_forwardA well-known company predominantly makes flat pack furniture for students. Variability with the automated machinery means the wood components are cut with a standard deviation in length of 0.45 mm. After they are cut the components are measured. If their length is more than 1.2 mm from the required length, the components are rejected. a) Calculate the percentage of components that get rejected. b) In a manufacturing run of 1000 units, how many are expected to be rejected? c) The company wishes to install more accurate equipment in order to reduce the rejection rate by one-half, using the same ±1.2mm rejection criterion. Calculate the maximum acceptable standard deviation of the new process.arrow_forward
- 5. Let X and Y be independent random variables and let the superscripts denote symmetrization (recall Sect. 3.6). Show that (X + Y) X+ys.arrow_forward8. Suppose that the moments of the random variable X are constant, that is, suppose that EX" =c for all n ≥ 1, for some constant c. Find the distribution of X.arrow_forward9. The concentration function of a random variable X is defined as Qx(h) = sup P(x ≤ X ≤x+h), h>0. Show that, if X and Y are independent random variables, then Qx+y (h) min{Qx(h). Qr (h)).arrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL



