
Concept explainers
Answer questions on costs and production. (LO 5), AP
The ledger of Hasgrove Company has the following work in process account.
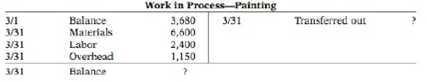
Production records show that there were 800 units in the beginning inventory. 30% complete, 1,100 units started, and 1,500 units transferred out. The units in ending inventory were 40% complete. Materials are entered at the beginning of the painting process. Hasgrove uses the FIFO method to compute equivalent units.
Instructions
Answer the following questions.
(a) How many units are in process at March 31?
(b) What is the unit materials cost for March?
(c) What is the unit conversion cost for March?
(d) What is the total cost of units started in February and completed in March?
(e) What is the total cost of units started and finished in March?
(f) What is the cost of the March 31 inventory?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Corporate Finance (4th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance) - Standalone book
Foundations Of Finance
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in Intro to Business)
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Financial Chapters (Book & Access Card)
- Give me solutionarrow_forwardFinancial Accounting Questionarrow_forwardOn January 1, 2020, Nexus Technologies purchased a machine for $15,000. The machine was estimated to have a 10-year useful life and a residual value of $800. Straight-line depreciation is used. On January 1, 2022, the machine was exchanged for office equipment with a fair value of $12,500. Assuming that the exchange had commercial substance, how much would be recorded as a gain on disposal of the machine on January 1, 2022?arrow_forward
- Variable and Absorption Costing Summarized data for the first year of operations for Gorman Products, Inc., are as follows: Sales (70,000 units) Production costs (80,000 units) Direct material Direct labor Manufacturing overhead: Variable Fixed Operating expenses: Variable $2,800,000 880,000 720,000 544,000 320,000 175,000 Fixed 240,000 Depreciation on equipment 60,000 Real estate taxes 18,000 Personal property taxes (inventory & equipment) 28,800 Personnel department expenses 30,000 a. Prepare an income statement based on full absorption costing. Only use a negative sign with your answer for net income (loss), if the answer represents a net loss. Otherwise, do not use negative signs with any answers. Round answers to the nearest whole number, when applicable. Sales Cost of Goods Sold: Absorption Costing Income Statement Beginning Inventory $ 2,800,000 Direct materials Direct labor Manufacturing overhead Less: Ending Inventory Cost of Goods Sold Gross profit $ 880,000 720,000 864,000…arrow_forwardAccurate answerarrow_forwardanswer plzarrow_forward
- What is the sales margin for the division of the financial accounting?arrow_forwardMartin Corporation incurs a cost of $38.65 per unit, of which $22.35 is variable, to make a product that normally sells for $60.50. A foreign wholesaler offers to buy 6,100 units at $34.20 each. Martin will incur additional costs of $2.85 per unit to imprint a logo and to pay for shipping. Compute the increase or decrease in net income Martin will realize by accepting the special order, assuming the company has sufficient excess operating capacity.arrow_forwardTitan Industries purchased a machine for $40,000 with a residual value of $6,000 and an estimated useful life of 12 years. What is the annual depreciation under the straight-line method?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College


