
(a)
Interpretation:
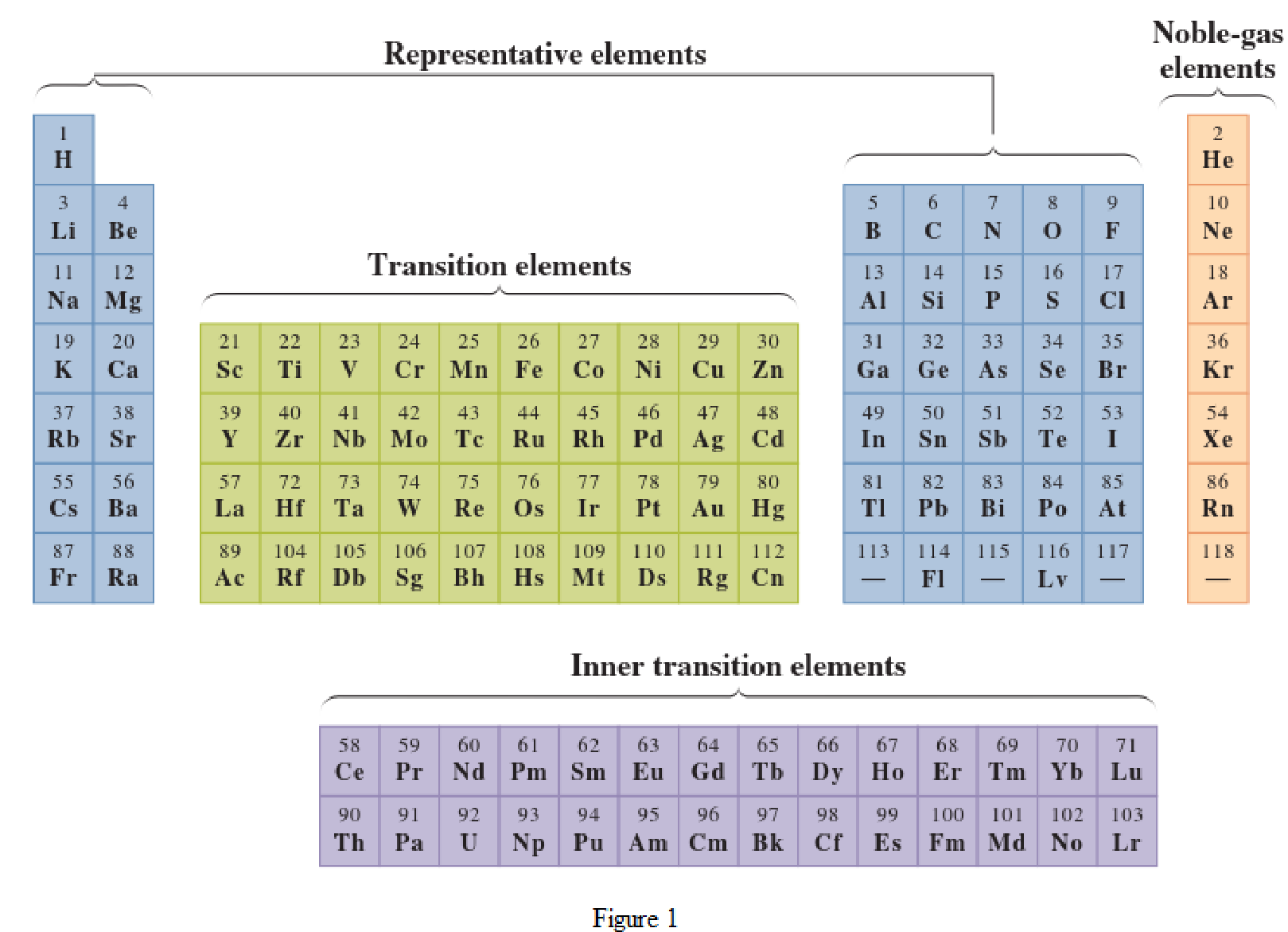
In the given periodic table, how many elements those are highlighted which represent inner
Concept Introduction:
Elements in the periodic table are classified in several different ways and out of them two most common systems are,
- System based on the physical properties in which they are classified as metals and nonmetals.
- System based on electronic configuration in which they are classified as noble-gas, representative elements, transition elements, or inner-transition elements.
Noble-gas elements are the ones that are located in far right of periodic table. The physical state of these elements at room temperature is gas. The noble gases have their electronic configuration ending with
Representative elements are the ones that are in s area and area of the periodic table. They have partially filled s subshell or p subshell in their electronic configurations. Some of the elements are nonmetals while others are metals.
Transition elements are the ones that are located in d area of periodic table. They have the distinguishing electrons in their d subshell. All the transition elements are metals.
Inner transition elements are the ones that are located in f area of the periodic table. They have the distinguishing electrons in their f subshell. All inner transition elements are metals.
(b)
Interpretation:
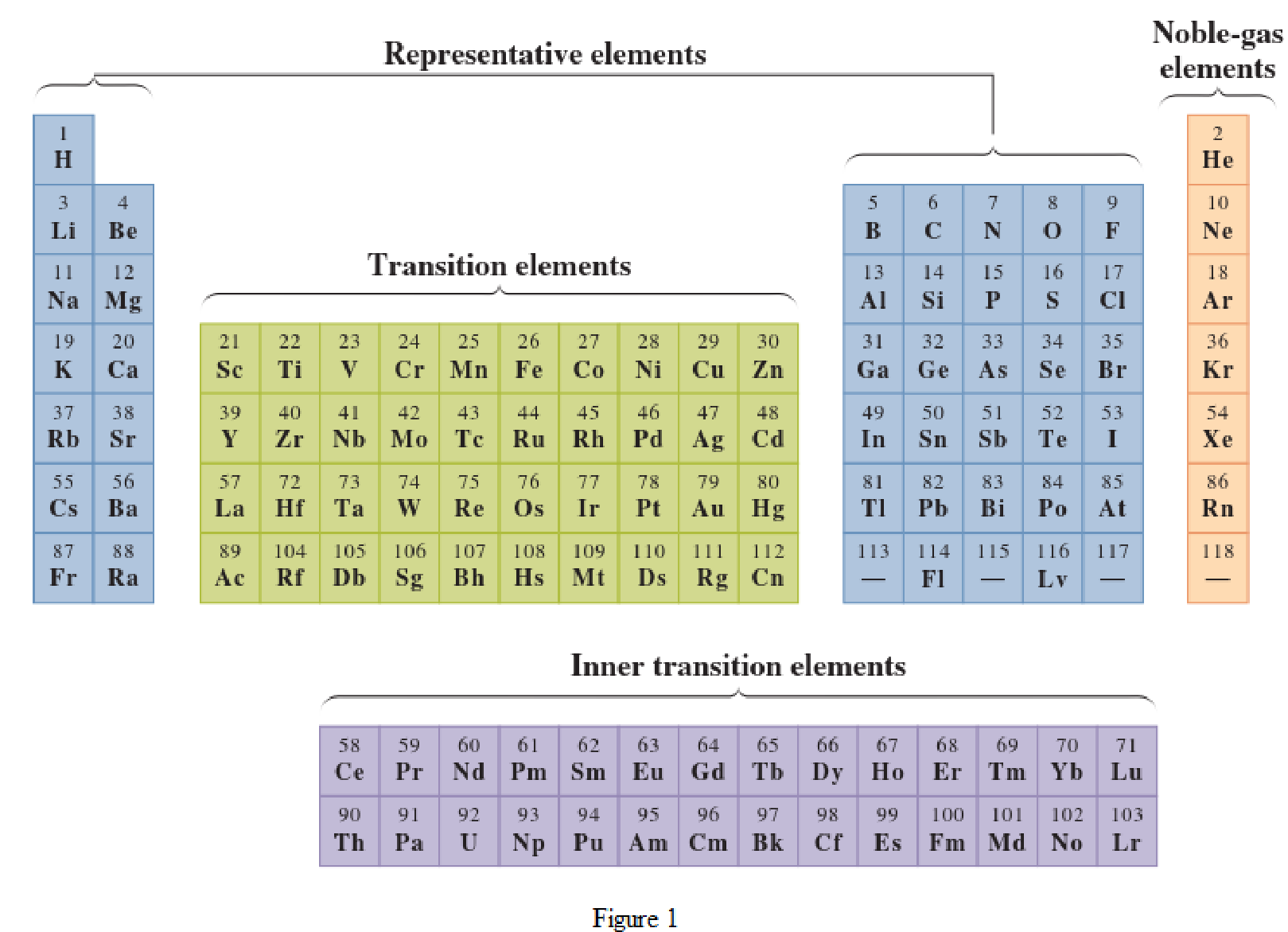
In the given periodic table, how many elements those are highlighted which represent transition have to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Elements in the periodic table are classified in several different ways and out of them two most common systems are,
- System based on the physical properties in which they are classified as metals and nonmetals.
- System based on electronic configuration in which they are classified as noble-gas, representative elements, transition elements, or inner-transition elements.
Noble-gas elements are the ones that are located in far right of periodic table. The physical state of these elements at room temperature is gas. The noble gases have their electronic configuration ending with
Representative elements are the ones that are in s area and area of the periodic table. They have partially filled s subshell or p subshell in their electronic configurations. Some of the elements are nonmetals while others are metals.
Transition elements are the ones that are located in d area of periodic table. They have the distinguishing electrons in their d subshell. All the transition elements are metals.
Inner transition elements are the ones that are located in f area of the periodic table. They have the distinguishing electrons in their f subshell. All inner transition elements are metals.
(c)
Interpretation:
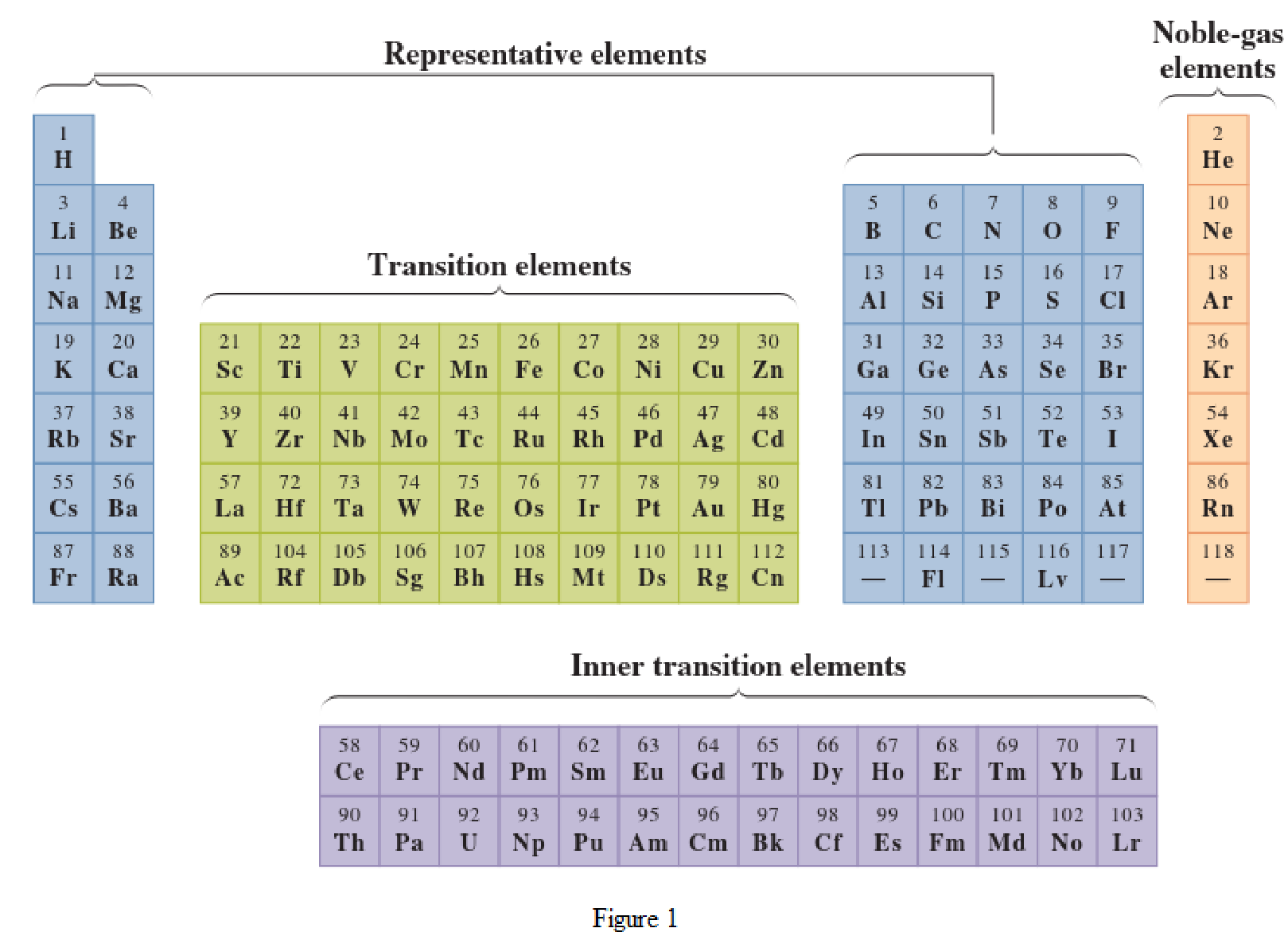
In the given periodic table, how many elements those are highlighted which represent metallic representative elements have to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Elements in the periodic table are classified in several different ways and out of them two most common systems are,
- System based on the physical properties in which they are classified as metals and nonmetals.
- System based on electronic configuration in which they are classified as noble-gas, representative elements, transition elements, or inner-transition elements.
Noble-gas elements are the ones that are located in far right of periodic table. The physical state of these elements at room temperature is gas. The noble gases have their electronic configuration ending with
Representative elements are the ones that are in s area and area of the periodic table. They have partially filled s subshell or p subshell in their electronic configurations. Some of the elements are nonmetals while others are metals.
Transition elements are the ones that are located in d area of periodic table. They have the distinguishing electrons in their d subshell. All the transition elements are metals.
Inner transition elements are the ones that are located in f area of the periodic table. They have the distinguishing electrons in their f subshell. All inner transition elements are metals.
(d)
Interpretation:
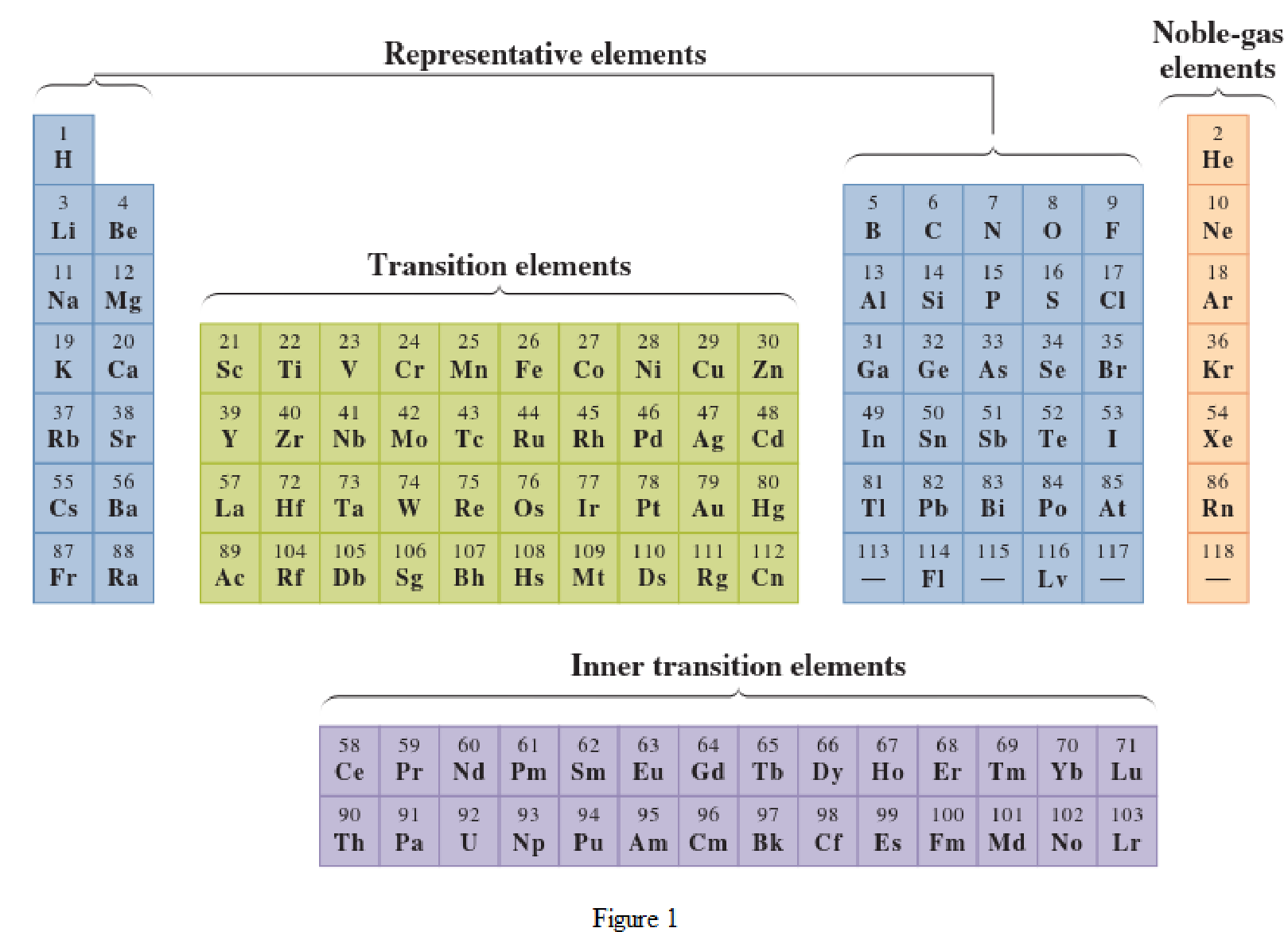
In the given periodic table, how many elements those are highlighted which represent nonmetals have to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Elements in the periodic table are classified in several different ways and out of them two most common systems are,
- System based on the physical properties in which they are classified as metals and nonmetals.
- System based on electronic configuration in which they are classified as noble-gas, representative elements, transition elements, or inner-transition elements.
Noble-gas elements are the ones that are located in far right of periodic table. The physical state of these elements at room temperature is gas. The noble gases have their electronic configuration ending with
Representative elements are the ones that are in s area and area of the periodic table. They have partially filled s subshell or p subshell in their electronic configurations. Some of the elements are nonmetals while others are metals.
Transition elements are the ones that are located in d area of periodic table. They have the distinguishing electrons in their d subshell. All the transition elements are metals.
Inner transition elements are the ones that are located in f area of the periodic table. They have the distinguishing electrons in their f subshell. All inner transition elements are metals.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC,+BIO.CHEM.-MINDTAP
- Give the organic products: (benzyne) Br ? CH3 + K* :NH, liq NH3 HINT: Two products are formed. Each is a substituted aniline; they are isomers of each other. NH2 II I H₂N. CH3 CH3 III Select one: ○ A. I and II ○ B. I and III O C. I and IV O D. II and III O E. III and IV H₂N CH3 IV CH₂-NH2arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: HBr (1 equiv) cold ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of this reaction in the drawing area below. • You can draw the products in any arrangement you like. • Pay careful attention to the reaction conditions, and only include the major products. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • Note that there is only 1 equivalent of HBr reactant, so you need not consider the case of multiple additions. Erase something Explanation Check 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terarrow_forwardQ14. Fill this chart: (please refer to ppt notes/browser to answer these questions) What alcohol is also called wood alcohol? What is the common name of ethanol? Draw the structure of phenol and thiophene? Are bigger chain alcohol like heptanol and octanol are soluble or insoluble in water and explain it ? Are ethers soluble or insoluble in water? What suffix and prefix are used for alcohol while naming alcohol and ether? What the process called when we add water to any alkene to make alcohol? Q16. Draw the diagram of following aromatic compound (practice from previous module) Aniline Phenol Benzoic acid Methyl benzoate Q17. a. Write the oxidation reactions for the 2 propanol. b. Write the oxidation reaction of the ethanol.arrow_forward
- Question 11 of 18 (1 point) Question Attempt: 3 of How many signals do you expect in the 'H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Br Br Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red. Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. 1 For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional Hs to color in top molecule Check For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box…arrow_forwardOrganic Chemistry Esterification reactions 1. Write the steps to prepare ester. 2. Write complete reaction of ethanol and acetic acid to make ester. 3. What does ester smell like? What are the uses of ester. 4. What the role of sulfuric acid in the esterification reactionarrow_forward11. Complete the following esterification reaction with names of all the reactants and products under. Hint: Remove the water and end up with ester R-C-OH + ROH R-C-OR + H₂O A carboxylic acid An alcohol An ester Water BYJU'S H-C-C O-H Нин C-C-C-H HAAA H O-C-C-C-H AAA Ethanoic acid Propanol Water Propyl ethanoate By com CH3COOH + CH3CH2CH2CH₂CH₂OH → Practice for alcohols aldehydes and ketones: 12. Draw the structures from the following names mixed of alcohol/aldehyde and ketone: a. 4-methyl cyclohexanone b. 3-methyl-2-pentenal c. 2,3-dimethylcyclohexanone d. 1,3propanediol or Propane 1,3 diol 13. Write systematic names for the following compounds identify functional group: a. b. (CH3)2CH-C OH c) CH(CH₂)-- OH -,-,arrow_forward
- may you please show all steps! i am having a hard time understanding and applying in this format, thank you!arrow_forward10. Complete the substitution reaction of 2 pentanol with these reagents. Reagents & Reaction Conditions use practice sheet. Please write only major products, minor product like water, other gases are not required. Hint: In substitution of alcohol, we generally substitute OH group with Halogens like cl, Br, F using some reagent containing halogens. Ensure to add halogens to the same carbon number where you are removing OH from Examples Alcohols can be converted to Alkyl Halides with HX acids HBr H₂O HCI + H₂O HI + H₂O CH,CH₂OH + SOCI₂ CH,CH₂OH + PCI₁₂ A BBYJU'S CH CHCI + SO₂+ HCI CH₂CH CIP(OH), + HCI CH,CH₂OH + PCI CHCHCI + POCI + HCI CH,CH₂OH + PBr, CH,CH,Br + P(OH), + HBr 1. Reaction with HBr with 2 Pentanol 2.Reaction with HI with 2 pentanol © Byjus.com 3.Reaction with HCI+ZnCl,, with 2 pentanol (Zncl2 is catalyst no role) 4.Reaction with SOCI,, with 2 Pentanol 5.Reaction with PBr; or PCl, with 2 pentanolarrow_forward3. Is 2-methyl-2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-methyl-2-propanol and also any oxidation products of 2- methyl-2- propanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 4. 2-Propanol is the IUPAC systematic name of this alcohol. It has a common name by which it is much better known (You'll see it in the grocery store or pharmacy). Give that common name 5. Aldehydes can be synthesized by the oxidation of. Please choose from below choices A. Primary alcohols B. Secondary alcohols C. Organic acids D. Inorganic acids 6. Tertiary alcohol Can undergo oxidation. yes or no. ? If yes then answer the product.arrow_forward
- Finish the reactions hand written pleasearrow_forwardPart A Identify each alcohol as primary, secondary, or tertiary Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. CH₂ H₂C- -C-OH HO CH₂ Primary Он OH CH₂ OH CCH₂OH CH₂ сн Secondary Tertiary Reset Help CH,CH₂ (CH)CHCH,OH CH,CH,CH,CCH, CHOH CH₂ Different types of alcohol groups Alcohol and its reaction: 8. Combing two alcohol molecules below and completing the reaction with Product .( Hint Reaction called etherification as ether is formed and name the ether once you complete the reaction. Hint.: R-O-H+H-O-RR-O-R Do the reaction: CH₂OH + CH₂OH---→ + H-O-H 9. Write the reaction of formation of alcohol from alkene by adding water: Addition reaction also called hydration reaction as we are adding water which occur always in presence of acid Hint: Break the double bond and add H and OH if symmetrical then add anywhere if unsymmetrical then follow Markovnikov rule H should go to that double bone carbon which has more hydrogen CH2=CH2 + H₂O-→arrow_forwardComplete the reaction hand written pleasearrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





