
1.
Calculate the regular earnings for the weekly payroll ended December 13, 2019.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the regular earnings for the weekly payroll ended December 13, 2019.
Step 1: Calculate the annual salary of Employee LR, Employee RB and Employee GL.
| Employee | Monthly salary (A) | Annual salary (A×12months) |
| Employee JR | $7,280 per month | $87,360.00 |
| Employee OJ | $5,265 per month | $63,180.00 |
| Employee MK | $3,400 per month | $40,800.00 |
Table (1)
Step 2: Calculate the regular earnings of each employees.
| Employee | Annual salary (A) | Regular Weekly earnings |
| Employee WH | $99,840.00 | $1,920.00 |
| Employee PB | $96,200.00 | $1,850.00 |
| Employee JR | $87,360.00 | $1,680.00 |
| Employee OJ | $63,180.00 | $1,215.00 |
| Employee MK | $40,800.00 | $784.62 |
| Total | $387,380.00 | $7,449.62 |
Table (2)
Thus, the total regular earnings for the weekly payroll ended December 13, 2019 is $7,449.62
2.
Calculate the overtime earnings if any applicable to any employee.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the overtime earnings for Employee GL.
| Employee | Weekly earnings (A) | Regular hourly rate (B) |
Overtime hourly rate (C) |
Overtime earnings (D) |
| Employee MK | $784.62 | $19.62 | $29.42 | $176.54 |
Table (3)
Thus, the overtime earnings for Employee GL is $176.54.
3.
Calculate the total regular, overtime earnings and bonus.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the total regular, overtime earnings and bonus.
| Employee | Regular Weekly earnings | Overtime earnings | Annual bonus | Total earnings |
| Employee WH | $1,920.00 | $0.00 | $35,000 | $36,920.00 |
| Employee PB | $1,850.00 | $0.00 | $25,000 | $26,850.00 |
| Employee JR | $1,680.00 | $0.00 | $20,000 | $21,680.00 |
| Employee OJ | $1,215.00 | $0.00 | $15,000 | $16,215.00 |
| Employee MK | $784.62 | $176.54 | $8,000 | $8,961.16 |
| Total | $7,449.62 | $176.54 | $103,000 | $110,626.16 |
Table (4)
Calculation for total regular, overtime earnings and bonus is as follows.
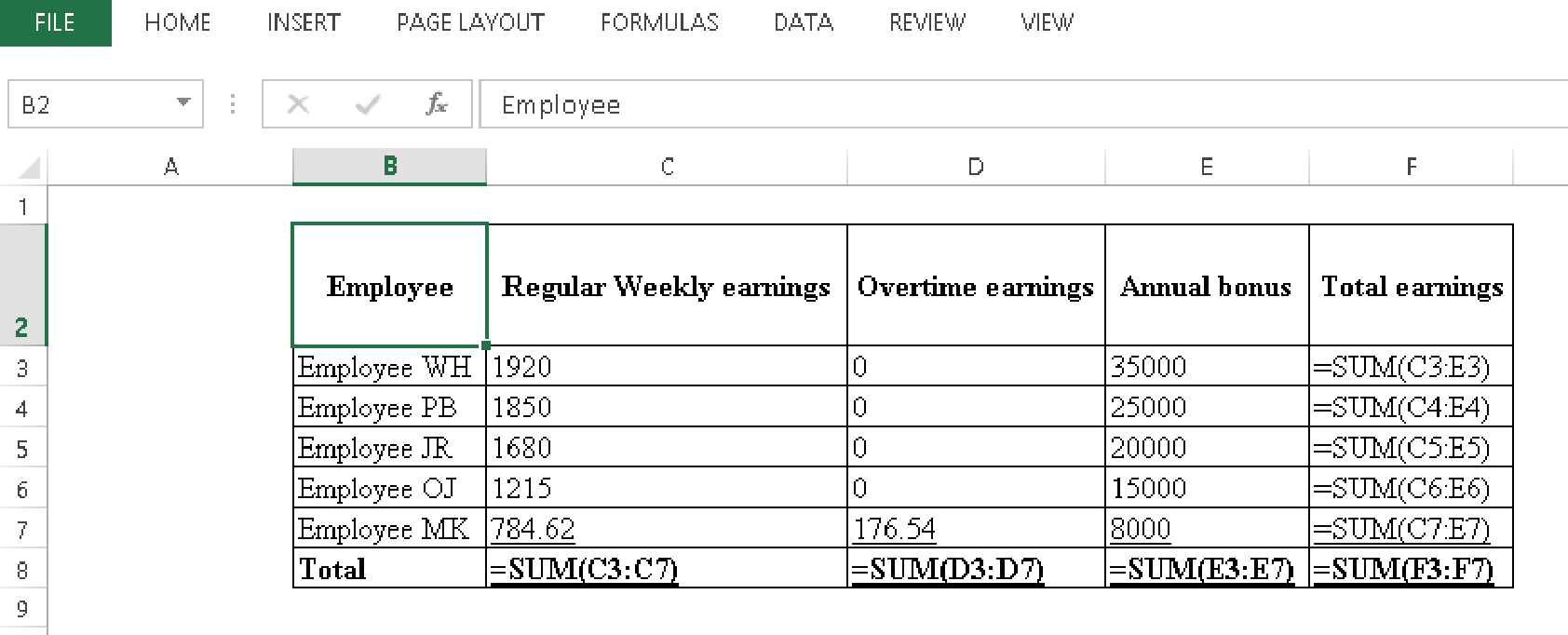
Table (5)
4 and 5.
Calculate the FICA taxable wages for this period and FICA taxes to be withheld for this period.
4 and 5.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the FICA taxable wages for this period and FICA taxes to be withheld for this period.
| Cumulative earnings as of Last Pay Period | FICA Taxable Wages This Pay Period | FICA Taxes to be Withheld | Employees | ||
| OASDI (A) | HI (B) | OASDI | HI | ||
| $94,080.00 | $36,920.00 | $36,920.00 | $2,289.04 | $535.34 | Employee WH |
| $90,650.00 | $26,850.00 | $26,850.00 | $1,664.70 | $389.33 | Employee PB |
| $82,332.00 | $21,680.00 | $21,680.00 | $1,344.16 | $314.36 | Employee JR |
| $59,535.00 | $16,215.00 | $16,215.00 | $1,005.33 | $235.12 | Employee OJ |
| $38,446.38 | $8,961.16 | $8,961.16 | $555.59 | $129.94 | Employee MK |
| $110,626.16 | $110,626.16 | $6,858.82 | $1,604.08 | Totals | |
Table (6)
Step 3: Calculate the employer’s portion of the FICA taxes for the week ended.
Calculate the OASDI taxes.
Calculate the HI taxes.
Calculate the total FICA taxes.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Cengagenowv2, 1 Term Printed Access Card For Bieg/toland's Payroll Accounting 2019, 29th

 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning





