
An Introduction to Physical Science
14th Edition
ISBN: 9781305079120
Author: James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher: Brooks Cole
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 16SA
Two masses are attached to a spring scale as shown in ● Fig. 3.25. If both masses are 1 kg, which force, in newtons, would the scale read? (Hint: Think of holding a free end of the rope on one side of the scale with only the weight on the other.)
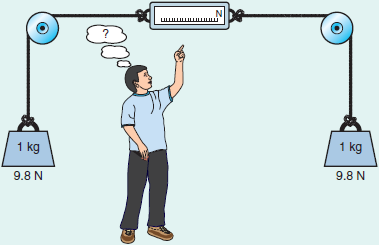
Figure 3.25 What Does the Scale Read? See Short Answer 16.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solution
how would i express force in vector form I keep getting a single number
please help me solve this questions. show all calculations and a good graph too :)
Chapter 3 Solutions
An Introduction to Physical Science
Ch. 3.1 - Does a force always produce motion?Ch. 3.1 - What is the condition for motion when more than...Ch. 3.2 - If you were moving with a constant velocity in...Ch. 3.2 - How can the inertias of objects be compared?Ch. 3.3 - How are force and motion related?Ch. 3.3 - Which is generally greater, static friction or...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 3.1CECh. 3.3 - On the surface of Mars, the acceleration due to...Ch. 3.4 - Whats the difference between an action and a...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 2PQ
Ch. 3.5 - What keeps the Moon in orbit around the Earth?Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 2PQCh. 3.5 - Prob. 3.3CECh. 3.6 - Prob. 1PQCh. 3.6 - Prob. 2PQCh. 3.7 - When is the linear momentum of a system conserved?Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 2PQCh. 3.7 - Suppose you were not given the values of the...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 3.5CECh. 3 - KEY TERMS 1. force (3.1) 2. unbalanced, or net,...Ch. 3 - KEY TERMS 1. force (3.1) 2. unbalanced, or net,...Ch. 3 - KEY TERMS 1. force (3.1) 2. unbalanced, or net,...Ch. 3 - KEY TERMS 1. force (3.1) 2. unbalanced, or net,...Ch. 3 - KEY TERMS 1. force (3.1) 2. unbalanced, or net,...Ch. 3 - Prob. FMCh. 3 - Prob. GMCh. 3 - Prob. HMCh. 3 - Prob. IMCh. 3 - Prob. JMCh. 3 - Prob. KMCh. 3 - Prob. LMCh. 3 - Prob. MMCh. 3 - KEY TERMS 1. force (3.1) 2. unbalanced, or net,...Ch. 3 - KEY TERMS 1. force (3.1) 2. unbalanced, or net,...Ch. 3 - Prob. PMCh. 3 - Prob. QMCh. 3 - KEY TERMS 1. force (3.1) 2. unbalanced, or net,...Ch. 3 - Prob. SMCh. 3 - A net force ___. (3.1) (a) can produce motion (b)...Ch. 3 - What is a possible state of an object in the...Ch. 3 - What term refers to the tendency of an object to...Ch. 3 - A net force can produce ___. (3.3) (a) an...Ch. 3 - According to Newtons second law of motion, when an...Ch. 3 - Mass is related to an objects ___. (3.3) (a)...Ch. 3 - Prob. 7MCCh. 3 - Which is true of the force pair of Newtons third...Ch. 3 - Which is true about the acceleration due to...Ch. 3 - What is true about the constant G? (3.5) (a) It is...Ch. 3 - A childs toy floats in a swimming pool. The...Ch. 3 - If a submerged object displaces an amount of...Ch. 3 - If a submerged object displaces a volume of liquid...Ch. 3 - A change in linear momentum requires which of the...Ch. 3 - Angular momentum is conserved in the absence of...Ch. 3 - A force is a quantity that is ___ of producing...Ch. 3 - Forces are ___ quantities. (3.1)Ch. 3 - Prob. 3FIBCh. 3 - Prob. 4FIBCh. 3 - The inertia of an object is related to its ___....Ch. 3 - Prob. 6FIBCh. 3 - Prob. 7FIBCh. 3 - Prob. 8FIBCh. 3 - Prob. 9FIBCh. 3 - Prob. 10FIBCh. 3 - Prob. 11FIBCh. 3 - Milk is ___ dense than the cream that floats on...Ch. 3 - The total linear momentum is not conserved if...Ch. 3 - Prob. 14FIBCh. 3 - Prob. 1SACh. 3 - Prob. 2SACh. 3 - Consider a child holding a helium balloon in a...Ch. 3 - An old party trick is to pull a tablecloth out...Ch. 3 - Prob. 5SACh. 3 - When a paper towel is torn from a roll on a rack,...Ch. 3 - It is said that Newtons first law can be derived...Ch. 3 - Can an object be at rest if forces are being...Ch. 3 - Prob. 9SACh. 3 - What is the unbalanced force acting on a moving...Ch. 3 - The coefficient of kinetic friction is generally...Ch. 3 - A 10-lb rock and a 1-lb rock are dropped...Ch. 3 - When a rocket blasts off, is it the fiery exhaust...Ch. 3 - There is an equal and opposite reaction for every...Ch. 3 - When a person pushes on a wall, the wall pushes on...Ch. 3 - Two masses are attached to a spring scale as shown...Ch. 3 - Prob. 17SACh. 3 - The gravitational force is said to have an...Ch. 3 - Explain why the acceleration due to gravity on the...Ch. 3 - An astronaut has a mass of 70 kg when measured on...Ch. 3 - Prob. 21SACh. 3 - In Chapter 1.6 in the discussion of the...Ch. 3 - What is a major consideration in constructing a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 24SACh. 3 - Prob. 25SACh. 3 - Is it easier for a large person to float in a lake...Ch. 3 - Prob. 27SACh. 3 - Prob. 28SACh. 3 - Explain how the conservation of linear momentum...Ch. 3 - Prob. 30SACh. 3 - When a high diver in a swimming event springs from...Ch. 3 - Visualize the connections for the descriptions of...Ch. 3 - Astronauts walking on the Moon are seen bounding...Ch. 3 - A person places a bathroom scale in the center of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3AYKCh. 3 - Prob. 4AYKCh. 3 - In a washing machine, water is extracted from...Ch. 3 - When you push on a heavy swinging door to go into...Ch. 3 - When unable to loosen the lug nut on an automobile...Ch. 3 - What is the net force of a 5.0-N force and an...Ch. 3 - A horizontal force of 250 N is applied to a...Ch. 3 - Determine the net force necessary to give an...Ch. 3 - A force of 2.1 N is exerted on a 7.0-g rifle...Ch. 3 - A 1000-kg automobile is pulled by a horizontal tow...Ch. 3 - A 6.0-N net force is applied to a 15-kg object....Ch. 3 - What is the weight in newtons of a 6.0-kg package...Ch. 3 - What is the force in newtons acting on a 4.0-kg...Ch. 3 - (a) What is the weight in newtons of a 120-lb...Ch. 3 - A 75-kg person is standing on a scale in an...Ch. 3 - Two 3.0-kg physical science textbooks on a...Ch. 3 - (a) What is the force of gravity between two...Ch. 3 - How would the force of gravity between two masses...Ch. 3 - The separation distance between two 1.0-kg masses...Ch. 3 - (a) Determine the weight on the Moon of a person...Ch. 3 - Suppose an astronaut has landed on Mars. Fully...Ch. 3 - A childs cubic play block has a mass of 120 g and...Ch. 3 - A ball with a radius of 8.00 cm and a mass of 600...Ch. 3 - Calculate the linear momentum of a pickup truck...Ch. 3 - A small car with a mass of 900 kg travels...Ch. 3 - Two ice skaters stand together as illustrated in ...Ch. 3 - For the couple in Fig. 3.28, suppose you were told...Ch. 3 - A comet goes around the Sun in an elliptical...Ch. 3 - Taking the density of air to be 1.29 kg/m3, what...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the force (in N) on the 2.0 μC charge placed at the center of the square shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) 5.0 με 4.0 με 2.0 με + 1.0 m 1.0 m -40 με 2.0 μCarrow_forwardWhat is the force (in N) on the 5.4 µC charge shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) −3.1 µC5.4 µC9.2 µC6.4 µCarrow_forwardAn ideal gas in a sealed container starts out at a pressure of 8900 N/m2 and a volume of 5.7 m3. If the gas expands to a volume of 6.3 m3 while the pressure is held constant (still at 8900 N/m2), how much work is done by the gas? Give your answer as the number of Joules.arrow_forward
- The outside temperature is 25 °C. A heat engine operates in the environment (Tc = 25 °C) at 50% efficiency. How hot does it need to get the high temperature up to in Celsius?arrow_forwardGas is compressed in a cylinder creating 31 Joules of work on the gas during the isothermal process. How much heat flows from the gas into the cylinder in Joules?arrow_forwardThe heat engine gives 1100 Joules of energy of high temperature from the burning gasoline by exhausting 750 Joules to low-temperature . What is the efficiency of this heat engine in a percentage?arrow_forward
- L₁ D₁ L₂ D2 Aluminum has a resistivity of p = 2.65 × 10 8 2. m. An aluminum wire is L = 2.00 m long and has a circular cross section that is not constant. The diameter of the wire is D₁ = 0.17 mm for a length of L₁ = 0.500 m and a diameter of D2 = 0.24 mm for the rest of the length. a) What is the resistance of this wire? R = Hint A potential difference of AV = 1.40 V is applied across the wire. b) What is the magnitude of the current density in the thin part of the wire? Hint J1 = c) What is the magnitude of the current density in the thick part of the wire? J₂ = d) What is the magnitude of the electric field in the thin part of the wire? E1 = Hint e) What is the magnitude of the electric field in the thick part of the wire? E2 =arrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardA cheetah spots a gazelle in the distance and begins to sprint from rest, accelerating uniformly at a rate of 8.00 m/s^2 for 5 seconds. After 5 seconds, the cheetah sees that the gazelle has escaped to safety, so it begins to decelerate uniformly at 6.00 m/s^2 until it comes to a stop.arrow_forward
- A projectile is fired with an initial speed of 40.2 m/s at an angle of 35.0 degree above the horizontal on a long flat firing range. Determine. please help and show work for them so i can understand.arrow_forwardpls helparrow_forwardJ K L The graph in the figure shows the position of an object as a function of time. The letters H-L represent particular moments of time. At which moments shown (H, I, etc.) is the speed of the object the greatest? + Position H I K Timearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)
Physics
ISBN:9781337399920
Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's First Law of Motion: Mass and Inertia; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1XSyyjcEHo0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY