
Principles of Corporate Finance (Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259144387
Author: Richard A Brealey, Stewart C Myers, Franklin Allen
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 12PS
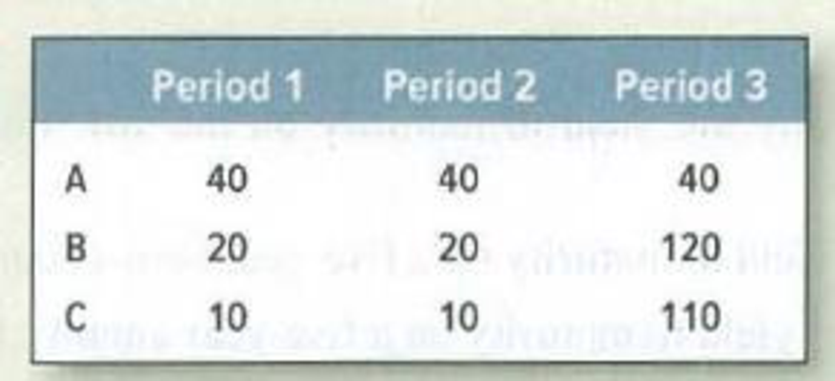
Duration Calculate the durations and volatilities of securities A, B, and C. Their cash flows are shown below. The interest rate is 8%.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Write as like research paper: abstrac,litut review,model.current problem
questionire,table,graph, charts, image, analysis, result,conclusion, referencce15-20
1. Provide literature as research paper" liturature review" content as journal
2. article,textbooks.current newspaper article.organizational doccument and
website **citation as liturature citation reference 15-20 in liturature review
content paragraph.
2. Show latest problem of current knowledge ang give a **model immage, and display
show awareness of that problem and questionire.
3. Current that research methodology.show graph.table.chrts.assesment task
4. Design and Result,5. Conclution, 6. Referance 15-20
TASK DESCRIPTION
Children
educatio
Spouse's
willingn allowanc
travel
Spouseoverseas
job
assistanc
Host
country
housing
assistanc
Income
tax
equalisati
on policy
Overseas
health
care plan
Length of
the
foreign
assignme dareer
and
repatriati
Cross-
Personali
cultural
compete
Prior
ncies internati
Receptivity
to
Internation
al…
Write in memo format a response to your Manager, based on the information presented below for the Duncan Company and also based on your additional research. Your Manager has advised you to make any assumptions where necessary.
Duncan Company is a large manufacturer and distributor of cake supplies. It is based in United Kingdon (Headquarters) It sends supplies to firms throughout the United States and the Caribbean . It markets its supplies through periodic mass mailings of catalogues to those firms. Its clients can make orders over the phone and Duncan ships the supplies upon demand. The main competition for Duncan’s comes from one U.S. firm and one Canadian firm. Another British firm has a small share of the U.S. market but is at a disadvantage because of its distance. The British firm’s marketing and transportation costs in the U.S. market are relatively high. a) Duncan Company plans to penetrate either the Canadian market or two other Caribbean Countries (Jamaica and Haiti). What…
Answer of the question in the picture
Chapter 3 Solutions
Principles of Corporate Finance (Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
Ch. 3 - (PRICE) In February 2009, Treasury 8.5s of 2020...Ch. 3 - (YLD) On the same day, Treasury 3.5s of 2018 were...Ch. 3 - (DURATION) What was the duration of the Treasury...Ch. 3 - (MDURATION) What was the modified duration of the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 1PSCh. 3 - Bond prices and yields The following statements...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3PSCh. 3 - Bond prices and yields A 10-year German government...Ch. 3 - Bond prices and yields Construct some simple...Ch. 3 - Spot interest rates and yields Which comes first...
Ch. 3 - Prob. 7PSCh. 3 - Spot interest rates and yields Assume annual...Ch. 3 - Prob. 9PSCh. 3 - Prob. 10PSCh. 3 - Duration True or false? Explain. a....Ch. 3 - Duration Calculate the durations and volatilities...Ch. 3 - Term-structure theories The one-year spot interest...Ch. 3 - Real interest rates The two-year interest rate is...Ch. 3 - Duration Here are the prices of three bonds with...Ch. 3 - Prob. 16PSCh. 3 - Prob. 17PSCh. 3 - Spot interest rates and yields A 6% six-year bond...Ch. 3 - Spot interest rates and yields Is the yield on...Ch. 3 - Prob. 20PSCh. 3 - Prob. 21PSCh. 3 - Duration Find the spreadsheet for Table 3.4 in...Ch. 3 - Prob. 23PSCh. 3 - Prob. 25PSCh. 3 - Prob. 26PSCh. 3 - Prob. 27PSCh. 3 - Prob. 28PSCh. 3 - Prob. 29PSCh. 3 - Prices and yields If a bonds yield to maturity...Ch. 3 - Prob. 31PSCh. 3 - Price and spot interest rates Find the arbitrage...Ch. 3 - Prob. 33PSCh. 3 - Prices and spot interest rates What spot interest...Ch. 3 - Prices and spot interest rates Look one more time...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A sporting goods manufacturer has decided to expand into a related business. Management estimates that to build and staff a facility of the desired size and to attain capacity operations would cost $450 million in present value terms. Alternatively, the company could acquire an existing firm or division with the desired capacity. One such opportunity is a division of another company. The book value of the division’s assets is $250 million and its earnings before interest and tax are presently $50 million. Publicly traded comparable companies are selling in a narrow range around 12 times current earnings. These companies have book value debt-to-asset ratios averaging 40 percent with an average interest rate of 10 percent. a. Using a tax rate of 34 percent, estimate the minimum price the owner of the division should consider for its sale. b. What is the maximum price the acquirer should be willing to pay? c. Does it appear that an acquisition is feasible? Why or why not? d. Would a 25…arrow_forwardLarry Davis borrows $80,000 at 14 percent interest toward the purchase of a home. His mortgage is for 25 years. a. How much will his annual payments be? (Although home payments are usually on a monthly basis, we shall do our analysis on an annual basis for ease of computation. We will get a reasonably accurate answer.) b. How much interest will he pay over the life of the loan? c. How much should be willing to pay to get out of a 14 percent mortgage and into a 10 percent mortgage with 25 years remaining on the mortgage? Assume current interest rates are 10 percent. Carefully consider the time value of money. Disregard taxes.arrow_forwardYou are chairperson of the investment fund for the local closet. You are asked to set up a fund of semiannual payments to be compounded semiannually to accumulate a sum of $250,000 after nine years at a 10 percent annual rate (18 payments). The first payment into the fund is to take place six months from today, and the last payment is to take place at the end of the ninth year. Determine how much the semiannual payment should be. (a) On the day, after the sixth payment is made (the beginning of the fourth year), the interest rate goes up to a 12 percent annual rate, and you can earn a 12 percent annual rate on funds that have been accumulated as well as all future payments into the funds. Interest is to be compounded semiannually on all funds. Determine how much the revised semiannual payments should be after this rate change (there are 12 payments and compounding dates). The next payment will be in the middle of the fourth year.arrow_forward
- If your Uncle borrows $60,000 from the bank at 10 percent interest over the seven-year life of the loan, what equal annual payments must be made to discharge the loan, plus pay the bank its required rate of interest? How much of his first payment will be applied to interest? To principal? How much of his second payment will be applied to each?arrow_forwardQ1: You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually.What is NEWER’s stock price?The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8.The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually.What is OLDER’s stock price?Now assume that both stocks have a required…arrow_forwardQ1: Blossom is 30 years old. She plans on retiring in 25 years, at the age of 55. She believes she will live until she is 105. In order to live comfortably, she needs a substantial retirement income. She wants to receive a weekly income of $5,000 during retirement. The payments will be made at the beginning of each week during her retirement. Also, Blossom has pledged to make an annual donation to her favorite charity during her retirement. The payments will be made at the end of each year. There will be a total of 50 annual payments to the charity. The first annual payment will be for $20,000. Blossom wants the annual payments to increase by 3% per year. The payments will end when she dies. In addition, she would like to establish a scholarship at Toronto Metropolitan University. The first payment would be $80,000 and would be made 3 years after she retires. Thereafter, the scholarship payments will be made every year. She wants the payments to continue after her death, therefore…arrow_forward
- Q1: Blossom is 30 years old. She plans on retiring in 25 years, at the age of 55. She believes she will live until she is 105. In order to live comfortably, she needs a substantial retirement income. She wants to receive a weekly income of $5,000 during retirement. The payments will be made at the beginning of each week during her retirement. Also, Blossom has pledged to make an annual donation to her favorite charity during her retirement. The payments will be made at the end of each year. There will be a total of 50 annual payments to the charity. The first annual payment will be for $20,000. Blossom wants the annual payments to increase by 3% per year. The payments will end when she dies. In addition, she would like to establish a scholarship at Toronto Metropolitan University. The first payment would be $80,000 and would be made 3 years after she retires. Thereafter, the scholarship payments will be made every year. She wants the payments to continue after her death, therefore…arrow_forwardJerome Moore invests in a stock that will pay dividends of $2.00 at the end of the first year; $2.20 at the end of the second year; and $2.40 at the end of the third year. also, he believes that at the end of the third year he will be able to sell the stock for $33. what is the present value of all future benefits if a discount rate of 11 percent is applied?arrow_forwardQ1: You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually.What is NEWER’s stock price?The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8.The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually.What is OLDER’s stock price?Now assume that both stocks have a required…arrow_forward
- Q1: You are an analyst in charge of valuing common stocks. You have been asked to value two stocks. The first stock NEWER Inc. just paid a dividend of $6.00. The dividend is expected to increase by 60%, 45%, 30% and 15% per year, respectively, in the next four years. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 4% per year in perpetuity. Calculate NEWER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.The required rate of return for NEWER stock is 14% compounded annually.What is NEWER’s stock price?The second stock is OLDER Inc. OLDER Inc. will pay its first dividend of $10.00 three (3) years from today. The dividend will increase by 30% per year for the following four (4) years after its first dividend payment. Thereafter, the dividend will increase by 3% per year in perpetuity. Calculate OLDER’s expected dividend for t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8.The required rate of return for OLDER stock is 16% compounded annually.What is OLDER’s stock price?Now assume that both stocks have a required…arrow_forwardQ1: Blossom is 30 years old. She plans on retiring in 25 years, at the age of 55. She believes she will live until she is 105. In order to live comfortably, she needs a substantial retirement income. She wants to receive a weekly income of $5,000 during retirement. The payments will be made at the beginning of each week during her retirement. Also, Blossom has pledged to make an annual donation to her favorite charity during her retirement. The payments will be made at the end of each year. There will be a total of 50 annual payments to the charity. The first annual payment will be for $20,000. Blossom wants the annual payments to increase by 3% per year. The payments will end when she dies. In addition, she would like to establish a scholarship at Toronto Metropolitan University. The first payment would be $80,000 and would be made 3 years after she retires. Thereafter, the scholarship payments will be made every year. She wants the payments to continue after her death, therefore…arrow_forwardTrue and False 1. There are no more than two separate phases to decision making and problem solving. 2. Every manager always has complete control over all inputs and factors. 3. Opportunity cost is only considered by accountants as a way to calculate profits 4. Standard error is always used to evaluate the overall strength of the regression model 5. The t-Stat is used in a similar way as the P-valued is used 6. The P-value is used as R-square is used. 7. R-square is used to evaluate the overall strength of the model. 8. Defining the problem is one of the last things that a manager considers Interpreting Regression Printouts (very brief answers) R² = .859 Intercept T N = 51 Coefficients 13.9 F= 306.5 Standard Error .139 SER=.1036 t Stat P value 99.8 0 .275 .0157 17.5 0 The above table examines the relationship between the nunber, of poor central city households in the U.S. and changes in the costs of college tuition from 1967 to 2019. 9. What is the direction of this relationship? 10.…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Liquidity Risk (FRM Part 2 – Book 4 – Chapter 1); Author: AnalystPrep;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TguAvyxM6vg;License: Standard Youtube License