
PHY F/SCIENTIST MOD MASTERING 24 MO
17th Edition
ISBN: 9780137319497
Author: Knight
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 29, Problem 71EAP
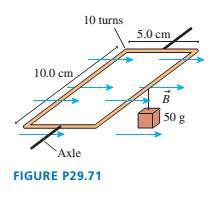
The 10-turn loop of wire shown in FIGURE P29.71 lies in a horizontal plane, parallel to a uniform horizontal magnetic field, and carries a 2.0 A current. The loop is free to rotate about a nonmagnetic axle through the center. A 50 g mass hangs from one edge of the loop. What magnetic field strength will prevent the loop from rotating about the axle?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A player kicks a football at the start of the game. After a 4 second flight, the ball touches the ground 50 m from the kicking tee. Assume air resistance is negligible and the take-off and landing height are the same (i.e., time to peak = time to fall = ½ total flight time). (Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.) Calculate and answer all parts. Only use equations PROVIDED:
A shot putter releases a shot at 13 m/s at an angle of 42 degrees to the horizontal and from a height of 1.83 m above the ground. (Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.) Calculate and answer all parts. Only use equations PROVIDED:
If a person jumps upwards with a vertical velocity of 5 m/s, What is their velocity 0.5 second into the jump?
Chapter 29 Solutions
PHY F/SCIENTIST MOD MASTERING 24 MO
Ch. 29 - The lightweight glass sphere in FIGURE Q29.1 hangs...Ch. 29 - The metal sphere in FIGURE Q29.2 hangs by a...Ch. 29 - Prob. 3CQCh. 29 - Prob. 4CQCh. 29 - What is the current direction in the wire of...Ch. 29 - What is the initial direction of deflection for...Ch. 29 - What is the initial direction of deflection for...Ch. 29 - Determine the magnetic field direction that causes...Ch. 29 - Determine the magnetic field direction that causes...Ch. 29 - Prob. 10CQ
Ch. 29 - The south pole of a bar magnet is brought toward...Ch. 29 - Prob. 12CQCh. 29 - Prob. 1EAPCh. 29 - Prob. 2EAPCh. 29 - 3. A proton moves along the x-axis with rn/s. As...Ch. 29 - An electron moves along the z-axis with vz=2.0107...Ch. 29 - What is the magnetic field at the position of the...Ch. 29 - What is the magnetic field at the position of the...Ch. 29 - Prob. 7EAPCh. 29 - Prob. 8EAPCh. 29 - Prob. 9EAPCh. 29 - A biophysics experiment uses a very sensitive...Ch. 29 - The magnetic field at the center of a 1.0...Ch. 29 - 12. What are the magnetic fields at points a to c...Ch. 29 - Prob. 13EAPCh. 29 - What are the magnetic field strength and direction...Ch. 29 - Prob. 15EAPCh. 29 - 16. The on-axis magnetic field strength cm from...Ch. 29 - A A current circulates around a -mm-diameter...Ch. 29 - 18. A small, square loop carries a A current. The...Ch. 29 - Prob. 19EAPCh. 29 - 20. What is the line integral of integral points...Ch. 29 - 21. What is the line integral of between points i...Ch. 29 - The value of the line integral of around the...Ch. 29 - 23. The value of the line integral of around the...Ch. 29 - 24. What is the line integral of between points i...Ch. 29 - Prob. 25EAPCh. 29 - 26. A proton moves in the magnetic field with a...Ch. 29 - Prob. 27EAPCh. 29 - 28. Radio astronomers detect electromagnetic...Ch. 29 - Prob. 29EAPCh. 29 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 29 - The microwaves in a microwave oven are produced in...Ch. 29 - The Hall voltage across a conductor in a 55mT...Ch. 29 - 33. What magnetic field strength and direction...Ch. 29 - 34. The two -cm-long parallel wires in FIGURE...Ch. 29 - The right edge of the circuit in FIGURE EX29.35...Ch. 29 - Prob. 36EAPCh. 29 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 29 - 38. A square current loop cm on each side carries...Ch. 29 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 29 - 40. a. What is the magnitude of the torque on the...Ch. 29 - A long wire carrying a 5.0A current perpendicular...Ch. 29 - Prob. 42EAPCh. 29 - What are the strength and direction of the...Ch. 29 - At what distance on the axis of a current loop is...Ch. 29 - 45. Find an expression for the magnetic field...Ch. 29 - Prob. 46EAPCh. 29 - Prob. 47EAPCh. 29 - 48. A -m-long, -mm-diameter aluminum wire has a...Ch. 29 - Prob. 49EAPCh. 29 - Prob. 50EAPCh. 29 - Prob. 51EAPCh. 29 - Weak magnetic fields can be measured at the...Ch. 29 - The heart produces a weak magnetic field that can...Ch. 29 - Prob. 54EAPCh. 29 - 55. The toroid of FIGURE P29.55 is a coil of wire...Ch. 29 - 56. The coaxial cable shown in FIGURE P29.56...Ch. 29 - 57. A long, hollow wire has inner radius and...Ch. 29 - 58. A proton moving in a uniform magnetic field...Ch. 29 - 59. An electron travels with speed m/s between...Ch. 29 - Prob. 60EAPCh. 29 - An antiproton (same properties as a proton except...Ch. 29 - a. A 65 -cm-diameter cyclotron uses a 500 V...Ch. 29 - An antiproton is identical to a proton except it...Ch. 29 - Prob. 64EAPCh. 29 - Prob. 65EAPCh. 29 - Particle accelerators, such as the Large Hadron...Ch. 29 - 67. A particle of charge q and mass m moves in the...Ch. 29 - 68. A Hall-effect probe to measure magnetic field...Ch. 29 - Prob. 69EAPCh. 29 - Prob. 70EAPCh. 29 - The 10-turn loop of wire shown in FIGURE P29.71...Ch. 29 - The two springs in FIGURE P29.72 each have a...Ch. 29 - Prob. 73EAPCh. 29 - Prob. 74EAPCh. 29 - A conducting bar of length I and mass m rests at...Ch. 29 - Prob. 76EAPCh. 29 - A wire along the x-axis carries current I in the...Ch. 29 - Prob. 78EAPCh. 29 - Prob. 79EAPCh. 29 - a. Derive an expression for the magnetic field...Ch. 29 - Prob. 81EAPCh. 29 - A long, straight conducting wire of radius R has a...Ch. 29 - Prob. 83EAP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A solid sphere 22 cm in radius carries 17 μC, distributed uniformly throughout its volume. Part A Find the electric field strength 12 cm from the sphere's center. Express your answer using two significant figures. E₁ = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ха Хь b Submit Previous Answers Request Answer <☑ × Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining ▾ Part B ? |X| X.10" <☑ Find the electric field strength 22 cm from the sphere's center. Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ E2 = Submit Request Answer ▾ Part C ? MN/C Find the electric field strength 44 cm from the sphere's center. Express your answer using two significant figures. ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ E3 = Submit Request Answer ? MN/C MN/Carrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardIn a naval battle, a battleship is attempting to fire on a destroyer. The battleship is a distance d1 = 2,150 m to the east of the peak of a mountain on an island, as shown in the figure below. The destroyer is attempting to evade cannon shells fired from the battleship by hiding on the west side of the island. The initial speed of the shells that the battleship fires is vi = 245 m/s. The peak of the mountain is h = 1,840 m above sea level, and the western shore of the island is a horizontal distance d2 = 250 m from the peak. What are the distances (in m), as measured from the western shore of the island, at which the destroyer will be safe from fire from the battleship? (Note the figure is not to scale. You may assume that the height and width of the destroyer are small compared to d1 and h.)arrow_forward
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardThe law of reflection applies to Question 14Select one: a. specular reflection b. irregular reflection c. All of these d. diffuse reflectionarrow_forwardAccording to your book "normal" human body temperature is considered to be ________? Select one: a. none of these b. 98.6°C c. 37°C d. 100°Carrow_forward
- Problem Seven. A football receiver running straight downfield at 5.60 m/s is 11.5 m in front of the quarterback when a pass is thrown downfield at an angle of 35.0° above the horizon. 8.) If the receiver never changes speed and the ball is caught at the same height from which it was thrown, find the distance between the quarterback and the receiver when the catch is made. (A) 21.3 (B) 17.8 (C) 18.8 (D) 19.9 (E) 67.5arrow_forwardWhen two bar magnets are near each other, the north pole of one of the magnets experiences what type of force from the other magnet? 1. both an attractive force and a repulsive force 2. a Coulomb force 3. only an attractive force 4. only a repulsive forcearrow_forwardWhat can be said about the electric force between two charged particles? It varies as 1/r. It depends only on the magnitudes of the charges. It is much, much greater than the attractive gravitational force. It is repulsive for unlike charges.arrow_forward
- A piece of copper originally 305mm long is pulled in tension with a stress of 276MPa. If the deformation is elastic, what will be the resultant elongation. E for copper is 110Gpaarrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the problem correctly please. Be sure to give explanations on each step and write neatly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardIn the figures, the masses are hung from an elevator ceiling. Assume the velocity of the elevator is constant. Find the tensions in the ropes (in N) for each case. Note that 0₁ = 35.0°, 0₂ = 55.0°, 03 = 60.0°, m₁ = 3.00 kg, and m2 = 7.00 kg. (Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values-including answers submitted in WebAssign-in your calculations.) (a) Τι WY NY MY T3 e₁ T₁ = N = N = N (b) 18 Τι = Τι T3 = || || || = T T Ts m₂ N N N 02 T₂ T3 m₁arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Magnets and Magnetic Fields; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IgtIdttfGVw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY