
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780100257061
Author: BEER
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2.9, Problem 61P
A standard tension test is used to determine the properties of an experimental plastic. The test specimen is a
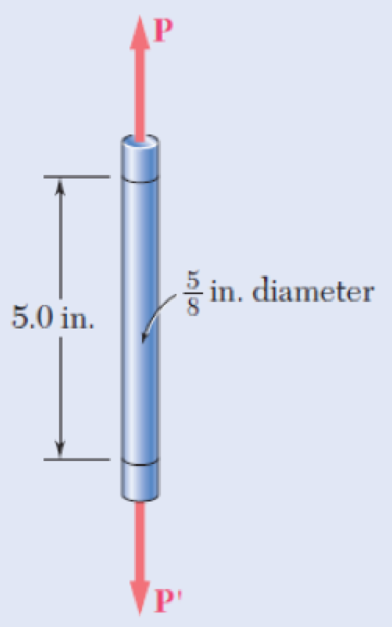
Fig. P2.61
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The gears shown in the figure have a diametral pitch of 2 teeth per inch and a 20° pressure angle.
The pinion rotates at 1800 rev/min clockwise and transmits 200 hp through the idler pair to gear
5 on shaft c. What forces do gears 3 and 4 transmit to the idler shaft?
TS
I
y
18T
32T
This
a
12
x
18T
C
48T
5
Question 1. Draw 3 teeth for the following pinion and gear respectively. The teeth
should be drawn near the pressure line so that the teeth from the pinion should
mesh those of the gear. Drawing scale (1:1). Either a precise hand drawing or
CAD drawing is acceptable. Draw all the trajectories of the involute lines and the
circles.
Specification: 18tooth pinion and 30tooth gear. Diameter pitch=P=6 teeth /inch.
Pressure angle:20°, 1/P for addendum (a) and 1.25/P for dedendum (b). For fillet,
c=b-a.
5. The figure shows a gear train. There is no friction at the bearings except for the gear tooth forces.
The material of the milled gears is steel having a Brinell hardness of 170. The input shaft speed (n2)
is 800 rpm. The face width and the contact angle for all gears are 1 in and 20° respectively. In this
gear set, the endurance limit (Se) is 15 kpsi and nd (design factor) is 2.
(a) Find the revolution speed of gear 5.
(b) Determine whether each gear satisfies the design factor of 2.0 for bending fatigue.
(c) Determine whether each gear satisfies the design factor of 2.0 for surface fatigue (contact stress).
(d) According to the computation results of the questions (b) and (c), explain the possible failure
mechanisms for each gear.
N4=28
800rpm
N₁=43
N5=34
N₂=14
P(diameteral pitch)=8 for all gears
Coupled to 2.5hp motor
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 2.1 - A nylon thread is subjected to a 8.5-N tension...Ch. 2.1 - A 4.8-ft-long steel wire of 14 -in.-diameter is...Ch. 2.1 - An 18-m-long steel wire of 5-mm diameter is to be...Ch. 2.1 - Two gage marks are placed exactly 250 mm apart on...Ch. 2.1 - An aluminum pipe must not stretch more than 0.05...Ch. 2.1 - A control rod made of yellow brass must not...Ch. 2.1 - A steel control rod is 5.5 ft long and must not...Ch. 2.1 - A cast-iron tube is used to support a compressive...Ch. 2.1 - A 4-m-long steel rod must not stretch more than 3...Ch. 2.1 - A nylon thread is to be subjected to a 10-N...
Ch. 2.1 - A block of 10-in. length and 1.8 1.6-in. cross...Ch. 2.1 - A square yellow-brass bar must not stretch more...Ch. 2.1 - Rod BD is made of steel (E = 29 106 psi) and is...Ch. 2.1 - The 4-mm-diameter cable BC is made of a steel with...Ch. 2.1 - A single axial load of magnitude P = 15 kips is...Ch. 2.1 - A 250-mm-long aluminum tube (E = 70 GPa) of 36-mm...Ch. 2.1 - The specimen shown has been cut from a...Ch. 2.1 - The brass tube AB (E = 105 GPa) has a...Ch. 2.1 - Both portions of the rod ABC are made of an...Ch. 2.1 - The rod ABC is made of an aluminum for which E =...Ch. 2.1 - For the steel truss (E = 200 GPa) and loading...Ch. 2.1 - For the steel truss (E = 29 106 psi) and loading...Ch. 2.1 - Members AB and BC are made of steel (E = 29 106...Ch. 2.1 - The steel frame (E = 200 GPa) shown has a diagonal...Ch. 2.1 - Link BD is made of brass (E = 105 GPa) and has a...Ch. 2.1 - Members ABC and DEF are joined with steel links (E...Ch. 2.1 - Each of the links AB and CD is made of aluminum (E...Ch. 2.1 - The length of the 332-in.-diameter steel wire CD...Ch. 2.1 - A homogenous cable of length L and uniform cross...Ch. 2.1 - The vertical load P is applied at the center A of...Ch. 2.1 - Denoting by the "engineering strain'' in a...Ch. 2.1 - The volume of a tensile specimen is essentially...Ch. 2.3 - An axial centric force of magnitude P = 450 kN is...Ch. 2.3 - An axial centric force of magnitude P = 450 kN is...Ch. 2.3 - The 4.5-ft concrete post is reinforced with six...Ch. 2.3 - The 4.5-ft concrete post is reinforced with six...Ch. 2.3 - An axial force of 200 kW is applied to the...Ch. 2.3 - The length of the assembly shown decreases by 0.40...Ch. 2.3 - A polystyrene rod consisting of two cylindrical...Ch. 2.3 - Three steel rods (E = 29 106 psi) support an...Ch. 2.3 - Fig. P2.41 2.41 Two cylindrical rods, one of steel...Ch. 2.3 - Solve Prob. 2.41, assuming that rod AC is made of...Ch. 2.3 - Each of the rods BD and CE is made of brass (E =...Ch. 2.3 - The rigid bar AD is supported by two steel wires...Ch. 2.3 - The rigid bar ABC is suspended from three wines of...Ch. 2.3 - The rigid bar AD is supported by two steel wires...Ch. 2.3 - The aluminum shell is fully bonded to the brass...Ch. 2.3 - The aluminum shell is fully bonded to the brass...Ch. 2.3 - The brass shell (b = 11.6 10-6/F) is fully bonded...Ch. 2.3 - The concrete post (Ec = 3.6 106) psi and c = 5.5 ...Ch. 2.3 - A rod consisting of two cylindrical portions AB...Ch. 2.3 - A rod consisting of two cylindrical portions AB...Ch. 2.3 - Fig. P2.52 2.52 A rod consisting of two...Ch. 2.3 - The steel rails of a railroad (rack (Es = 200GPa,...Ch. 2.3 - Two steel bars (Es = 200 GPa and s = 11.7 10-6/C)...Ch. 2.3 - Determine the maximum load P that can be applied...Ch. 2.3 - An aluminum rod (Ea = 70 GPa, a = 23.6 10-6/C)...Ch. 2.3 - Knowing that a 0.02-in. gap exists when the...Ch. 2.3 - Determine (a) the compressive force in the bars...Ch. 2.3 - At room temperature (20C) a 0.5-mm gap exists...Ch. 2.9 - A standard tension test is used to determine the...Ch. 2.9 - A 2-m length of an aluminum pipe of 240-nun outer...Ch. 2.9 - A line of slope 4:10 has been scribed on a...Ch. 2.9 - A 2.75-kN tensile load is applied to a test coupon...Ch. 2.9 - Fig. P2.65 2.65 In a standard tensile test a steel...Ch. 2.9 - The change in diameter of a large steel bolt is...Ch. 2.9 - The brass rod AD is fitted with a jacket that is...Ch. 2.9 - A fabric used in air-inflated structures is...Ch. 2.9 - A 1-in. square was scribed on the side of a large...Ch. 2.9 - The block shown is made of a magnesium alloy for...Ch. 2.9 - The homogeneous plate ABCD is subjected to a...Ch. 2.9 - For a member under axial loading, express the...Ch. 2.9 - In many situations it is known that the normal...Ch. 2.9 - In many situations physical constraints prevent...Ch. 2.9 - The plastic block shown is bonded to a rigid...Ch. 2.9 - The plastic block shown is bonded to a rigid...Ch. 2.9 - Two blocks of rubber with a modulus of rigidity G...Ch. 2.9 - Fig. P2.77 and P2.78 2.78 Two blocks of rubber...Ch. 2.9 - An elastomeric bearing (G = 130 psi) is used to...Ch. 2.9 - 2.80 For the elastomeric bearing In Prob. 2.79...Ch. 2.9 - A vibration isolation unit consists of two blocks...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 82PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 83PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 84PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 85PCh. 2.9 - A 2.75-kN tensile load is applied to a test coupon...Ch. 2.9 - A vibration isolation support consists of a rod A...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 88PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 89PCh. 2.9 - Show that for any given material, the ratio G/E of...Ch. 2.9 - Prob. 91PCh. 2.9 - Prob. 92PCh. 2.13 - Knowing that, for the plate shown, the allowable...Ch. 2.13 - Knowing that P = 38 kN, determine the maximum...Ch. 2.13 - A hole is to be drilled in the plate at A. The...Ch. 2.13 - Fig. P2.95 and P2.96 2.96 (a) For P = 13 kips and...Ch. 2.13 - 2.97 Knowing that the hole has a diameter of 9 mm,...Ch. 2.13 - For P = 100 kN, determine the minimum plate...Ch. 2.13 - Prob. 99PCh. 2.13 - A centric axial force is applied to the steel bar...Ch. 2.13 - The cylindrical rod AB has a length L = 5 ft and a...Ch. 2.13 - Fig. P2.101 and P.102 2.102 The cylindrical rod AB...Ch. 2.13 - Rod AB is made of a mild steel that is assumed to...Ch. 2.13 - Prob. 104PCh. 2.13 - Rod ABC consists of two cylindrical portions and...Ch. 2.13 - Prob. 106PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 107PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 108PCh. 2.13 - Each cable has a cross-sectional area of 100 mm2...Ch. 2.13 - Prob. 110PCh. 2.13 - Two tempered-steel bars, each 316 in. thick, are...Ch. 2.13 - Prob. 112PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 113PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 114PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 115PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 116PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 117PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 118PCh. 2.13 - Prob. 119PCh. 2.13 - For the composite bar in Prob. 2.111, determine...Ch. 2.13 - Prob. 121PCh. 2.13 - Bar AB has a cross-sectional area of 1200 mm2 and...Ch. 2.13 - Bar AB has a cross-sectional area of 1200 mm2 and...Ch. 2 - The uniform wire ABC, of unstretched length 2l, is...Ch. 2 - The aluminum rod ABC (E = 10.1 106 psi), which...Ch. 2 - Two solid cylindrical rods are joined at B and...Ch. 2 - Prob. 127RPCh. 2 - Prob. 128RPCh. 2 - Prob. 129RPCh. 2 - A 4-ft concrete post is reinforced with four steel...Ch. 2 - The steel rods BE and CD each have a 16-mm...Ch. 2 - Prob. 132RPCh. 2 - Prob. 133RPCh. 2 - The aluminum test specimen shown is subjected to...Ch. 2 - Prob. 135RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. The rotating steel shaft is simply supported by bearings at points of B and C, and is driven by a spur gear at D, which has a 6-in pitch diameter. The force F from the drive gear acts at a pressure angle of 20°. The shaft transmits a torque to point A of TA =3000 lbĘ in. The shaft is machined from steel with Sy=60kpsi and Sut=80 kpsi. (1) Draw a shear force diagram and a bending moment diagram by F. According to your analysis, where is the point of interest to evaluate the safety factor among A, B, C, and D? Describe the reason. (Hint: To find F, the torque Tд is generated by the tangential force of F (i.e. Ftangential-Fcos20°) When n=2.5, K=1.8, and K₁ =1.3, determine the diameter of the shaft based on (2) static analysis using DE theory (note that fatigue stress concentration factors need to be used for this question because the loading condition is fatigue) and (3) a fatigue analysis using modified Goodman. Note) A standard diameter is not required for the questions. 10 in Darrow_forward3 N2=28 P(diametral pitch)=8 for all gears Coupled to 25 hp motor N3=34 Full depth spur gears with pressure angle=20° N₂=2000 rpm (1) Compute the circular pitch, the center-to-center distance, and base circle radii. (2) Draw the free body diagram of gear 3 and show all the forces and the torque. (3) In mounting gears, the center-to-center distance was reduced by 0.1 inch. Calculate the new values of center-to-center distance, pressure angle, base circle radii, and pitch circle diameters. (4)What is the new tangential and radial forces for gear 3? (5) Under the new center to center distance, is the contact ratio (mc) increasing or decreasing?arrow_forward2. A flat belt drive consists of two 4-ft diameter cast-iron pulleys spaced 16 ft apart. A power of 60 hp is transmitted by a pulley whose speed is 380 rev/min. Use a service factor (Ks) pf 1.1 and a design factor 1.0. The width of the polyamide A-3 belt is 6 in. Use CD=1. Answer the following questions. (1) What is the total length of the belt according to the given geometry? (2) Find the centrifugal force (Fc) applied to the belt. (3) What is the transmitted torque through the pulley system given 60hp? (4) Using the allowable tension, find the force (F₁) on the tight side. What is the tension at the loose side (F2) and the initial tension (F.)? (5) Using the forces, estimate the developed friction coefficient (f) (6) Based on the forces and the given rotational speed, rate the pulley set. In other words, what is the horse power that can be transmitted by the pulley system? (7) To reduce the applied tension on the tight side, the friction coefficient is increased to 0.75. Find out the…arrow_forward
- The tooth numbers for the gear train illustrated are N₂ = 24, N3 = 18, №4 = 30, №6 = 36, and N₁ = 54. Gear 7 is fixed. If shaft b is turned through 5 revolutions, how many turns will shaft a make? a 5 [6] barrow_forwardCE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answerarrow_forwardCE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answerarrow_forward
- CE-112 solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answer pleasearrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Relationship Between Elastic Constants and Connecting Equations; Author: Engineers Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=whW5PnM7Pug;License: Standard Youtube License