
Concept explainers
Draw the organic products formed in each reaction.
a.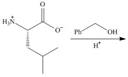 d.
d. 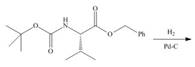
b.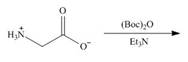 e.
e. 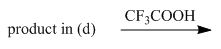
c. f.
f. 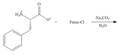
(a)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: An ester is formed by the reaction of carboxylic with alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. This reaction is known as Fischer Esterification.
Answer to Problem 29.60P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
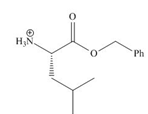
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, the oxygen of carboxyl group takes a proton from an acid. The carbon of carbonyl carbon acts as an electrophile where the attacking of oxygen of alcohol takes place and gives 1, 2-addition. The transfer of proton takes place leads to the elimination of water molecule. In the final step, deprotonation takes place. The corresponding reaction is shown below.
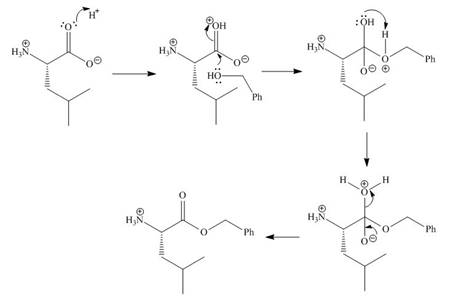
Figure 1
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Treatment of amine with t-butoxypyrocarbonate in the presence of triethyl amine yields t-butoxy carbonyl group.
Answer to Problem 29.60P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
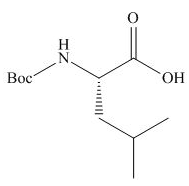
Explanation of Solution
The full form of
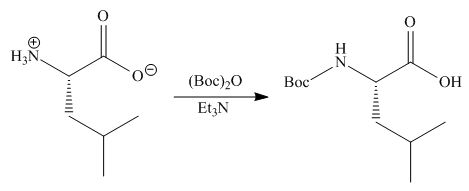
Figure 2
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
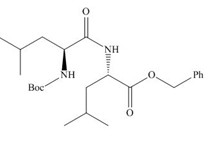
(c)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The full form of DCC is dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. It is a dehydrating agent which is used to synthesized amides, nitriles and ketones.
Answer to Problem 29.60P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
As amine are basic in nature and they have tendency to convert carboxylic acid to carboxylate. In the given reaction, carboxylic acid adds to the DCC and forms a good leaving group which displaces by amine in nucleophilic substitution reaction. DCC forms an amide linkage. The corresponding reaction is shown below.
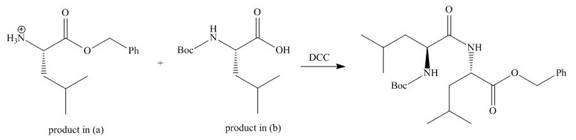
Figure 3
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 29.60P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, the reactant undergoes catalytic reduction in the presence of
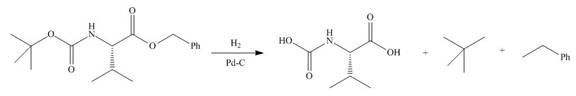
Figure 4
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 4.
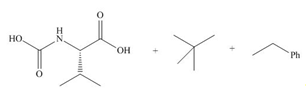
(e)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The halogenated derivative of acetic acid is TFA. The full form of TFA is trifluoroacetic acid. It is used to break the ester bond in peptide synthesis.
Answer to Problem 29.60P
The organic products formed in given reaction are,
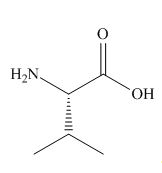
Explanation of Solution
Treatment of given compound with trifluoroacetic acid cleaves the bond
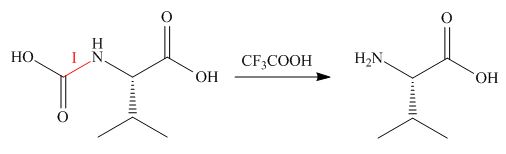
Figure 5
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The organic products formed in given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The full form of Fmoc-Cl is fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl chloride. The molecular formula of Fmoc-Cl is
Answer to Problem 29.60P
The organic product formed in given reaction is,
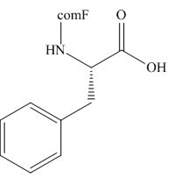
Explanation of Solution
The Fmoc-Cl introduces a group i.e. comF which protects the amine group towards action of sodium carbonate. In the given reaction, treatment of given compound with sodium carbonate in the presence of Fmoc-Cl forms a product with comF group as shown below.
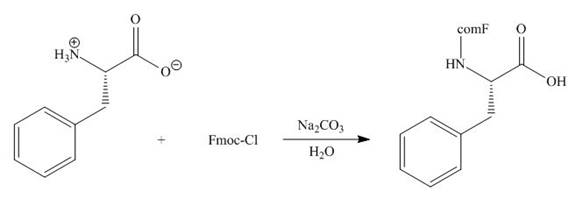
Figure 6
The organic product formed in given reaction is shown in Figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 29 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- Write all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forwardHow can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

