
To Label: The muscular artery wall in Fig 29.2.
Introduction: The circulatory system is the vital system in the human body and it is composed of heart, blood vessels, and capillaries. The main function of the circulatory system to provide all the organs and tissues with oxygen and nutrients, and help in the removal of
Answer to Problem 1.2BGL
Pictorial representation:
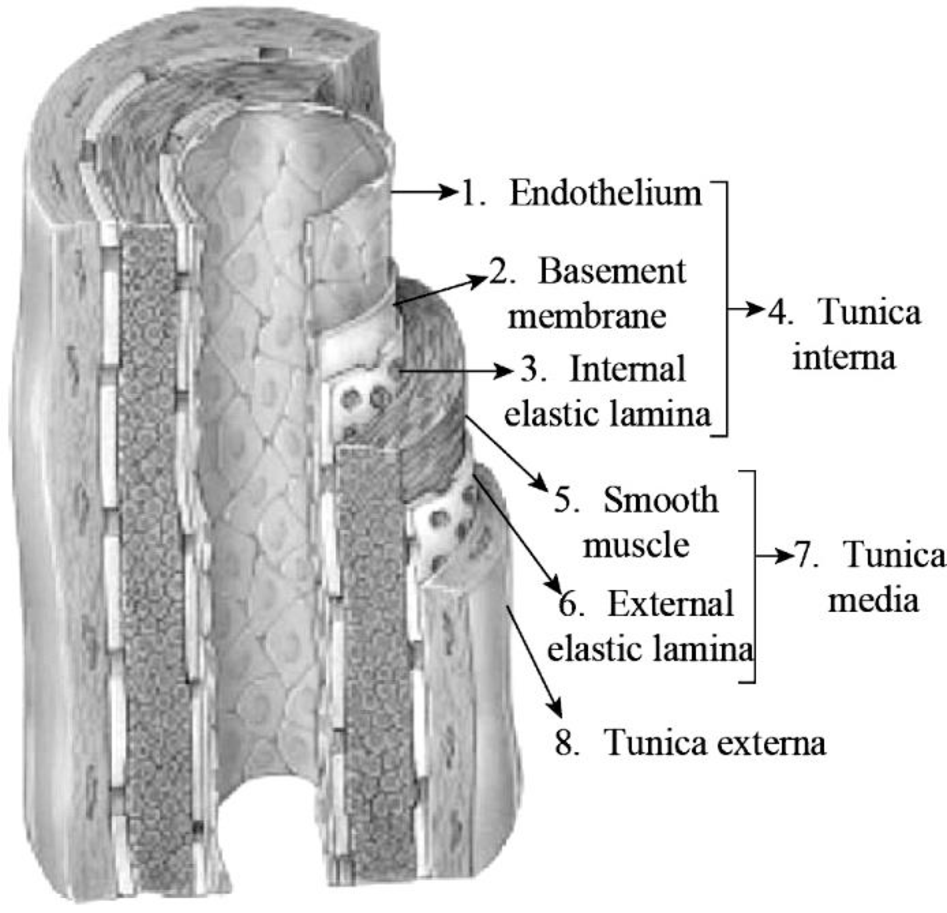
Fig 1: Muscular structure of artery wall
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the muscular arteries is composed of the following:
Tunica interna: The tunica interna or intima is the innermost layer of the arteries which is composed of simple squamous epithelium and inter elastic lamina that provide elasticity to the arteries. The lumen of the arteries is lined up by the endothelium cell that is smooth and helps in smooth blood flow. If there is any damage to the arteries, the endothelium helps the platelets to bind to the walls of the arteries and form plaques to reduce the blood flow, as the arterial blood pressure is high which may cause excessive blood loss.
Tunica media: The tunica media is the middle layer of the arterial wall and it is the thickest of the tunics. The tunica media is composed of elastic fibers and smooth muscle fibers that regulate the flow of blood by vasodilation and vasoconstriction. The elastic fibers help the artery to retain its original structure after vasodilation and vasoconstriction of the smooth muscle fibers.
Tunica externa: The tunica externa is the outermost layer of the arteries and composed of collagen fibers and elastic fibers. The collagen fibers are the connective tissue which provides the blood vessel with support and protection, while the elastic fibers provide with flexibility and elasticity to constrict, dilate, and to retain its original structure.
Basement membrane: The tunica interna is composed of simple squamous endothelium. The tunica interna is the supported basement membrane which is made up of extracellular matrix that gives structural stability to the endothelium cells of the tunica interna.
External elastic lamina: The external elastic lamina is found between the tunica externa and tunia media. The external elastic lamina is composed of elastic fibers and collagen. The external elastic lamina provides the tunica media with elasticity to vasoconstrict and vasodilate.
Internal elastic lamina: The internal elastic lamina is found between the tunica media and tunia interna. The internal elastic lamina is composed of elastic fibers and collagen. The internal elastic lamina provides the tunica media and tunica interna with elasticity to vasoconstrict and vasodilate.
Smooth muscle: The smooth muscle is present in the tunica media of the arteries, which is the thickest of the three layers of the tunics. The smooth muscle helps in the vasocontrict and vasodilate of the arteries to maintain blood flow.
Endothelium: The endothelium is present in the tunica interna of the arteries, which is composed of simple squamous epithelial cells. The lumen of the arteries is lined up by the endothelium cell that is smooth and helps in smooth blood flow.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 29 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e WileyPLUS (next generation) + Loose-leaf
- Identify the indicated tissue. (Tilia stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma xylem phloem none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure. (Cucurbita stem l.s.) pit lenticel stomate tendril none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the specific cell? (Zebrina leaf peel) vessel element sieve element companion cell tracheid guard cell subsidiary cell none of thesearrow_forward
- What type of cells flank the opening on either side? (leaf x.s.) vessel elements sieve elements companion cells tracheids guard cells none of thesearrow_forwardWhat specific cell is indicated. (Cucurbita stem I.s.) vessel element sieve element O companion cell tracheid guard cell none of thesearrow_forwardWhat specific cell is indicated? (Aristolochia stem x.s.) vessel element sieve element ○ companion cell O O O O O tracheid O guard cell none of thesearrow_forward
- Identify the tissue. parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma ○ xylem O phloem O none of thesearrow_forwardPlease answer q3arrow_forwardRespond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: How might CRISPR-Cas 9 be used in research or, eventually, therapeutically in patients? What are some potential ethical issues associated with using this technology? Do the advantages of using this technology outweigh the disadvantages (or vice versa)? Explain your position.arrow_forward
- You are studying the effect of directional selection on body height in three populations (graphs a, b, and c below). (a) What is the selection differential? Show your calculation. (2 pts) (b) Which population has the highest narrow sense heritability for height? Explain your answer. (2 pts) (c) If you examined the offspring in the next generation in each population, which population would have the highest mean height? Why? (2 pts) (a) Midoffspring height (average height of offspring) Short Short Short Short (c) Short (b) Short Tall Short Tall Short Short Tall Midparent height (average height of Mean of population = 65 inches Mean of breading parents = 70 inches Mean of population = 65 inches Mean of breading parents = 70 inches Mean of population = 65 inches Mean of breading parents = 70 inchesarrow_forwardP You are studying a population of 100 flowers that has two alleles at a locus for flower color, blue (B) and green (G). There are 15 individuals with the BB genotype, 70 individuals with the BG genotype, and 15 individuals with the GG genotype. (a) What are the allele frequencies of B and G in the starting population? Show your calculations. (2 pts) (b) Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? Show your calculations. (3 pts) 12pt v Paragraph BIU UA AV & VT2V f CO Varrow_forwardIn a natural population of outbreeding plants, the variance of the total number of seeds per plant is 16. From the natural population, 20 plants are taken into the laboratory and developed into separate true-breeding lines by self- fertilization-with selection for high, low, or medium number of seeds-for 10 generations. The average variance in the tenth generation in each of the 20 sets is about equal and averages 5.8 across all the sets. Estimate the broad-sense heritability for seed number in this population. (4 pts) 12pt v Paragraph BIUA V V T² v B ① O wordsarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





