
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation:
List anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the given amino acids.
AAU
Concept introduction:
The main function of messenger RNA (mRNA) is to give the direction to biosynthesis of thousands of diverse peptides and proteins required by organisms. The mechanics of protein biosynthesis take place on ribosomes, small granular particles in the cytoplasm of a cell that consist of 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% protein.
The specific sequence of mRNA forms a message which determines the sequences of amino acid residues which are to be joined known as “codon”. Each “word” or codon consist of three ribonucleotides that is specific for a given amino acid. The message embedded in mRNA is read by transfer RNA (tRNA) in a process called translation.
Codon assignments of base triplets are given below:
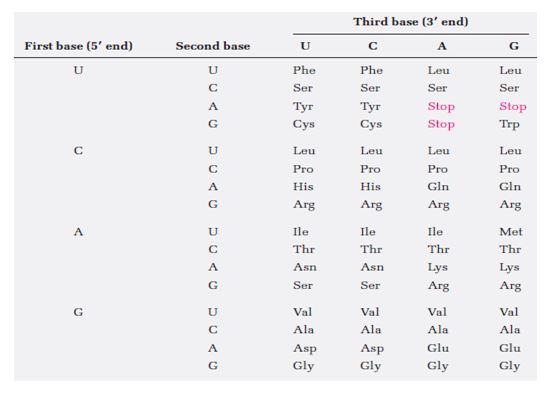
Note: The bounded amino acid sequence is always written from 5’→3’ direction. The codon sequences on mRNA are read by tRNA which are having complementary anticodon base.
Answer to Problem 28AP
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
AAU
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-AAU-(3’) | (5’)-AUU-(3’) |
Explanation of Solution
As the anticodon sequence on tRNAs are the complement of the mRNAs, therefore, we will just replace A by U, G by C, U by A and C by G. The number of sequence of anticodon will remain same as that of the codons.
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
AAU
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-AAU-(3’) | (5’)-AUU-(3’) |
b)
Interpretation:
List anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the given amino acids.
GAG
Concept introduction:
The main function of messenger RNA (mRNA) is to give the direction to biosynthesis of thousands of diverse peptides and proteins required by organisms. The mechanics of protein biosynthesis take place on ribosomes, small granular particles in the cytoplasm of a cell that consist of 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% protein.
The specific sequence of mRNA forms a message which determines the sequences of amino acid residues which are to be joined known as “codon”. Each “word” or codon consist of three ribonucleotides that is specific for a given amino acid. The message embedded in mRNA is read by transfer RNA (tRNA) in a process called translation.
Codon assignments of base triplets are given below:

Note: The bounded amino acid sequence is always written from 5’→3’ direction. The codon sequences on mRNA are read by tRNA which are having complementary anticodon base.
Answer to Problem 28AP
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
GAG
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-GAG-(3’) | (5’)-CUC-(3’) |
Explanation of Solution
As the anticodon sequence on tRNAs are the complement of the mRNAs, therefore, we will just replace A by U, G by C, U by A and C by G. The number of sequence of anticodon will remain same as that of the codons.
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
GAG
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-GAG-(3’) | (5’)-CUC-(3’) |
c)
Interpretation:
List anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the given amino acids.
UCC
Concept introduction:
The main function of messenger RNA (mRNA) is to give the direction to biosynthesis of thousands of diverse peptides and proteins required by organisms. The mechanics of protein biosynthesis take place on ribosomes, small granular particles in the cytoplasm of a cell that consist of 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% protein.
The specific sequence of mRNA forms a message which determines the sequences of amino acid residues which are to be joined known as “codon”. Each “word” or codon consist of three ribonucleotides that is specific for a given amino acid. The message embedded in mRNA is read by transfer RNA (tRNA) in a process called translation.
Codon assignments of base triplets are given below:

Note: The bounded amino acid sequence is always written from 5’→3’ direction. The codon sequences on mRNA are read by tRNA which are having complementary anticodon base.
Answer to Problem 28AP
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
UCC
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-UCC-(3’) | (5’)-GGA-(3’) |
Explanation of Solution
As the anticodon sequence on tRNAs are the complement of the mRNAs, therefore, we will just replace A by U, G by C, U by A and C by G. The number of sequence of anticodon will remain same as that of the codons.
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
UCC
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-UCC-(3’) | (5’)-GGA-(3’) |
d)
Interpretation:
List anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the given amino acids.
CAU
Concept introduction:
The main function of messenger RNA (mRNA) is to give the direction to biosynthesis of thousands of diverse peptides and proteins required by organisms. The mechanics of protein biosynthesis take place on ribosomes, small granular particles in the cytoplasm of a cell that consist of 60% ribosomal RNA and 40% protein.
The specific sequence of mRNA forms a message which determines the sequences of amino acid residues which are to be joined known as “codon”. Each “word” or codon consist of three ribonucleotides that is specific for a given amino acid. The message embedded in mRNA is read by transfer RNA (tRNA) in a process called translation.
Codon assignments of base triplets are given below:

Note: The bounded amino acid sequence is always written from 5’→3’ direction. The codon sequences on mRNA are read by tRNA which are having complementary anticodon base.
Answer to Problem 28AP
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
CAU
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-CAU-(3’) | (5’)-AUG-(3’) |
Explanation of Solution
As the anticodon sequence on tRNAs are the complement of the mRNAs, therefore, we will just replace A by U, G by C, U by A and C by G. The number of sequence of anticodon will remain same as that of the codons.
The anticodon sequence on the tRNAs of the amino acids are given below:
Note: As in the previous question (80485-28-27AP), the codon sequences formed are the mRNAs and hence the complement of mRNAs will give rise tRNAs.
CAU
| Codon Sequence (mRNA) | Anticodon Sequence (tRNA) |
| (5’)-CAU-(3’) | (5’)-AUG-(3’) |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Bundle: Organic Chemistry, 9th, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- When anisole is treated with excess bromine, the reaction gives a product which shows two singlets in 1H NMR. Draw the product.arrow_forward(ii) Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction: CI NaOH heat OH (hint: SNAr Reaction) :arrow_forwardDraw the major product in each of the following reaction:arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the following Friedel-Craft reaction. AlBr3 Brarrow_forward(a) Draw the structures of A and B in the following reaction. (i) NaNH2, NH3(1) A + B (ii) H3O+arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Consider the following decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 → NO2 + NO3 (K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: d[N2O5] = -k₁[N₂O₂] + K¸₁[NO₂][NO3] - K¸[NO₂]³ dtarrow_forwardIn a reaction of A + B to give C, another compound other than A, B or C may appear in the kinetic equation.arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Given the reaction R + Q → P, indicate the rate law with respect to R, with respect to P and with respect to P.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardk₁ Given the reaction A B, indicate k-1 d[A] (A). the rate law with respect to A: (B). the rate law with respect to B: d[B] dt dtarrow_forward

 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





