
Concept explainers
(a)
The energy difference between the first excited state and the ground state.
(a)
Answer to Problem 64P
The energy difference is
Explanation of Solution
The length of the box is
Write the expression for energy of the quantized level.
Here,
Write the expression for energy of the quantized level in terms of the ground state energy.
Here,
Substituting
Here,
Write the expression for energy difference between the first excited state and the ground state.
Here,
Substituting (III) in (IV)
Substituting (I) in (V)
Substituting
Thus, the energy difference is
(b)
The wavelength and frequency of the emitted photon.
(b)
Answer to Problem 64P
The wavelength of the emitted photon is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the energy of a photon.
Here,
Rearranging (I)
Write the expression for frequency.
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the wavelength of the photon is
Substitute
Thus, the wavelength of the photon is
This wavelength and frequency corresponds to the gamma ray of the electromagnetic spectrum.
(c)
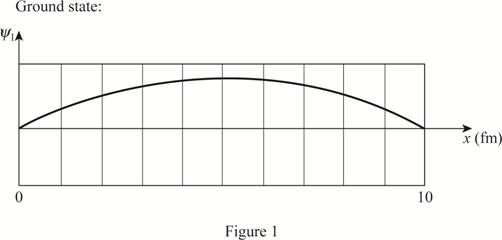
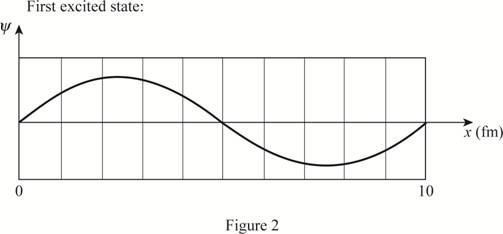
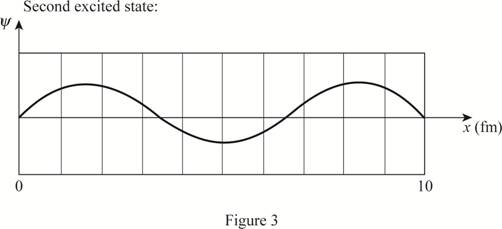
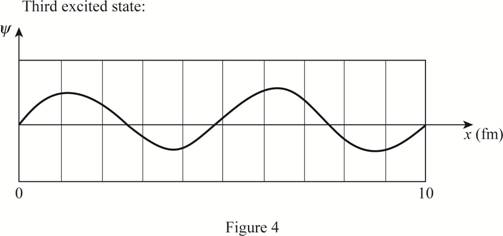
The plot of the wave function of the electron in the ground state and first three excited states.
(c)
Answer to Problem 64P
The wave function is a sine wave.
Explanation of Solution
The length of the box is
Write the expression for the wave function of a particle in a box.
Here,
Substitute
The plot of the wave function versus position is given below:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Physics
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardwhy did the expert subtract the force exerted by the hand and the elbow by the force due to the weight of the hand and forearm and force exerted by the tricep. Does the order matter and how do you determine what to put first. Question 4 AP, CHAPTER 13 FROM BASIC BIOMECHANICS 8TH EDITIONarrow_forwardThe drawing illustrates the dispersion of light by a prism. The prism is made from a certain type of glass, and has a cross section shaped like an equilateral triangle. The indices of refraction for the red and violet light in this type of glass are 1.649 and 1.694, respectively. The angle of incidence for both the red and violet light is 60.0°. Find the angles of refraction at which the (a) red and (b) violet rays emerge into the air from the prism. Glass prism Incident light Normal (a) Normal Incident light Red (660 nm) (b) Violet (410 nm)arrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardA glass block (n = 1.56) is immersed in a liquid. A ray of light within the glass hits a glass- liquid surface at a 70.0° angle of incidence. Some of the light enters the liquid. What is the smallest possible refractive index for the liquid?arrow_forwardThe drawing shows a crystalline slab (refractive index 1.995) with a rectangular cross section. A ray of light strikes the slab at an incident angle of 01 = 35.0°, enters the slab, and travels to point P. This slab is surrounded by a fluid with a refractive index n. What is the maximum value of n such that total internal reflection occurs at point P? Ме Buarrow_forward
- What is the amount of M112 needed to breach a 5-foot thick dense concrete wall utilizing an internal charge placed in the center of the target?arrow_forwardA small postage stamp is placed in front of a concave mirror (radius = 1.1 m), such that the image distance equals the object distance. (a) What is the object distance? (b) What is the magnification of the mirror (with the proper sign)?arrow_forwardCalculate the anti-clockwise torque and the clockwise torque of the system with the ruler and the washers. Record these values in Data Table 5. Ruler = 11.56 g, small washer = 1.85 g, large washer = 24.30 g. Calculate the % Difference in the Torques and record the values in Data Table 5. Is ΣAnticlockwise torque and Anticlockwise torque the same thing, are they solved in the same way?arrow_forward
- A window washer stands on a uniform plank of mass M = 142 kg and length l = 2.80 m supported by 2 ropes attached at the ends of the plank. The window washer has a mass m = 68.0 kg. What is the tension in each of the ropes, T1 and T2, if the window washer's displacement from the center of mass of the plank is x = 0.930 m as shown in Figure 1: Window Washer Problem?arrow_forwardA man holds a double-sided spherical mirror so that he is looking directly into its convex surface, 33 cm from his face. The magnification of the image of his face is +0.17. What will be the image distance when he reverses the mirror (looking into its concave surface), maintaining the same distance between the mirror and his face? Be sure to include the algebraic sign (+ or -) with your answer.arrow_forwardHow do you draw a diagram of the ruler and mass system in equilibrium identifying the anti-clockwise torque and clockwise torque? How do I calculate the anti-clockwise torque and the clockwise torque of the system with the ruler and the washers, does it come from the data in table 4? Please help, thank you!arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





