
PHYSICS F/ SCI +ENGRS W/ WEBASSIGN ACCES
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337888509
Author: SERWAY
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 28, Problem 3P
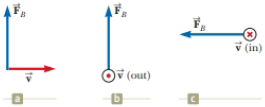
Find the direction of the magnetic field acting on a positively charged particle moving in the various situations shown in Figure P28.3 if the direction of the magnetic force acting on it is as indicated.
Figure P28.3
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Part A
m
2πkT
) 3/2
Calculate the integral (v) = f vƒ (v)dv. The function f(v) describing the actual distribution of molecular speeds is called the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution,
=
ƒ(v) = 4π (· v²e-mv²/2kT
. (Hint: Make the change of variable v² =x and use the tabulated integral foxne
integer and a is a positive constant.)
Express your answer in terms of the variables T, m, and appropriate constants.
-ax dx
n!
-
an+1
where n is a positive
(v)
=
ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ
Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
?
× Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
Al Study Tools
Looking for some guidance? Let's work through a few related
practice questions before you go back to the real thing.
This won't impact your score, so stop at anytime and ask for
clarification whenever you need it.
Ready to give it a try?
Start
Starter the rule of significant
Please solve this problem and give step by step explanations on each step while breaking it down please. Thank you!!
Chapter 28 Solutions
PHYSICS F/ SCI +ENGRS W/ WEBASSIGN ACCES
Ch. 28.1 - An electron moves in the plane of this paper...Ch. 28.2 - Prob. 28.2QQCh. 28.4 - A wire carries current in the plane of this paper...Ch. 28.5 - (i) Rank the magnitudes of the torques acting on...Ch. 28 - At the equator, near the surface of the Earth, the...Ch. 28 - Consider an electron near the Earths equator. In...Ch. 28 - Find the direction of the magnetic field acting on...Ch. 28 - A proton moving at 4.00 106 m/s through a...Ch. 28 - A proton travels with a speed of 5.02 106 m/s in...Ch. 28 - A laboratory electromagnet produces a magnetic...
Ch. 28 - A proton moves perpendicular to a uniform magnetic...Ch. 28 - An accelerating voltage of 2.50103 V is applied to...Ch. 28 - A proton (charge + e, mass mp), a deuteron (charge...Ch. 28 - Review. A 30.0-g metal hall having net charge Q =...Ch. 28 - Review. One electron collides elastically with a...Ch. 28 - Review. One electron collides elastically with a...Ch. 28 - Review. An electron moves in a circular path...Ch. 28 - A cyclotron designed to accelerate protons has a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 15PCh. 28 - Singly charged uranium-238 ions are accelerated...Ch. 28 - A cyclotron (Fig. 28.16) designed to accelerate...Ch. 28 - A particle in the cyclotron shown in Figure 28.16a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 19PCh. 28 - A straight wire earning a 3.00-A current is placed...Ch. 28 - A wire carries a steady current of 2.40 A. A...Ch. 28 - Why is the following situation impossible? Imagine...Ch. 28 - Review. A rod of mass 0.720 kg and radius 6.00 cm...Ch. 28 - Review. A rod of mass m and radius R rests on two...Ch. 28 - A wire having a mass per unit length of 0.500 g/cm...Ch. 28 - Consider the system pictured in Figure P28.26. A...Ch. 28 - A strong magnet is placed under a horizontal...Ch. 28 - In Figure P28.28, the cube is 40.0 cm on each...Ch. 28 - A magnetized sewing needle has a magnetic moment...Ch. 28 - A 50.0-turn circular coil of radius 5.00 cm can be...Ch. 28 - You are in charge of planning a physics magic show...Ch. 28 - You are working in your dream job: an assistant...Ch. 28 - A rectangular coil consists of N = 100 closely...Ch. 28 - A rectangular loop of wire has dimensions 0.500 m...Ch. 28 - A wire is formed into a circle having a diameter...Ch. 28 - A Hall-effect probe operates with a 120-mA...Ch. 28 - Prob. 37APCh. 28 - Figure 28.11 shows a charged particle traveling in...Ch. 28 - Within a cylindrical region of space of radius 100...Ch. 28 - Prob. 40APCh. 28 - Prob. 41APCh. 28 - (a) A proton moving with velocity v=ii experiences...Ch. 28 - A proton having an initial velocity of 20.0iMm/s...Ch. 28 - You have been called in as an expert witness in a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 45APCh. 28 - Why is the following situation impossible? Figure...Ch. 28 - A heart surgeon monitors the flow rate of blood...Ch. 28 - Review. (a) Show that a magnetic dipole in a...Ch. 28 - Consider an electron orbiting a proton and...Ch. 28 - Protons having a kinetic energy of 5.00 MeV (1 eV...Ch. 28 - Review. A wire having a linear mass density of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Car A starts from rest at t = 0 and travels along a straight road with a constant acceleration of 6 ft/s^2 until it reaches a speed of 60ft/s. Afterwards it maintains the speed. Also, when t = 0, car B located 6000 ft down the road is traveling towards A at a constant speed of 80 ft/s. Determine the distance traveled by Car A when they pass each other.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forwardIn the given circuit the charge on the plates of 1 μF capacitor, when 100 V battery is connected to the terminals A and B, will be 2 μF A 1 µF B 3 µFarrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forward
- The velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed. NOT AI PLSarrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forward
- The velocity of a particle moves along the x-axis and is given by the equation ds/dt = 40 - 3t^2 m/s. Calculate the acceleration at time t=2 s and t=4 s. Calculate also the total displacement at the given interval. Assume at t=0 s=5m.Write the solution using pen and draw the graph if needed.arrow_forwardPlease don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Magnets and Magnetic Fields; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IgtIdttfGVw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY