
To describe:
The normal anatomy and physiology of the renal system.
Introduction:
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
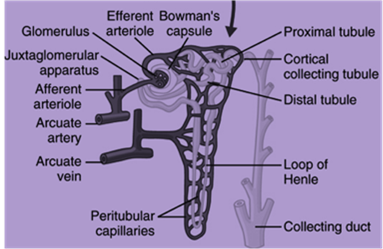
The normal anatomy and physiology of the renal system are described below:
The principal system that is involved in the excretion of waste is the urinary system. From the blood, the metabolic waste is removed by the kidney. The kidney plays an important role in regulating blood pressure and blood volume. The back of the abdominal cavity is the place where the kidney (bean shaped) is located. Vertebrae T12 to L3 is the level where the kidney lies. The left kidney is located slightly higher than the right kidney (lower). This is due to the large right lobe of the liver that occupies the space above the right kidney. The middle part of the left kidney is nearly crossed by Rib 12. The kidneys are retroperitoneal, along with the renal artery, vein, ureters, adrenal glands, and the urinary bladder.
The structural unit of the kidney is referred to as nephron. One million nephrons are present in each kidney. The filtering process takes in the glomerulus. The glomerulus is a bunch of capillaries that is encapsulated by the glomerular capsule. The time taken for filtering the blood is called as glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
The glomerular filtration rate is controlled by the afferent arterioles (approaching the glomerulus) and the efferent arterioles (exiting the glomerulus). The proximal tubule or proximal convoluted tubule plays an important role in returning 60% - 70% of water and sodium from the filtered fluid into the blood. The nephron is surrounded by the blood vessels that permit the reabsorbed substances directly to reach the blood stream. This process (one of the active transport) needs the adenosine triphosphate molecule as an energy source. The active transportation of potassium and sodium ions returns back into the bloodstream, which is known as passive reabsorption (water and chloride). The water and chloride ions follow (passively) the potassium and sodium ions by means of osmosis. The loop of Henle (ascending) is the area where 20% - 25% of sodium ion is reabsorbed back into the blood. In the loop of Henle, sodium is passively reabsorbed, and chloride is actively reabsorbed.
In the distal convoluted tubule or distal tubule, the remaining (5%-10%) sodium is reabsorbed. The sodium ion is actively filtered in the distal tubule. This process is controlled by aldosterone. The final pathway (common) for the remains that begin in the glomerulus is called as collecting duct. The antidiuretic hormone plays an important role to raise water absorption (into the blood). Hence, excess water is prevented from being excreted in the urine.
The glomerular filtration rate’s measurement is used in the detection of some kidney diseases. Yet, the quantity of NaCl could not be assumed by the glomerular filtration rate; there are two causes to explain this reason. (1) The glomerulus is not able to filter the NaCl in urine that is produced by the renal tubule. (2) The tubule reabsorbs all the NaCl that the glomerulus has filtered.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- The importance of monitoring resident's wound healing (bed sores, cuts, and scrapes, etc.) and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of seeing how it is to work as a chief in a nursing home and how they accommodate for special diets (low sodium, low sugar, heart healthy, etc.) and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of dealing with work confrontation (different healthcare departments fighting; diet aide and CNA) as a manager of a kitchen and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forward
- Question 1: You are the Community Dietitian for the local public health agency. Recent news coverage has highlighted the state of food insecurity and child hunger in your county. Initial reports indicate that 15% of the population is food insecure. Of this group, 28.4% are children. It is estimated that 86% of the food insecure population is eligible for federal nutrition assistance. You are asked to conduct a community needs assessment and, ultimately, develop an appropriate intervention aimed at reducing hunger. First, however, you must submit a plan for the needs assessment. Complete the following: 1. State the nutritional problem (10 pts) 2. Set the parameters of the assessment (20 pts, 5 pts per bullet) A. State the purpose of the assessment B. Identify the community and target population for this assessment C. Develop 2 goals and 2 SMART objectives for each goal D. Discuss the major categories of community data and target population data E. Specify the types of data you might…arrow_forwardAssignment Instructions: Nursing Research Essay Objective: Select a specific area of nursing that captivates your interest. Compose a comprehensive essay, ranging from 300 to 500 words, that delves into the intricacies of nursing research within your chosen area. It is recommended that you consider the topic carefully as this topic, should be the topic for your course research project: see week 4 assignments. Your essay should elucidate the following points: The Significance of Nursing Research: Explore how nursing research in your selected area contributes to advancements in applied medicine. Discuss the potential achievements and innovations that can arise from dedicated nursing research in this field. Articulate the value and impact of such research on patient care, healthcare practices, and overall medical knowledge. Research Methods and Approaches: Identify the most effective methods for conducting nursing research in your chosen area. Highlight specific topics or research…arrow_forwardThe importance of understanding low meal consumption of residents in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forward
- The importance of accommodating special diets (diabetic, low sodium, etc.) in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of making a weekly clean list for kitchen staff in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of keeping a clean food pantry in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forward
- I’m finding it a bit difficult to understand the Arrhenius equation and how shelf life relates to pH and temperature. Also in the question that says ‘this solution maintains 80% potency at 30C’, am I correct in thinking the formula would be:t = ln(0.8)/ -karrow_forward4.24 mmmarrow_forwardResearch videos and websites about mission and vision statements in health care organizations. What did you find most interesting? What did you find to be the most positive-sounding parts of the statements? Were there any mission and vision statements that seemed disconnected from each other or out of alignment with the goals of the organization? If so, how might you change them?arrow_forward
 Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC. Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders
Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,
Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer, Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science
Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning





