
Concept explainers
(a)
To determine: The range of [IPTG] expression level which vary from 10% to 90%
Introduction:
Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) binds to the lac repressor in similar way as allolactose. It releases the repressor in allosteric manner from the lac operator and the structural gene transcription of lac operon.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
10% expression of [IPTG] also represents 90% repression of. [IPTG] Hence, 10% of the repressor will show binding to the inducer, while remaining 90% of the repressor will be available for binding to the operator.
To calculate the range of 10% expression level of, the [IPTG] following formula is used with reference to equation 5-8.
So the range of expression level of [IPTG] is:
To calculate the range of 90% expression level of [IPTG],
So the range of expression level of [IPTG] is:
The range of expression of proteins of lac operon varies from 10-fold over the 10-fold expression of [IPTG] range.
The range of IPTG expression level varies from 10-90% or varies 10 folds.
(b)
To describe: The level of lac operon proteins present in E. coli cell before, during, and after IPTG induction.
Introduction:
Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) binds to the lac repressor in similar way as allolactose. It releases the repressor in allosteric manner from the lac operator and the structural gene transcription of lac operon.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
IPTG induces the expression of lac operon proteins. The level of lac protein is very low before the induction, and the expression of lac protein will increase during the induction. After induction, the proteins synthesis will stop thereby, decreasing the expression of lac proteins. The lac proteins will increase during induction, and it decreases before and after the induction.
(c)
To explain: The lac operon lacks both the characteristics: A. that is either fully on or fully off, B. both states are stable.
Introduction:
In normal lac operon regulation, when the repressor is bound to lactose (inducer), it no longer binds to the operator DNA. Binding of lactose to the repressor alters the conformation of repressor protein so that it does not have affinity for the operator. The change in the shape of repressor gene will not allow it to bind to lactose resulting in inhibition of translation of structural gene.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Lac operon has multiple expression levels, other than the on or off condition, as condition A is defined by only two states that are fully on or fully off, it is not followed by lac operon.
Lac operon expression depends on the binding of inducer molecule, as the removal of inducer decreases the expression of lac operon. Condition B is defined by “both states are stable” is not followed by lac operon.
Lac operon shows different expressions thus it cannot be fully on or fully off. It is also not present in stable condition as its expression depends on inducer molecule.
(d)
To explain: The proteins that are present and which promoter is being expressed for the states GFP-on and GFP-off
Introduction:
In normal lac operon regulation, when the repressor is bound to lactose (inducer), it no longer binds to the operator DNA. Binding of lactose to the repressor alters the conformation of the repressor protein so that it does not have affinity for the operator. The change in shape of repressor gene will not allow it to bind to lactose resulting in inhibition of translation of structural gene.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 represents the Plasmid (for the states GFP-on and GFP-ff)
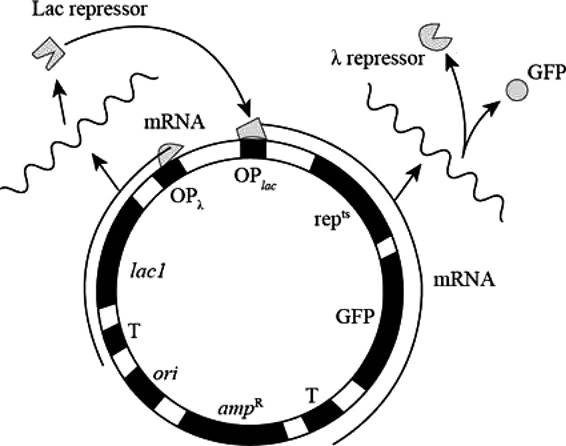
Fig. 1: Plasmid (for the states GFP-on and GFP-off )
Explanation:
GFP-on: The repts gene expresses the repts protein in high level which represses the expression of OPλ, and GFP are expressed at high level during GFP-on state.
GFP-off: high level expression of Lac I represses the expression of OPlac, repts and GFP.
In GFP-on state repts and GFP proteins are present, and in GFP-off state Lac I protein is present.
(e)
To determine: The state from which IPTG would toggle the system
Introduction:
IPTG induces the expression of lac operon proteins. The level of lac protein is very low before the induction while the expression of lac protein will increase during the induction. After the induction, the proteins synthesis will stop thereby decreasing the expression of lac proteins.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Presence of LacI protein enables the system for induction of IPTG, thus it induces the expression only in GFP-off state, and the induction is followed by expression of OPlac, repts and GFP. Thus, IPTG toggle the system from GFP-off to GFP-on.
The state from which IPTG would toggle the system is from GFP-off to GFP-on.
(f)
To determine: The state from which treatment with heat (42°C) would toggle the system.
Introduction:
In normal lac operon regulation, when the repressor is bound to lactose (inducer), it no longer binds to the operator DNA. Binding of lactose to the repressor alters the conformation of the repressor protein so that it does not have affinity for the operator. The change in shape of repressor gene will not allow it to bind to lactose resulting in inhibition of translation of structural gene.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Heat affects the system only in presence of repts, which is expressed only in GFP-on state. The repts which is inactivated due to heat exposure results in OPλ repression followed by the expression of lac I repressor which represses the GFP expression. Hence, heat toggles the system from GFP-on to GFP-off.
(g)
To determine: The reason that plasmid has characteristics A and B.
Introduction:
In normal lac operon regulation, when the repressor is bound to lactose (inducer), it no longer binds to the operator DNA. Binding of lactose to the repressor alters the conformation of the repressor protein so that it does not have affinity for the operator. The change in shape of repressor gene will not allow it to bind to lactose resulting in inhibition of translation of structural gene.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Plasmid system has two states of expression. In intermediate state, the system is not stable hence the plasmid follows the condition A which defines the only on and off condition.
Plasmid remains in a single state even after the removal of repressor from binding site, and as condition B defines that both the states are stable, it is followed by the plasmid.
Plasmid has characteristics A and B as it has only two states of expression, and it is stable in both states.
(h)
To explain: The characteristic of system A that demonstrates GFP expression level in individual cells at
Introduction:
IPTG induces the expression of lac operon proteins. The level of lac protein is very low before the induction while the expression of lac protein will increase during the induction. After the induction, the protein synthesis will stop thereby decreasing the expression of lac proteins.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Characters of system A is defined by only on or only off state, at intermediate concentration of inducer X. In the system, some cells are GFP-on and some are GFP-off, hence they define the system A.
As the cell population have both type GFP-on and GFP-off cells in the system, the expression level of
The cells’ population contains only GFP-on and GFP-off cells in the system. It defines the condition A. As two types of expression are there in the system, it shows bimodal distribution of expression level of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
- Indicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting D-Galactose with hydroxylamine.arrow_forward
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





