
Concept explainers
To Label: The components of the cardiac conduction system given in Fig 28.1.
Introduction: The cardiac conduction system includes specific cardiac muscle cells and conducting fibers that are present in the walls of the heart. In short, the cardiac system is formed of a set of nodes and specialized cardiac cells. These structures send signals to the muscles of the heart and so they contract.
Answer to Problem 1.1BGL
Pictorial representation:
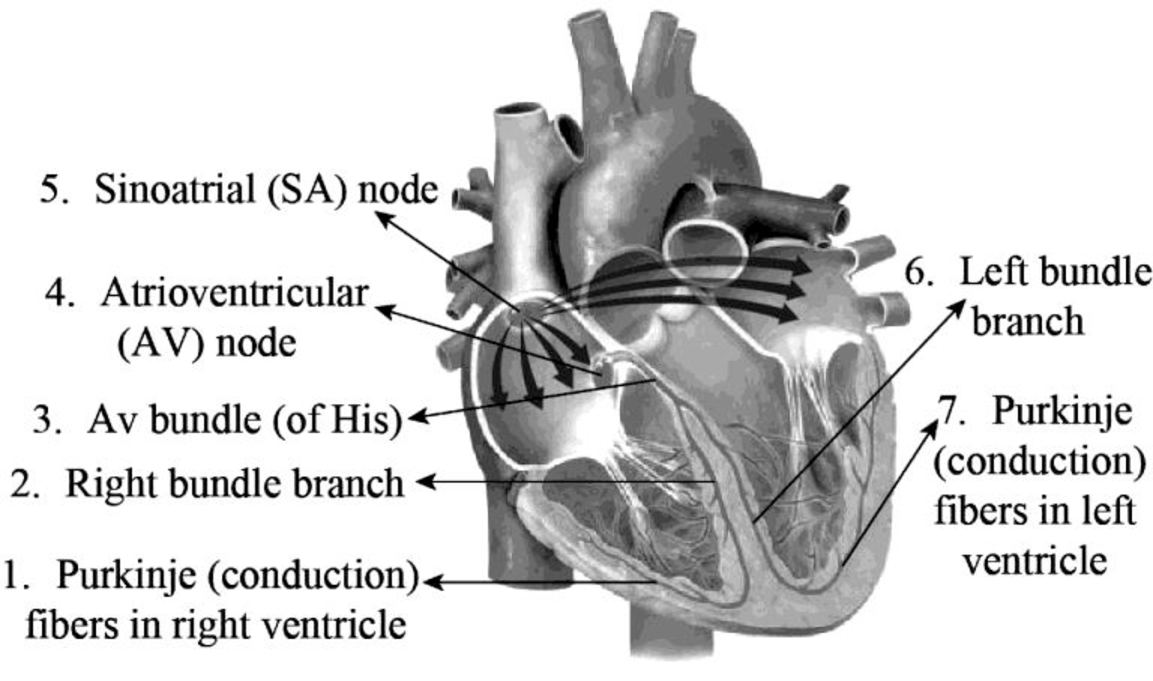
Fig.1: The structures of the cardiac conduction system
Explanation of Solution
The major components of the cardiac conduction system are the SA node, Purkinje fibers, AV node, bundle branches (left and right), and the bundle of His.
Purkinje or conduction fibers are found in the base of the myocardium and in the lateral walls of both the ventricles. They provide the ventricular muscle fibers of the heart and papillary muscles with action potential and induce them to contract.
The left and the right bundle branches are embedded in the interventricular septum and transmit action potential to the conduction fibers.
The AV bundle otherwise known as the bundle of His is located between the atria and the ventricles in a membranous septum that lies superior to the interventricular septum. It is the electrical link amid the ventricles and atria that transmits the action potential to the bundle branches.
The muscle fibers of atria provide action potential for the atrioventricular (AV) node that is present in the lower part of the interatrial septum. It lies in the front part of the coronary sinus opening and supplies action potential to the AV (bundle of His).
The sinoatrial (SA) node is otherwise known as the sinus node. It acts as a natural pacemaker of the heart. This node consists of a group of cells that produce electrical impulses. These impulses pass through the atrial walls and make them contract.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e WileyPLUS (next generation) + Loose-leaf
- What is the result of the acid-fast stain below: Stock Images by Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Image Getty Images St Soy Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Images Joy Getty encapsulated O endosporulating negative ○ positivearrow_forwardYou have a stock vial of diligence 75mg in 3ml and need to draw up a dose of 50mg for your patient.how many mls should you draw up to give this dosearrow_forwardYou are recquired to administer 150mg hydrocortisone intravenously,how many mls should you give?(stock =hydrocortisone 100mg in 2mls)arrow_forward
- If someone was working with a 50 MBq F-18 source, what would be the internal and external dose consequences?arrow_forwardWe will be starting a group project next week where you and your group will research and ultimately present on a current research article related to the biology of a pathogen that infects humans. The article could be about the pathogen itself, the disease process related to the pathogen, the immune response to the pathogen, vaccines or treatments that affect the pathogen, or other biology-related study about the pathogen. I recommend that you choose a pathogen that is currently interesting to researchers, so that you will be able to find plenty of articles about it. Avoid choosing a historical disease that no longer circulates. List 3 possible pathogens or diseases that you might want to do for your group project.arrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- DNK dagi nukleotidlar va undan sintezlangan oqsildagi peptid boglar farqi 901 taga teng bo'lib undagi A jami H boglardan 6,5 marta kam bo'lsa DNK dagi jami H bog‘lar sonini topingarrow_forwardOne of the ways for a cell to generate ATP is through the oxidative phosphorylation. In oxidative phosphorylation 3 ATP are produced from every one NADH molecule. In respiration, every glucose molecule produces 10 NADH molecules. If a cell is growing on 5 glucose molecules, how much ATP can be produced using oxidative phosphorylation/aerobic respiration?arrow_forwardIf a cell is growing on 5 glucose molecules, how much ATP can be produced using oxidative phosphorylation/aerobic respiration?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





