
Interpretation:
The position of the three hydroxyl groups present in cholic acid are to be located and whether they are axial or equatorial are to be identified. Further whether cholic acid is a A-B trans or a A-B cis steroid is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
If the two cyclohexane rings are fused in trans manner the two hydrogens at the ring junction will be diaxial. If the ring fusion is cis, then hydrogen at one ring junction is axial while that in the other junction is equatorial.
Among the disubstituted cyclohexanes, 1,2-cis, 1,3-trans and 1,4-cis substituents will have axial and equatorial arrangements. 1,2-trans, 1,3-cis and 1,4-trans substituents will have either diequatorial or diaxial arrangements.
To locate:
The position of the three hydroxyl groups present in cholic acid.
To identify:
Whether they are axial or equatorial.
To state:
Whether cholic acid is A-B trans or a A-B cis steroid.
Answer to Problem 11VC
The three hydroxyl groups are on C3, C6 and C12. The hydroxyl group on C3 is equatorial while those at C6 and C12 are axial. Cholic acid is A-B cis steroid.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of cholic acid represented by the model is
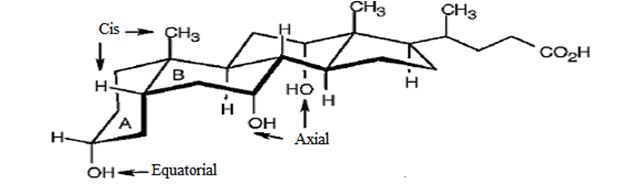
Since lithocholic acid has the rings A and B fused in cis manner, the methyl group on C9 has to be equatorial and the H C10 has to be axial for ring A. In lithocholic acid, the -OH on C3 (in ring A), is in 1,4 trans relationship with the methyl on C9. Hence the –OH on C3 occupies the equatorial position.
For ring B the methyl group on C9 is axial and the H C10 is equatorial. The OH group on C6 has 1,4 trans relationship with methyl on C9 it has to occupy the axial position.
The rings C and D are trans fused. The methyl on C13 and H on C14 has diaxial arrangement. Since the OH group on C12 has 1,2 trans relationship with methyl on C13 it has to occupy the axial position.
The H on C7 is axial for ring C. Since the OH group on C12 is three carbons away from C7 it has to occupy the axial position.
The three hydroxyl groups are on C3, C6 and C12. The hydroxyl group on C3 is equatorial while those at C6 and C12 are axial. Cholic acid is A-B cis steroid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- When anisole is treated with excess bromine, the reaction gives a product which shows two singlets in 1H NMR. Draw the product.arrow_forward(ii) Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction: CI NaOH heat OH (hint: SNAr Reaction) :arrow_forwardDraw the major product in each of the following reaction:arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the following Friedel-Craft reaction. AlBr3 Brarrow_forward(a) Draw the structures of A and B in the following reaction. (i) NaNH2, NH3(1) A + B (ii) H3O+arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Consider the following decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 → NO2 + NO3 (K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: d[N2O5] = -k₁[N₂O₂] + K¸₁[NO₂][NO3] - K¸[NO₂]³ dtarrow_forwardIn a reaction of A + B to give C, another compound other than A, B or C may appear in the kinetic equation.arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Given the reaction R + Q → P, indicate the rate law with respect to R, with respect to P and with respect to P.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardk₁ Given the reaction A B, indicate k-1 d[A] (A). the rate law with respect to A: (B). the rate law with respect to B: d[B] dt dtarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





