
Concept explainers
(a.)
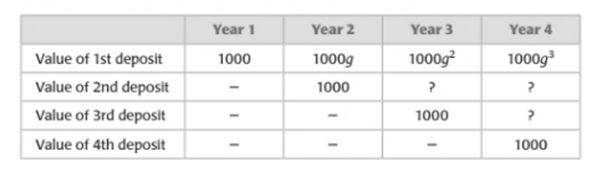
To Complete: The given table.
It has been determined that the value of the second deposit for year 3 is
Given:
An amount of
The growth factor
The following table shows the value of the deposits over the four-year period:
Concept used:
The amount after a year is given as the product of the principle (value of the deposit) at the start of the year and the growth factor.
Calculation:
The value of the second deposit for year 2 is
The growth factor is
Then, the value of the second deposit for year 3 is
The value of the third deposit for year 3 is
The growth factor is
Then, the value of the third deposit for year 4 is
These are the required values that complete the given table.
Conclusion:
It has been determined that the value of the second deposit for year 3 is
(b.)
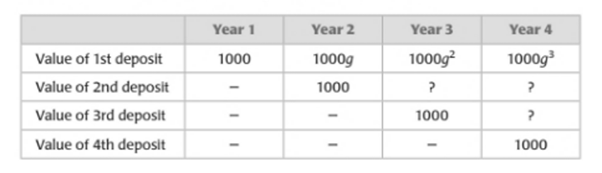
To Write: A polynomial function that gives the value
It has been determined that a polynomial function that gives the value
Given:
An amount of
The growth factor
The following table shows the value of the deposits over the four-year period:
Concept used:
The value of the account at the end of the fourth summer is the sum of the values of all the deposits at the end of the fourth summer.
Calculation:
According to the completed table obtained in part (a), the value of the first deposit at the end of the fourth summer is
Then, the value
Conclusion:
It has been determined that a polynomial function that gives the value
(c.)
The growth factor and the annual interest rate needed to obtain the given amount.
It has been determined that the required growth factor is approximately
Given:
An amount of
The growth factor
The following table shows the value of the deposits over the four-year period:
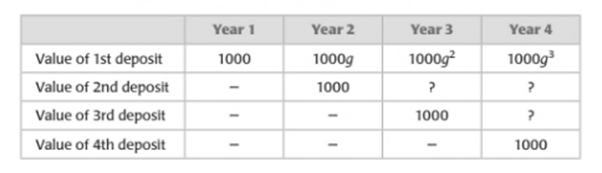
The amount to be saved is
Concept used:
The required growth factor and thus the required annual interest rate can be obtained by plugging in the given value of
Calculation:
As determined previously, the value
It is given that the amount to be saved is
Then,
Put
Simplifying,
On further simplification,
Finally,
The graph of the above polynomial is given as,
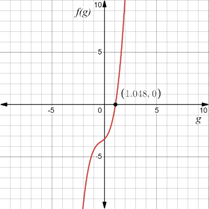
From the above graph, the only real root of the polynomial equation is
Hence, this is the required growth factor.
Now, as assumed,
Put
Solving,
This implies that the required annual interest rate is approximately
Conclusion:
It has been determined that the required growth factor is approximately
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK ALGEBRA 2
- Nasir invested $415 into a savings account that earns 2.5% annual interest. Tiana invested $295 into a saving account that earns 6.8% annual interest. Who will have more money after 7 years? How much more money will the person have?arrow_forwardSolve for the variable. 62k = 7776k- 8arrow_forwardSolve questionsarrow_forward
- Patterns in Floor Tiling A square floor is to be tiled with square tiles as shown. There are blue tiles on the main diagonals and red tiles everywhere else. In all cases, both blue and red tiles must be used. and the two diagonals must have a common blue tile at the center of the floor. If 81 blue tiles will be used, how many red tiles will be needed?arrow_forwardFind the values of n, if the points (n + 1, 2n), (3n, 2n + 3) and (5n + 1,5n) are collinear. Find the value of k that the four points (4,1,2), (5, k, 6), (5,1,-1) and (7,4,0) are coplanar. Find the value of r if the area of the triangle is formed by the points (-3,6),(4,4) and (r,-2) is 12 sq units. Find the volume of tetrahedron whose vertices are A(1,1,0), B(-4,3,6), C(-1,0,3) and D(2,4,-5).arrow_forward- Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables a,b,c,d: 5a-3b 7c - 2d = 2 2ab 2c+ 5d = -3 → (*) 4a 3b 5d = 3 6a b+2c+ 7d = −7 (a) Solve the system (*) by using Gauss elimination method. (b) Solve the system (*) by using Cramer's rule method.arrow_forward
- Solve for a 25 55 30 a=?arrow_forward9:41 … 93 Applying an Exponential Function to Newton's Law of Cooling 60. Water in a water heater is originally Aa ← 122°F. The water heater is shut off and the water cools to the temperature of the surrounding air, which is 60°F. The water cools slowly because of the insulation inside the heater, and the value of k is measured as 0.00351. a. Write a function that models the temperature T (t) (in °F) of the water t hours after the water heater is shut off. b. What is the temperature of the water 12 hr after the heater is shut off? Round to the nearest degree. c. Dominic does not like to shower with water less than 115°F. If Dominic waits 24 hr. will the water still be warm enough for a shower? Mixed Exercises ger-ui.prod.mheducation.comarrow_forwardPlease use the infinite series formula and specify how you did each step. Thank you.arrow_forward
- 8) Solve the given system using the Gaussian Elimination process. 2x8y = 3 (-6x+24y = −6arrow_forward7) Solve the given system using the Gaussian Elimination process. (5x-4y = 34 (2x - 2y = 14arrow_forward33 (a) (b) Let A(t) = = et 0 0 0 cos(t) sin(t) 0-sin(t) cos(t)) For any fixed tЄR, find det(A(t)). Show that the matrix A(t) is invertible for any tЄ R, and find the inverse (A(t))¹.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





