
Concept explainers
1. Three objects are at rest in three beakers of water as shown.
- Compare the mass, volume, and density of the objects to the mass, volume, and density of the displaced water. Explain your reasoning in each case.
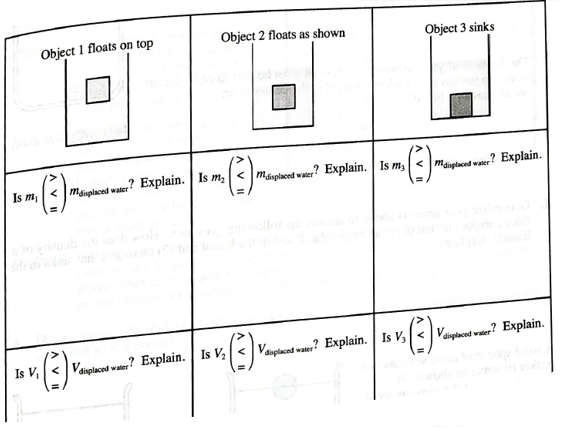
The comparison of mass, volume and density of the object with the displaced water.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Three objects are at rest in three beakers of water as shown:
FormulaUsed:
Use Archimedes principle which is expressed as follows:
Here, the buoyant force is
Calculation:
For Object 1
Free body diagram of the 1st object is shown below:
As the object floats on the top of the surface, the displaced volume must be less than the volume of the object. Thus,
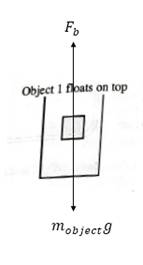
As the body is floating on the top surface, then the weight of the body is equal to the buoyant force. Thus, for equilibrium,
Thus, the mass of the object is equal to the mass of the displaced water.
For density, apply summation of force in the vertical direction as follows:
As the
For Object 2, Free body diagram of the 2nd object is shown below:
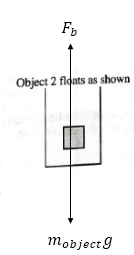
As the object floats inside the water, the displaced volume must be equal to the volume of the object. Thus,
As the body is floating inside the water then the weight of the body is equal to the buoyant force. Thus, for equilibrium,
Thus, the mass of the object is equal to the mass of the displaced water.
For density apply summation of force in the vertical direction as follows:
Thus, the density of the object must be equal to the density of water.
For Object 3,
Free body diagram of the 3rd object is shown below:
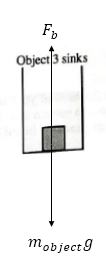
The displaced volume must be equal to the volume of the object as it is kept inside the tank completely. Thus,
As the body is not floating inside the water, then the weight of the body is more than the buoyant force. Thus, for equilibrium,
Thus, the mass of the object is more than the mass of the displaced water.
For density, apply summation of force in the vertical direction as follows:
Thus, the density of object must be more thanthe density of water.
Conclusion:
For object 1,
For object 2,
For object 3,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- 4a Which of the following values COULD NOT be a magnitude? Choose all that apply. 626 0 -0.806 8.63 -48.5 72 131 156 4b Px = -1248 & Py = 261. Determine P.P = Qx = -1540 & Qy = 375. Determine Q.Q = 4c. T = 1105 & Ty = 425. Determine the two possible values for Tx. 4d. Uy = -38. Which of the following COULD NOT be the value of U? Choose all that apply. 10 70 72 31 47 0 75 38 4e. R has a magnitude of 165. Which of the following COULD be Rx? Choose all that apply. 165 -171 155 0 -156 -165 172 -130arrow_forward9.arrow_forward10.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





