
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 26.1, Problem 2TH
A W-shaped piece of glassware is partially filled with water as shown. Point X is at the same height as the water level in the center of the tube.
For each of the following points, slate whether the pressure is greater than, less than, or equal to atmospheric pressure. Explain your reasoning.
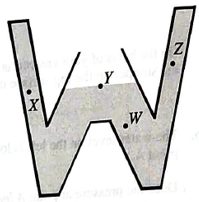
• pointW
• pointX
• pointY
• pointZ
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The figure gives the acceleration a versus time t for a particle moving along an x axis. The a-axis scale is set by as = 12.0 m/s². At t = -2.0
s, the particle's velocity is 11.0 m/s. What is its velocity at t = 6.0 s?
a (m/s²)
as
-2
0
2
t(s)
4
Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded together at B and loaded as shown. Knowing that the average normal stress must not
exceed 150 MPa in either rod, determine the smallest allowable values of the diameters d₁ and d2. Take P= 85 kN.
P
125 kN
B
125 kN
C
0.9 m
1.2 m
The smallest allowable value of the diameter d₁ is
The smallest allowable value of the diameter d₂ is
mm.
mm.
Westros, from Game of Thrones, has an area of approximately 6.73⋅106 miles26.73⋅106miles2. Convert the area of Westros to km2 where 1.00 mile = 1.609 km.
Chapter 26 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 26.1 - Prob. 1aTHCh. 26.1 - 1. A U-tube filled with water is closed on one...Ch. 26.1 - 1. A U-tube filled with water is closed on one...Ch. 26.1 - 1. A U-tube filled with water is closed on one...Ch. 26.1 - 1. A U-tube filled with water is closed on one...Ch. 26.1 - A W-shaped piece of glassware is partially filled...Ch. 26.1 - Prob. 3aTHCh. 26.1 - A U-tube is partly filled with water. Oil is then...Ch. 26.1 - Prob. 3cTHCh. 26.2 - 1. Three objects are at rest in three beakers of...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What are four functions of connective tissue?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
DRAW IT Each female of a particular fish species produces millions of eggs per year. Draw and label the most l...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Approximately how many feet is the Missouri River above sea level? Height above sea level: _________ feet
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Q1. What is the empirical formula of a compound with the molecular formula
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
If someone at the other end of a room smokes a cigarette, you may breathe in some smoke. The movement of smoke ...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
2. Whether an allele is dominant or recessive depends on
a. how common the allele is, relative to other alleles...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a) What is the lenght of x? b) Findθ c) Find ϕarrow_forwardA surveyor measures the distance across a straight river by the following method: Starting directly across from a tree on the opposite bank, he walks x = 97.7 m along the riverbank to establish a baseline. Then he sights across to the tree. The angle from his baseline to the tree is θ = 33.0 °. How wide is the river?arrow_forwardA small turtle moves at a speed of 697. furlong/fortnight. Find the speed of the turtle in centimeters per second. Note that 1.00 furlong = 220. yards, 1.00 yard = 3.00 feet, 1.00 foot = 12.0 inches, 1.00 inch = 2.54 cm, and 1.00 fortnight = 14.0 days.arrow_forward
- The landmass of Sokovia lifted in the air in Avengers: Age of Ultron had a volume of about 1.98 km3. What volume is that in m3?arrow_forwardA fathom is a unit of length, usually reserved for measuring the depth of water. A fathom is exactly 6.00 ft in length. Take the distance from Earth to the Moon to be 252,000 miles, and use the given approximation to find the distance in fathoms. 1 mile = 5280 ft. (Answer in sig fig.)arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- One of the earliest video games to have a plot, Zork, measured distances in “Bloits” where 1 Bloit was defined as the distance the king’s favorite pet could run in one hour, 1,090 m. In the same game the king has a statue made that is 9.00 Bloits high. What is this in meters?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Defination of voltagearrow_forwardAt point A, 3.20 m from a small source of sound that is emitting uniformly in all directions, the intensity level is 58.0 dB. What is the intensity of the sound at A? How far from the source must you go so that the intensity is one-fourth of what it was at A? How far must you go so that the sound level is one-fourth of what it was at A?arrow_forwardMake a plot of the acceleration of a ball that is thrown upward at 20 m/s subject to gravitation alone (no drag). Assume upward is the +y direction (and downward negative y).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY