
Concept explainers
A toroid is a solenoid-like coil bent into a circle (Fig. 26.52a). Toroids are the configuration of choice in magnetic-confinement nuclear fusion experiments, which, if successful, could provide us with an almost unlimited energy source using deuterium fuel extracted from seawater.
The ITER consortium, an international collaboration, is building a large toroidal fusion experiment in France; it’s expected to be the first fusion device to produce energy on a large scale. Figure 26.52b shows a cross section of a toroid, with current emerging from the page at the inner edge and descending at the outer edge. The black circle is an Ampèrian loop.
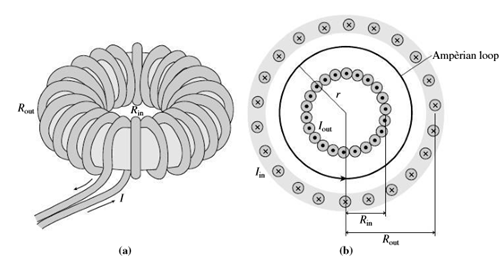
FIGURE 26.52 Diagram of (a) a toroidal coil and (b) a cross section of the coil (Passage Problems 88–91)
88. The magnetic field associated with the toroid is nonzero
- a. only within the “hole” in the donut-shaped coil.
- b. only within the region bounded by the coils.
- c. only outside the coils.
- d. everywhere.
89. In Fig. 26.52b, the magnetic field lines must be
- a. straight, and pointing into the page.
- b. straight, and pointing out of the page.
- c. straight, and pointing radially.
- d. circular.
90. Doubling the total number of turns N in the toroid, without changing its size or the current, will
- a. double the magnetic field.
- b. quadruple the magnetic field.
- c. halve the magnetic field.
- d. not change the magnetic field.
91. The toroid has inner radius Rin and outer radius Rout, while r is the radial coordinate measured from the center. The toroid is made from wire wound into a total of N turns, and carries current I. Which of the following is the correct formula for the magnetic field within the coils?
- a. B = μ0NI
- b. B = μ0NI/2πRin
- c. B = μ0NI/2πRout
- d. B = μ0NI/2πr
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 26 Solutions
Essential University Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
- 8. With the aid of a diagram draw the following electric circuit and use the resistor as the load, (a) Closed circuit (b) Open circuitarrow_forwardLab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forward

 Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





