
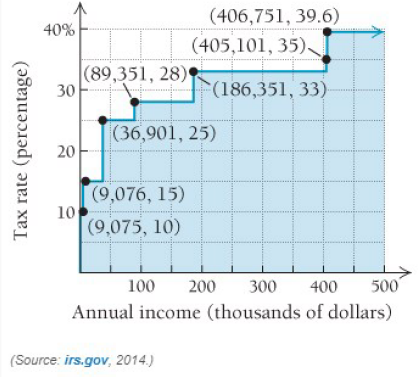
Businesses and individuals are frequently concerned about their marginal tax rate, or the rate at which the next dollar earned is taxed In progressive taxation, the 80,001 st dollar earned is taxed at a higher rate than the 25.001 st dollar earned and at a lower rate than the 140,001 st dollar earned Use the following graph, showing the marginal tax rate for 2014 for single filers, to answer Exercises 23-26.
| Single Filers Income Bracket | Rate |
|---|---|
| 0–9075 | 10% |
| 9076–36900 | 15% |
| 36901–89350 | 25% |
| 89351–186350 | 28% |
| 186351–405100 | 33% |
| 405101–406750 | 35% |
| 406751+ | 39.6% |
Marcy and Tyrone work for the same marketing agency Because she is not yet a partner Marcy’s year-end income is approximately $95,000, Tyrone’s year-end income is approximately $185,000 Suppose one of them is to receive another $5000, 000, in income for the year Which one would keep more of that $5000 after taxes ? Why?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Calculus and Its Applications, Books a la Carte Plus MyLab Math Access Card Package (11th Edition)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
- The position of a moving hockey puck after t seconds is s(t) = tan a. Find the velocity of the hockey puck at any time t. v(t) ===== b. Find the acceleration of the puck at any time t. -1 a (t) = (t) where s is in meters. c. Evaluate v(t) and a (t) for t = 1, 4, and 5 seconds. Round to 4 decimal places, if necessary. v (1) v (4) v (5) a (1) = = = = a (4) = a (5) = d. What conclusion can be drawn from the results in the previous part? ○ The hockey puck is decelerating/slowing down at 1, 4, and 5 seconds ○ The hockey puck has a constant velocity/speed at 1, 4, and 5 seconds ○ The hockey puck is accelerating/speeding up at 1, 4, and 5 secondsarrow_forwardquestion 8arrow_forwardFind the area of the surface obtained by rotating the circle x² + y² = r² about the line y = r.arrow_forward
- do question 2arrow_forwardA chemical reaction involving the interaction of two substances A and B to form a new compound X is called a second order reaction. In such cases it is observed that the rate of reaction (or the rate at which the new compound is formed) is proportional to the product of the remaining amounts of the two original substances. If a molecule of A and a molecule of B combine to form a molecule of X (i.e., the reaction equation is A + B ⮕ X), then the differential equation describing this specific reaction can be expressed as: dx/dt = k(a-x)(b-x) where k is a positive constant, a and b are the initial concentrations of the reactants A and B, respectively, and x(t) is the concentration of the new compound at any time t. Assuming that no amount of compound X is present at the start, obtain a relationship for x(t). What happens when t ⮕∞?arrow_forwardConsider a body of mass m dropped from rest at t = 0. The body falls under the influence of gravity, and the air resistance FD opposing the motion is assumed to be proportional to the square of the velocity, so that FD = kV2. Call x the vertical distance and take the positive direction of the x-axis downward, with origin at the initial position of the body. Obtain relationships for the velocity and position of the body as a function of time t.arrow_forwardAssuming that the rate of change of the price P of a certain commodity is proportional to the difference between demand D and supply S at any time t, the differential equations describing the price fluctuations with respect to time can be expressed as: dP/dt = k(D - s) where k is the proportionality constant whose value depends on the specific commodity. Solve the above differential equation by expressing supply and demand as simply linear functions of price in the form S = aP - b and D = e - fParrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
 College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning





