
Concept explainers
Figure 26-15 shows cross sections through three long conductors of the same length and material, with square cross sections of edge lengths as shown. Conductor B fits snugly within conductor A, and conductor C fits snugly within conductor B. Rank the following according to their end-to-end resistances, greatest first: the individual conductors and the combinations of A + B (B inside A), B + C(C inside B), and A + B + C(B inside A inside C).
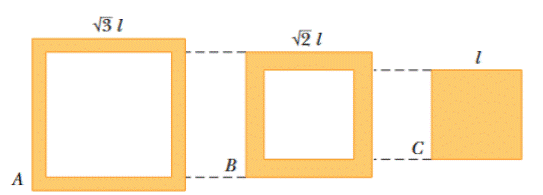
Figure 26-15 Question 1.
To find:
Ranking of resistances from greatest to lowest.
Answer to Problem 1Q
Solution:
Ranking of resistances from greatest to lowest is
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
We use the formula of resistance related to resistivity, length, and area. Here, we have given the material and length as same for the given conductors, so the resistivity and length are same for all. So, the resistance will be proportional to only the area of cross section of the conductor. Using the proportionality relation, we can rank the resistances for given combinations.
2) Formula:
3) Given:
Figure 26-15 is the cross sections of conductors.
4) Calculation:
We can calculate the area of cross section of each conductor as,
Area of conductor C is
Similarly, area of conductor A is
We know the formula,
Here, the given conductors are of same material and length so the resistivity and length are the same for each conductor, so the resistance depends on only the area of cross section of the conductor as,
The resistancesof given combination of conductors are,
For combination of
For
For
From this, we can rank the resistances from greatest to lowest as follows,
Conclusion:
We can rank the combination of conductors of same material and length according to the resistance from their area of cross section.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- An object is placed 24.1 cm to the left of a diverging lens (f = -6.51 cm). A concave mirror (f= 14.8 cm) is placed 30.2 cm to the right of the lens to form an image of the first image formed by the lens. Find the final image distance, measured relative to the mirror. (b) Is the final image real or virtual? (c) Is the final image upright or inverted with respect to the original object?arrow_forwardConcept Simulation 26.4 provides the option of exploring the ray diagram that applies to this problem. The distance between an object and its image formed by a diverging lens is 5.90 cm. The focal length of the lens is -2.60 cm. Find (a) the image distance and (b) the object distance.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





