
Concept explainers
Complete this map, which presents some major concepts from this chapter.
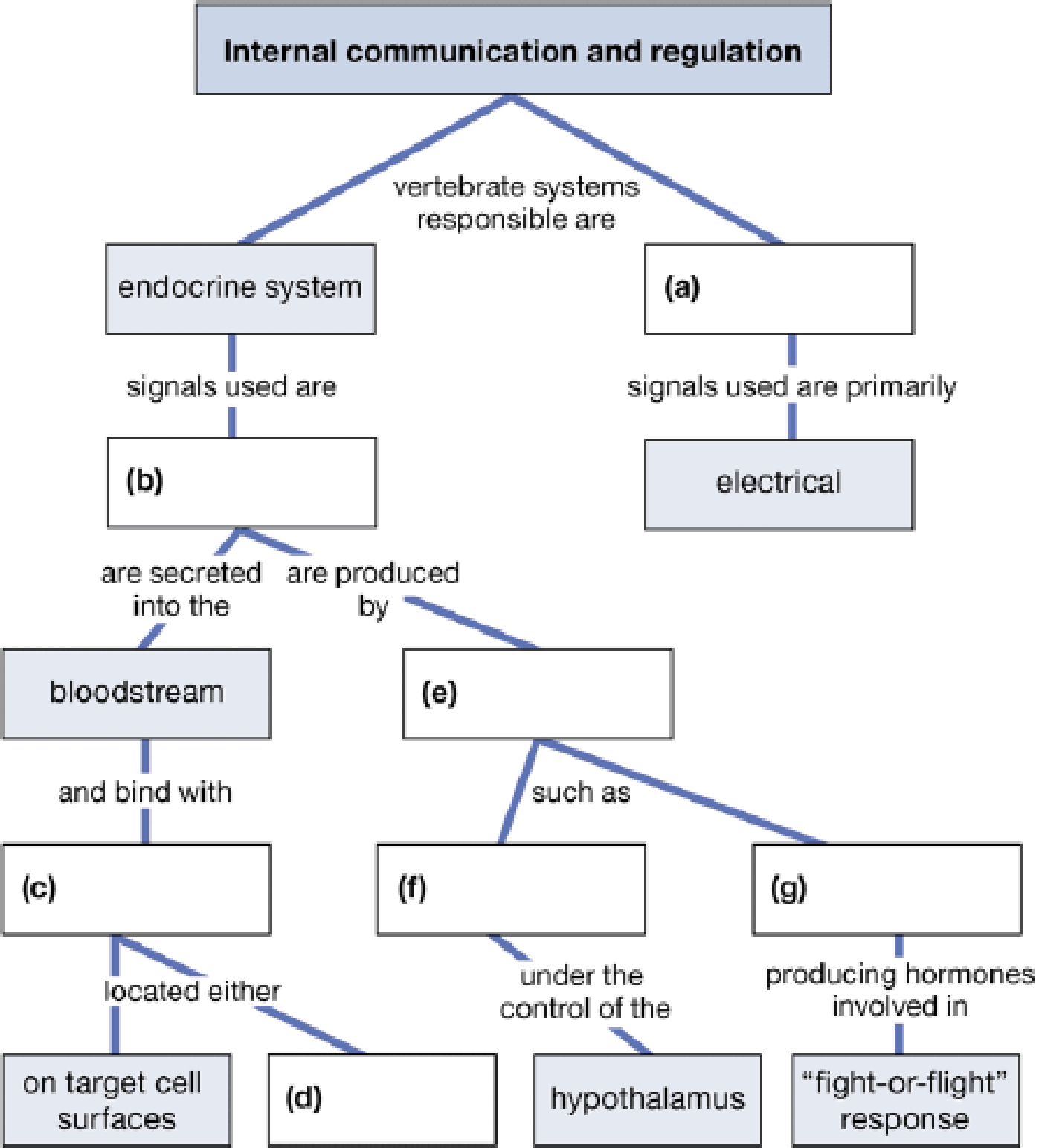
To complete: The given map that shows the internal communication and regulation.
Introduction: There are two major ways of internal regulation and communication. These are regulated by hormones (chemical substances) and neuronal communication (electrical signals). Neuronal regulation is carried out by neurons either electrically or by the help of neurotransmitters. Hormonal regulation is carried out by hormones that are usually peptides or steroid molecules.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Pictorial representation: Fig. 1 represents the chart of the internal communication and regulation by hormones in vertebrates.
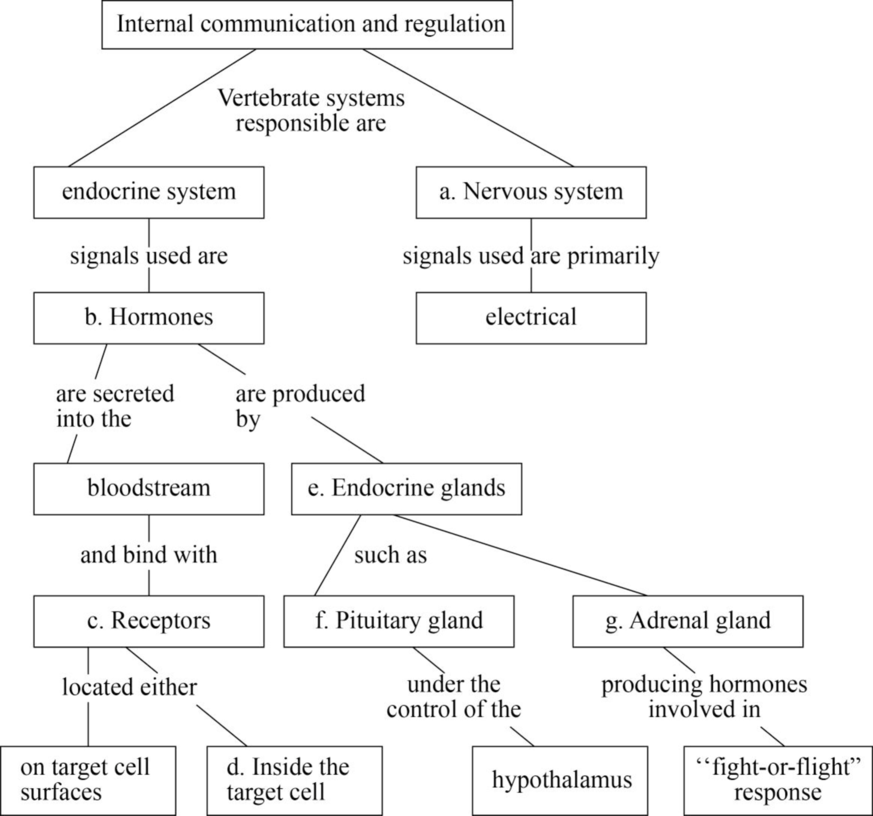
Fig. 1: Internal communication and regulation.
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Correct answer: Nervous system
The nervous system is the organ system of the body, which conducts nerve impulses in the form of electrical signals that pass along the dendrites to generate an action potential. Hence, the correct answer is nervous system.
(b)
Correct answer: Hormones
Hormones are the chemical substances that are secreted by a special group of cells or tissues called the endocrine glands. They pour their secretions into the bloodstream. The exocrine glands are also found in our bodies, which pour their secretions in a tube or a duct. Hence, the correct answer is hormones.
(c)
Correct answer: Receptors
Receptors are the structures that are mostly made up of proteins whose function, as the name suggests, is that they receive the signals or the chemicals or hormones and thereby transmit or elicit a response in the cell on which they are present. Hence, the correct answer is receptors.
(d)
Correct answer: Inside the target cell
Receptors are present inside or outside the cell. They receive the hormones that are secreted by the endocrine glands. Their functioning is regulated either by the hormone itself or by some other biomolecules. Hence, the correct answer is inside the target cell.
(e)
Correct answer: Endocrine glands
Hormones are the chemical substances or biomolecules that are secreted or formed by the endocrine cells. The chemical substances that are formed by the exocrine glands are called secretions. Secretions are poured into a tube or a duct, whereas the hormones are secreted directly into the bloodstream. Hence, the correct answer is endocrine glands.
(f)
Correct answer: Pituitary gland
The pituitary gland is also called the master gland as it controls the functioning of all the other endocrine glands. However, this gland is also regulated by the hypothalamus, which is a part of the brain. Hence, the correct answer is pituitary gland.
(g)
Correct answer: Adrenal gland
The adrenal gland is also called the suprarenal gland as it is located above the kidneys. It secretes a hormone called adrenaline, which is also called the 3F hormone or the emergency hormone as this provides the support for the response that is needed in emergency conditions like fighting or in fearful conditions. Hence, the correct answer is adrenal gland.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- This question has multiple parts (A, B & C), and under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forwardCalculate the CFU/ml of a urine sample if 138 E. coli colonies were counted on a Nutrient Agar Plate when0.5 mls were plated on the NA plate from a 10-9 dilution tube. You must highlight and express your answerin scientific notatioarrow_forwardDon't copy off the other answer if there is anyarrow_forward
- Use the following information to answer the question(s) below. Martin Wikelski and L. Michael Romero (Body size, performance and fitness in Galápagos marine iguanas, Integrative and Comparative Biology 43 [2003]:376-86) measured the snout-to-vent (anus) length of Galápagos marine iguanas and observed the percent survival of different-sized animals, all of the same age. The graph shows the log snout-vent length (SVL, a measure of overall body size) plotted against the percent survival of these different size classes for males and females. Survival (%) 100- 80- 60- 40- 20- 0+ 1.9 T 2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Log SVL (mm) 19) Examine the figure above. What type of selection for body size appears to be occurring in these marine iguanas? A) directional selection B) stabilizing selection C) disruptive selection D) You cannot determine the type of selection from the above information. 3arrow_forward24) Use the following information to answer the question below. Researchers studying a small milkweed population note that some plants produce a toxin and other plants do not. They identify the gene responsible for toxin production. The dominant allele (T) codes for an enzyme that makes the toxin, and the recessive allele (t) codes for a nonfunctional enzyme that cannot produce the toxin. Heterozygotes produce an intermediate amount of toxin. The genotypes of all individuals in the population are determined (see table) and used to determine the actual allele frequencies in the population. TT 0.49 Tt 0.42 tt 0.09 Refer to the table above. Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A) Yes. C) No; there are more homozygotes than expected. B) No; there are more heterozygotes than expected. D) It is impossible to tell.arrow_forward30) A B CDEFG Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following forms a monophyletic group? A) A, B, C, and D B) C and D C) D, E, and F D) E, F, and Garrow_forward
- Health Safety And Nutrition F/Young ChildHealth & NutritionISBN:9781305144767Author:MAROTZPublisher:Cengage
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage LearningCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage LearningCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage  Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning





