
Economics
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781319066604
Author: Paul Krugman, Robin Wells
Publisher: Worth Publishers
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 26, Problem 10P
To determine
To determine: The total change in real GDP and the value of the multiplier.
Concept Introduction:
The formula to calculate change in GDP is:
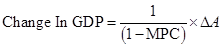
Here,
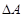 is autonomous spending.
is autonomous spending. - MPC is marginal propensity to consume.
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC): It is defined as the change which occurs in total consumption level due to change in income.
The formula to calculate MPC is:
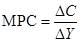
Here,
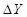 is change in income.
is change in income. 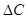 is change in consumption level.
is change in consumption level. - MPC is marginal propensity to consume.
Multiplier: It is defined as the ratio of total change in gross domestic product due to change in the autonomous spending.
The formula to calculate multiplier is:
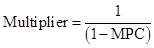
Here,
- MPC is marginal propensity to consume.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
With your team I would like you to complete the following questions after please post your replies and we will discuss in class
Choose a financial instrument or market (such as stocks, bonds, insurance, cash, gold, bitcoin). Explain how investments work for the individual investor mainly yourself. With the current market upheaval and uncertainty what would you and your team consider the best options for investment. Consider the idea of short term investing vs long term investing, laddering, safe haven, liquidity, and risk) Consider Roth IRA vs traditional IRA, ETF's, CD's, Mutual Funds. Always consider taxes and inflation your return should always be greater then inflation and taxes.
Short Description
Fiscal Policy
Graph Details
Shown is a Fiscal Policy diagram with the variable Real GDP (billions of dollars) on the x-axis and the variable Price Level on the y-axis.
The x-axis is scaled from 0 to 800 billion dollars with an increment of 40 billion dollars, and the y-axis is scaled from 30 to 150 units with an increment of 5 units.
Object Details
On the graph we have:Four Line Objects:An upward sloping Aggregate Supply, AS line with two endpoints:Point 1 at (160, 70)Point 2 at (720, 140)A downward sloping Aggregate Demand, AD1 line with two endpoints:Point 1 at (80, 110)Point 2 at (640, 40)A vertical Long-run Aggregate Supply, LRAS with two endpoints:Point 1 at (400, 145)Point 2 at (400, 30)A downward sloping Aggregate Demand, AD line with two endpoints:Point 1 at (720, 60)Point 2 at (160, 130)Two Reference Points:Lines AS, AD, and LRAS intersect at (400, 100)Lines AS and AD1 intersect at (280, 85)
a. How much does aggregate demand need to change to restore the…
Fiscal Policy
Graph Details
Shown is a Fiscal Policy diagram with the variable Real GDP (billions of dollars) on the x-axis and the variable Price Level on the y-axis.
The x-axis is scaled from 0 to 1000 billion dollars with an increment of 50 billion dollars, and the y-axis is scaled from 0 to 180 units with an increment of 10 units.
Object Details
On the graph we have:Four Line Objects:An upward sloping Aggregate Supply, AS line with two endpoints:Point 1 at (200, 40)Point 2 at (800, 160)A downward sloping Aggregate Demand, AD line with two endpoints:Point 1 at (200, 160)Point 2 at (800, 40)A downward sloping Aggregate Demand, AD1 line with two endpoints:Point 1 at (350, 170)Point 2 at (900, 60)A vertical Long-run Aggregate Supply, LRAS line with two endpoints:Point 1 at (500, 170)Point 2 at (500, 0)Two Reference Points:Lines AS and AD1 intersect at (600, 120)Lines AS, AD, and LRAS intersect at (500, 100)
a. How much does aggregate demand need to change to restore the…
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- a. How much does aggregate demand need to change to restore the economy to its long-run equilibrium? $ billion b. If the MPC is 0.6, how much does government purchases need to change to shift aggregate demand by the amount you found in part a? $ billion Suppose instead that the MPC is 0.95. c. How much does aggregate demand and government purchases need to change to restore the economy to its long-run equilibrium? Aggregate demand needs to change by $ billion and government purchases need to change by $ billion.arrow_forwardPrice P 1. Explain the distinction between outputs and outcomes in social service delivery 2. Discuss the Rawlsian theory of justice and briefly comment on its relevance to the political economy of South Africa. [2] [7] 3. Redistributive expenditure can take the form of direct cash transfers (grants) and/or in- kind subsidies. With references to the graphs below, discuss the merits of these two transfer types in the presence and absence of a positive externality. [6] 9 Quantity (a) P, MC, MB MSB MPB+MEB MPB P-MC MEB Quantity (6) MCarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- If 17 Ps are needed and no on-hand inventory exists fot any of thr items, how many Cs will be needed?arrow_forwardExercise 5Consider the demand and supply functions for the notebooks market.QD=10,000−100pQS=900pa. Make a table with the corresponding supply and demand schedule.b. Draw the corresponding graph.c. Is it possible to find the price and quantity of equilibrium with the graph method? d. Find the price and quantity of equilibrium by solving the system of equations.arrow_forward1. Consider the market supply curve which passes through the intercept and from which the marketequilibrium data is known, this is, the price and quantity of equilibrium PE=50 and QE=2000.a. Considering those two points, find the equation of the supply. b. Draw a graph for this equation. 2. Considering the previous supply line, determine if the following demand function corresponds to themarket demand equilibrium stated above. QD=.3000-2p.arrow_forward
- Supply and demand functions show different relationship between the price and quantities suppliedand demanded. Explain the reason for that relation and provide one reference with your answer.arrow_forward13:53 APP 簸洛瞭對照 Vo 56 5G 48% 48% atheva.cc/index/index/index.html The Most Trusted, Secure, Fast, Reliable Cryptocurrency Exchange Get started with the easiest and most secure platform to buy, sell, trade, and earn Cryptocurrency Balance:0.00 Recharge Withdraw Message About us BTC/USDT ETH/USDT EOS/USDT 83241.12 1841.50 83241.12 +1.00% +0.08% +1.00% Operating norms Symbol Latest price 24hFluctuation B BTC/USDT 83241.12 +1.00% ETH/USDT 1841.50 +0.08% B BTC/USD illı 83241.12 +1.00% Home Markets Trade Record Mine О <arrow_forwardThe production function of a firm is described by the following equation Q=10,000L-3L2 where Lstands for the units of labour.a) Draw a graph for this equation. Use the quantity produced in the y-axis, and the units of labour inthe x-axis. b) What is the maximum production level? c) How many units of labour are needed at that point?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education