PHYS 212 FOR SCI+ENG W/MAST PHYS >ICP<
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781323834831
Author: Knight
Publisher: PEARSON C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 25, Problem 7EAP
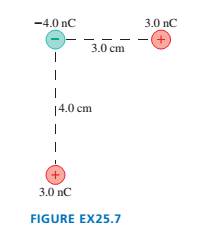
What is the electric potential energy of the group of charges in
FIGURE EX25.7?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten
5. An object moves in a horizontal plane with
constant speed on the path shown. At which
marked point is the magnitude of its
acceleration greatest?
A
B
Ꭰ
E
C
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 25 Solutions
PHYS 212 FOR SCI+ENG W/MAST PHYS >ICP<
Ch. 25 - a. Charge q1is distance r from a positive point...Ch. 25 - FIGURE Q25.2 shows the potential energy of a...Ch. 25 - An electron moves along the trajectory of FIGURE...Ch. 25 - Two protons are launched with the same speed from...Ch. 25 - Rank in order, from most positive to most...Ch. 25 - FIGURE Q25.6 shows the electric potential along...Ch. 25 - A capacitor with plates separated by distance d is...Ch. 25 - Prob. 8CQCh. 25 - FIGURE Q25.9 shows two points inside a capacitor....Ch. 25 - FIGURE Q25.10 shows two points near a positive...
Ch. 25 - ll. FIGURE Q25.11 shows three points near two...Ch. 25 - Reproduce FIGURE Q25.12 on your paper. Then draw a...Ch. 25 - I. The electric field strength is 20,000 N/C...Ch. 25 - The electric field strength is 50,000 N/C inside a...Ch. 25 - A proton is released from rest at the positive...Ch. 25 - A proton is released from rest at the positive...Ch. 25 - Prob. 5EAPCh. 25 - What is the electric potential energy of the group...Ch. 25 - What is the electric potential energy of the group...Ch. 25 - Two positive point charges are 5.0 cm apart. If...Ch. 25 - A water molecule perpendicular to an electric...Ch. 25 - FIGURE EX25.10 shows the potential energy of an...Ch. 25 - What is the speed of a proton that has been...Ch. 25 - I What is the speed of an electron that has been...Ch. 25 - What potential difference is needed to accelerate...Ch. 25 - Prob. 14EAPCh. 25 - A proton with an initial speed of 800,000 m/s is...Ch. 25 - Prob. 16EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 17EAPCh. 25 - In proton-beam therapy, a higher-energy beam of...Ch. 25 - Prob. 19EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 20EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 21EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 22EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 23EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 24EAPCh. 25 - Two 2.0-cm-diameter disks spaced 2.0 mm apart form...Ch. 25 - In FIGURE EX25.26, a proton is fired with a speed...Ch. 25 - Prob. 27EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 28EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 29EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 31EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 32EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 33EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 34EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 35EAPCh. 25 - A 5.0-cm-diamtere metal ball has a surface charge...Ch. 25 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 38EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 39EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 40EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 41EAPCh. 25 - The four 1.0 g sphere shown in FIGURE P25.42 are...Ch. 25 - A proton’s speed as it passes point A is 50,000...Ch. 25 - Prob. 44EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 45EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 46EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 47EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 48EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 49EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 50EAPCh. 25 - What is the escape speed of an electron launched...Ch. 25 - Prob. 52EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 53EAPCh. 25 - Il A 2.0-mm-diameter glass bead is positively...Ch. 25 - Prob. 55EAPCh. 25 - Il A proton is fired from far away toward the...Ch. 25 - Prob. 57EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 58EAPCh. 25 - Il One form of nuclear radiation, beta decay,...Ch. 25 - Il Two 10-cm-diameterelectrodes 0.50 cm a part...Ch. 25 - Il Two 10-cm-diameter electrodes 0.50 cm apart...Ch. 25 - Il Electrodes of area A are spaced distance d...Ch. 25 - Prob. 63EAPCh. 25 - Il Two spherical drops of mercury each have a...Ch. 25 - Prob. 65EAPCh. 25 - Il FIGURE P25.66 shows two uniformly charged...Ch. 25 - Prob. 67EAPCh. 25 - Il The arrangement of charges shown in FIGURE...Ch. 25 - Il FIGURE P25.69 shows a thin rod of length L and...Ch. 25 - Il FIGURE P25.69 shows a thin rod of length L and...Ch. 25 - I FIGURE P25.71 shows a thin rod with charge Q...Ch. 25 - Prob. 72EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 73EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 74EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 75EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 76EAPCh. 25 - Prob. 77EAPCh. 25 - Il A proton and an alpha particle (q = +2e, m = 4...Ch. 25 - Ill Bead A has a mass of 15 g and a charge of —5.0...Ch. 25 - Il Two 2.0-mm-diameter beads, C and D, are 10 mm...Ch. 25 - Il A thin rod of length L and total charge Q has...Ch. 25 - Il A hollow cylindrical shell of length L and...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardUniform Circular motion. 1. Mini Lecture 2. Let the position of a particle be given by: (t) = Rcos (wt)i + Rsin (wt)j 3. Calculate the expression for the velocity vector and show that the velocity vector is tangential to the circumference of the circle. 4. Calculate the expression for the acceleration vector and show that the acceleration vector points radially inward. 5. Calculate the magnitude of the velocity and magnitude of the acceleration, and therefore show that v2 a = Rarrow_forward4. A ball is thrown vertically up, its speed. slowing under the influence of gravity. Suppose (A) we film this motion and play the tape backward (so the tape begins with the ball at its highest point and ends with it reaching the point from which it was released), and (B) we observe the motion of the ball from a frame of reference moving up at the initial speed of the ball. The ball has a downward acceleration g in: a. A and B b. Only A c. Only B d. Neither A nor Barrow_forward
- 2. Consider a 2.4 m long propeller that operated at a constant 350 rpm. Find the acceleration of a particle at the tip of the propeller.arrow_forward2. A football is kicked at an angle 37.0° above the horizontal with a velocity of 20.0 m/s, as Calculate (a) the maximum height, (b) the time of travel before the football hits the ground, and (c) how far away it hits the ground. Assume the ball leaves the foot at ground level, and ignore air resistance, wind, and rotation of the ball.arrow_forwardPlease don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forward
- Cam mechanisms are used in many machines. For example, cams open and close the valves in your car engine to admit gasoline vapor to each cylinder and to allow the escape of exhaust. The principle is illustrated in the figure below, showing a follower rod (also called a pushrod) of mass m resting on a wedge of mass M. The sliding wedge duplicates the function of a rotating eccentric disk on a camshaft in your car. Assume that there is no friction between the wedge and the base, between the pushrod and the wedge, or between the rod and the guide through which it slides. When the wedge is pushed to the left by the force F, the rod moves upward and does something such as opening a valve. By varying the shape of the wedge, the motion of the follower rod could be made quite complex, but assume that the wedge makes a constant angle of 0 = 15.0°. Suppose you want the wedge and the rod to start from rest and move with constant acceleration, with the rod moving upward 1.00 mm in 8.00 ms. Take m…arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardA rectangular current loop (a = 15.0 cm, b = 34.0 cm) is located a distance d = 10.0 cm near a long, straight wire that carries a current (Iw) of 17.0 A (see the drawing). The current in the loop is IL = 21.0 A. Determine the magnitude of the net magnetic force that acts on the loop. Solve in N. a b IL Iwarrow_forwardTwo long, straight wires are separated by distance, d = 22.0 cm. The wires carry currents of I1 = 7.50 A and I2 = 5.50 A in opposite directions, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point (B). Let r₁ = 12.0 cm, r2 = 7.00 cm, and r3 = 13.0 cm. Solve in T. 12 d A √3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY